Mechanics lecture 7 Moment of a force, torque, equilibrium of a body
... isolated from other bodies in contact with it 3. Show all forces and torques acting on the body (Newton s 3rd law of opposition) 4. Select an appropriate reference frame 5. Establish all vectors and unit vectors 6. Apply equilibrium conditions ...
... isolated from other bodies in contact with it 3. Show all forces and torques acting on the body (Newton s 3rd law of opposition) 4. Select an appropriate reference frame 5. Establish all vectors and unit vectors 6. Apply equilibrium conditions ...
Unit 7 Forces and Motion Study Guide Answer Section
... ____ 24. As an astronaut travels far away from Earth, her weight a. decreases because gravity decreases. b. decreases because her mass decreases. c. increases because gravity increases. d. remains the same because her mass remains the same. Completion Complete each statement. 25. The SI unit for mea ...
... ____ 24. As an astronaut travels far away from Earth, her weight a. decreases because gravity decreases. b. decreases because her mass decreases. c. increases because gravity increases. d. remains the same because her mass remains the same. Completion Complete each statement. 25. The SI unit for mea ...
Phy I (AP Phy I) Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
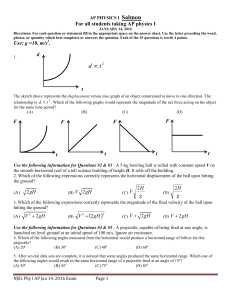
... Directions: For each question or statement fill in the appropriate space on the answer sheet. Use the letter preceding the word, phrase, or quantity which best completes or answers the question. Each of the 25 questions is worth 4 points. Use: g =10. m/s2. Use the following information for Questions ...
... Directions: For each question or statement fill in the appropriate space on the answer sheet. Use the letter preceding the word, phrase, or quantity which best completes or answers the question. Each of the 25 questions is worth 4 points. Use: g =10. m/s2. Use the following information for Questions ...
Ch 18 – Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... Charges exert forces on other charges over a distance. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. This force is directly proportional to the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two charges (Coulomb’s law). Coulomb’ law is covered in m ...
... Charges exert forces on other charges over a distance. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. This force is directly proportional to the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two charges (Coulomb’s law). Coulomb’ law is covered in m ...
Ch. 6 Newton`s Second law of Motion Force and Acceleration
... 6.6 Free Fall Explained F stands for the force (weight) acting on the cannonball, and m stands for the correspondingly large mass of the cannonball. The small F and m stand for the weight and mass of the stone. • The ratio of weight to mass is the same for these or any objects. • All freely falling ...
... 6.6 Free Fall Explained F stands for the force (weight) acting on the cannonball, and m stands for the correspondingly large mass of the cannonball. The small F and m stand for the weight and mass of the stone. • The ratio of weight to mass is the same for these or any objects. • All freely falling ...
Gravitational and Inertial Mass in General Relativity
... experiment, deviations from M G / M I 1 are smaller than a few parts in 1013 , and planned satellite tests (STEP) are expected to explore this to 1 part in 1018 [Will, 2005]. In contrast, the experimental evidence for the so-called strong equivalence principle (SEP) is spotty. Simply stated, SEP a ...
... experiment, deviations from M G / M I 1 are smaller than a few parts in 1013 , and planned satellite tests (STEP) are expected to explore this to 1 part in 1018 [Will, 2005]. In contrast, the experimental evidence for the so-called strong equivalence principle (SEP) is spotty. Simply stated, SEP a ...
lab A7 parts A and D ONLY
... box (box + added weight) and the corresponding pull force. An example of the table is above. It is crossed out so you are not tempted to write on the lab sheets! 2) As you were carrying out the measurements above, what did you notice about the reading on the scale just as the box began to move? Make ...
... box (box + added weight) and the corresponding pull force. An example of the table is above. It is crossed out so you are not tempted to write on the lab sheets! 2) As you were carrying out the measurements above, what did you notice about the reading on the scale just as the box began to move? Make ...
Chapter - St. John the Baptist Diocesan High School
... (II) An object is hanging by a string from your rearview mirror. While you are decelerating at a constant rate from 25 m/s to rest in 6.0 s, (a) what angle does the string make with the vertical, and (b) is it toward the windshield or away from it? [Hint: See Example 4–15.] ...
... (II) An object is hanging by a string from your rearview mirror. While you are decelerating at a constant rate from 25 m/s to rest in 6.0 s, (a) what angle does the string make with the vertical, and (b) is it toward the windshield or away from it? [Hint: See Example 4–15.] ...
Asymptotic Symmetries and Electromagnetic Memory
... sourcing the radiation are assumed to be at a small distance from the center of the sphere compared to the radius |rs | << |r|.) Also, when one “integrates over all time” the relevant changes in the gauge field should start after an early enough v and stop at some late enough u. If one thinks of the ...
... sourcing the radiation are assumed to be at a small distance from the center of the sphere compared to the radius |rs | << |r|.) Also, when one “integrates over all time” the relevant changes in the gauge field should start after an early enough v and stop at some late enough u. If one thinks of the ...