PHY2054 Exam II, Fall, 2011 Solutions 1.) A 5 kΩ resistor in series
... axis direction. This x-y plane is in the plane of the test paper, and gravity is directed into the paper. What current (units of Amps) has to flow in the wire and in which direction (+ or - y-direction) for the magnetic force to be up 'out of the paper' on the wire to equal the downward 'into the pa ...
... axis direction. This x-y plane is in the plane of the test paper, and gravity is directed into the paper. What current (units of Amps) has to flow in the wire and in which direction (+ or - y-direction) for the magnetic force to be up 'out of the paper' on the wire to equal the downward 'into the pa ...
F r
... particle starts from rest, its speed increases throughout the motion, and the particle is always moving in the positive x direction. These details about its speed and direction are not necessary for the calculation of the work done, however. ...
... particle starts from rest, its speed increases throughout the motion, and the particle is always moving in the positive x direction. These details about its speed and direction are not necessary for the calculation of the work done, however. ...
9-2 Conservation of Momentum During a collision, measurements
... The impulse is equal to the change in momentum: ...
... The impulse is equal to the change in momentum: ...
Physics 11 - BigEngine
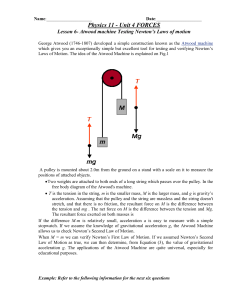
... A pulley is mounted about 2.0m from the ground on a stand with a scale on it to measure the positions of attached objects. Two weights are attached to both ends of a long string which passes over the pulley. In the free body diagram of the Atwood's machine. T is the tension in the string, m is t ...
... A pulley is mounted about 2.0m from the ground on a stand with a scale on it to measure the positions of attached objects. Two weights are attached to both ends of a long string which passes over the pulley. In the free body diagram of the Atwood's machine. T is the tension in the string, m is t ...
force - WordPress.com
... 2.1 Definition of a force, resolution of forces and resultant force A force may be defined as that which causes, or tends to cause, a change in the state of rest or the uniform motion, of a body. Two or more forces acting on a body can be replaced by a single force that is called a resultant force. ...
... 2.1 Definition of a force, resolution of forces and resultant force A force may be defined as that which causes, or tends to cause, a change in the state of rest or the uniform motion, of a body. Two or more forces acting on a body can be replaced by a single force that is called a resultant force. ...
A2 Fields Part II - Animated Science
... to a magnetic field of flux density 7.5 × 10–4 T. What is the value of the flux linkage for this coil? A B C D ...
... to a magnetic field of flux density 7.5 × 10–4 T. What is the value of the flux linkage for this coil? A B C D ...
Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion
... In a collision, an object experiences a force for a specific amount of time which results in a change in momentum (the object's mass either speeds up or slows down). The impulse experienced by the object equals the change in momentum of the object. In equation form, F * t = m * Delta v. ...
... In a collision, an object experiences a force for a specific amount of time which results in a change in momentum (the object's mass either speeds up or slows down). The impulse experienced by the object equals the change in momentum of the object. In equation form, F * t = m * Delta v. ...
Chapter 1
... The direction of the force points from q1 to q2. is called the permittivity and 0 = 8.854 10-12 F/m is for free space. If q1 and q2 are like charges, the resultant force will try to push q2 away from q1. Otherwise, the resultant force will try to pull q2 to q1. If a system of electric cha ...
... The direction of the force points from q1 to q2. is called the permittivity and 0 = 8.854 10-12 F/m is for free space. If q1 and q2 are like charges, the resultant force will try to push q2 away from q1. Otherwise, the resultant force will try to pull q2 to q1. If a system of electric cha ...
Free Fall of Elementary Particles
... This document is Copyright (c) 1994 by Nils Rognerud ([email protected]). All rights are reserved. Permission to use, copy and distribute this unmodified document by any means and for any purpose EXCEPT PROFIT PURPOSES is hereby granted, provided that both the above Copyright notice and this permission ...
... This document is Copyright (c) 1994 by Nils Rognerud ([email protected]). All rights are reserved. Permission to use, copy and distribute this unmodified document by any means and for any purpose EXCEPT PROFIT PURPOSES is hereby granted, provided that both the above Copyright notice and this permission ...
When and Where is a Current Electrically Neutral?
... be counterindicated. Neither outcome would appeal to the authorities I have cited, nor to those who have been highereducated to think like them. Therefore I predict it will be a long time before anybody tries the experiment. And still longer before a first-line physics journal accepts the results fo ...
... be counterindicated. Neither outcome would appeal to the authorities I have cited, nor to those who have been highereducated to think like them. Therefore I predict it will be a long time before anybody tries the experiment. And still longer before a first-line physics journal accepts the results fo ...
Homework #8: Magnetic Force and Biot-Savart Law
... but now it also has a horizontal component ( ), which opposes the flow of the current. Thus, whatever initiates the current (i.e. a voltage source like a battery) must do work against the backward component of the magnetic force. The total horizontal force on the top segment is given by . In a time ...
... but now it also has a horizontal component ( ), which opposes the flow of the current. Thus, whatever initiates the current (i.e. a voltage source like a battery) must do work against the backward component of the magnetic force. The total horizontal force on the top segment is given by . In a time ...