Which series of ionic compounds is decreasing according to
... above can all occur depending on how quickly the cart ...
... above can all occur depending on how quickly the cart ...
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit II Dynamics
... action force: a force initiated by object A on object B apparent weight: the negative of the normal force acting on an object coefficient of friction: proportionality constant relating the magnitude of the force of friction to the magnitude of the normal force field: a three-dimensional region of in ...
... action force: a force initiated by object A on object B apparent weight: the negative of the normal force acting on an object coefficient of friction: proportionality constant relating the magnitude of the force of friction to the magnitude of the normal force field: a three-dimensional region of in ...
18 th - Soran University
... speed parts of the body vary depending on the distance from the axis of rotation (ie, the radius of rotation), where the proportionality becomes directly proportional to the speed of the body ring on the circumference of a circle or part of it, and then the body about the axis of rotation, this as w ...
... speed parts of the body vary depending on the distance from the axis of rotation (ie, the radius of rotation), where the proportionality becomes directly proportional to the speed of the body ring on the circumference of a circle or part of it, and then the body about the axis of rotation, this as w ...
Section 2 What Is a Force?
... force has both direction particular direction and and magnitude. has a certain size. ...
... force has both direction particular direction and and magnitude. has a certain size. ...
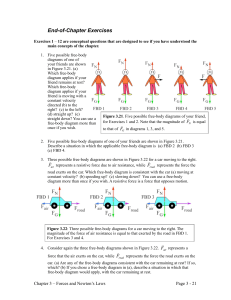
Exercises on Force and Motion Exercise 1.1 A small object is subject
... are on a frictionless surface. They are connected by a massless cord. A force of 30 Newtons pulls the 10 Kg block to the right. What is the tension in the cord? Let T be the tension in the cord. Since the cord is massless, this force T pulls the 5 Kg block to the right and it pulls the 10 Kg block ...
... are on a frictionless surface. They are connected by a massless cord. A force of 30 Newtons pulls the 10 Kg block to the right. What is the tension in the cord? Let T be the tension in the cord. Since the cord is massless, this force T pulls the 5 Kg block to the right and it pulls the 10 Kg block ...
T0900367-v1_ambient magnetic field coupling to stainle
... serial number 069 - max field at surface - 7.5 gauss serial number 079 - max field at surface - 0.4 gauss serial number 124 - max field at surface - 5.5 gauss serial number 113 - max field at surface - 0.25 gauss There were not too many sign reversals when scanning over the parts with the probe. The ...
... serial number 069 - max field at surface - 7.5 gauss serial number 079 - max field at surface - 0.4 gauss serial number 124 - max field at surface - 5.5 gauss serial number 113 - max field at surface - 0.25 gauss There were not too many sign reversals when scanning over the parts with the probe. The ...
Rigid bodies - general theory
... simple formulas, but limited use, since both angular velocities and torques are evaluated in a time dependent body-fixed frame (principal axes); used mostly for torque-free motion or partially constrained motion (examples follow) ...
... simple formulas, but limited use, since both angular velocities and torques are evaluated in a time dependent body-fixed frame (principal axes); used mostly for torque-free motion or partially constrained motion (examples follow) ...
SCEGGS Trial with Solutions
... testing a revolutionary propulsion system. The whole test spacecraft had ended up with a mass of only 2.54 x 106 kg after its construction on Earth. The spacecraft was propelled by a newly created anti-matter propulsion system that allows the engine to produce enormous thrust with only 50 kg of the ...
... testing a revolutionary propulsion system. The whole test spacecraft had ended up with a mass of only 2.54 x 106 kg after its construction on Earth. The spacecraft was propelled by a newly created anti-matter propulsion system that allows the engine to produce enormous thrust with only 50 kg of the ...
PHYS 1441 – Section 002 Lecture #21
... Apply the equations that specify the balance of forces at equilibrium. Set the net force in the x and y directions equal to 0. Select the most optimal rotational axis for torque calculations ! Selecting the axis such that the torque of one of the unknown forces become 0 makes the problem easier to s ...
... Apply the equations that specify the balance of forces at equilibrium. Set the net force in the x and y directions equal to 0. Select the most optimal rotational axis for torque calculations ! Selecting the axis such that the torque of one of the unknown forces become 0 makes the problem easier to s ...