CHAPTER 10 QUESTION SETS
... The objects will hit the ground at exactly the same time. 15. Name two types of elastic matter. A kitchen sponge and a basketball are two types of elastic matter. 16. Describe on example of a compression force in your home…not a couch! My bed is an example of a compression force. 17. Do the same wit ...
... The objects will hit the ground at exactly the same time. 15. Name two types of elastic matter. A kitchen sponge and a basketball are two types of elastic matter. 16. Describe on example of a compression force in your home…not a couch! My bed is an example of a compression force. 17. Do the same wit ...
Energy3
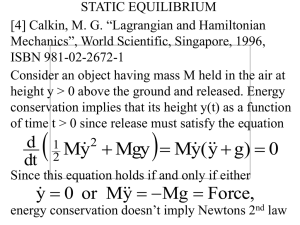
... If we set g = 0 in Example 2 we obtain the equations for a geodesic trajectory on the surface, that is the uniform speed trajectory whose distance between any two points is minimal. Albert Einstein showed that an object in any inertial frame, such as in space moving with constant speed or falling fr ...
... If we set g = 0 in Example 2 we obtain the equations for a geodesic trajectory on the surface, that is the uniform speed trajectory whose distance between any two points is minimal. Albert Einstein showed that an object in any inertial frame, such as in space moving with constant speed or falling fr ...
pages 251-300 - Light and Matter
... plane starts out flying upside-down, straight and level, then begins curving up along the circular loop, and is right-side up when it reaches the top. (The plane may slow down somewhat on the way up.) How fast must the plane be going at the top if the pilot is to experience no force from the seat or ...
... plane starts out flying upside-down, straight and level, then begins curving up along the circular loop, and is right-side up when it reaches the top. (The plane may slow down somewhat on the way up.) How fast must the plane be going at the top if the pilot is to experience no force from the seat or ...
Unit 4 Vocabulary Terms
... The acceleration an object experience as it travels in a circle is called the centripetal acceleration. Although the object is traveling at a constant speed, its direction is continuously changing thus its velocity is also constantly changing. As a result, the object experiences an acceleration towa ...
... The acceleration an object experience as it travels in a circle is called the centripetal acceleration. Although the object is traveling at a constant speed, its direction is continuously changing thus its velocity is also constantly changing. As a result, the object experiences an acceleration towa ...
國立彰化師範大學八十八學年度碩士班招生考試試題
... 3. (a) A proton of mass 1.0 u traveling with a speed of 2104 m/s has an elastic head-on collision with a helium nucleus of mass 4.0 u initially at rest. The velocity of the proton after the collision is vP=_________ m/s. (b) If these two particles are observed to move off at 45, proton above the x ...
... 3. (a) A proton of mass 1.0 u traveling with a speed of 2104 m/s has an elastic head-on collision with a helium nucleus of mass 4.0 u initially at rest. The velocity of the proton after the collision is vP=_________ m/s. (b) If these two particles are observed to move off at 45, proton above the x ...
1st Term Exam
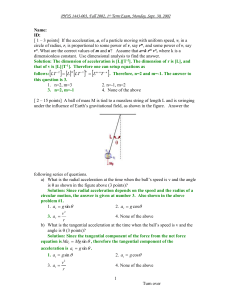
... 3. There is no gravitational acceleration 4. None of the above b) What are the forces exerting on the cart? (2 points) Solution: There is a gravitational force. Since the cart is not falling through the incline, there must be a force balancing the weight or gravitational force on the cart, the norma ...
... 3. There is no gravitational acceleration 4. None of the above b) What are the forces exerting on the cart? (2 points) Solution: There is a gravitational force. Since the cart is not falling through the incline, there must be a force balancing the weight or gravitational force on the cart, the norma ...
International Space Station - University of Toronto Physics
... you to walk! Walking certainly involves speeding up, and this would not be possible if the floor were frictionless or covered in marbles! ...
... you to walk! Walking certainly involves speeding up, and this would not be possible if the floor were frictionless or covered in marbles! ...
The Galaxy Education System S. N. Kansagra School Sub: Physics
... 27) A body of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically up with an initial speed of 5 ms-1. What is the magnitude and direction of force due to gravity acting on the body when it is at its highest point? Take g = 9.8 ms-2 [ 1 kg or 9.8 N vertically downwards] 28) A body of mass 1.5 kg is dropped from a height ...
... 27) A body of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically up with an initial speed of 5 ms-1. What is the magnitude and direction of force due to gravity acting on the body when it is at its highest point? Take g = 9.8 ms-2 [ 1 kg or 9.8 N vertically downwards] 28) A body of mass 1.5 kg is dropped from a height ...