* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 國立彰化師範大學八十八學年度碩士班招生考試試題
Survey
Document related concepts
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
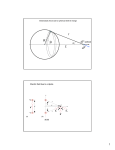
國立彰化師範大學九十一學年度碩士班招生考試試題 系所:物理學系碩士班 ☆☆請在答案紙上作答☆☆ 科目:普通物理 共 2 頁,第 1 頁 注意: 1. The unified atomic mass unit 1u=1.66 10-27 kg. 2. The mass of the electron is me =9.110-31 kg. 一、 填 充 題: (每格 6 分, 共 60 分) 【 Note: You could make an estimate of the number s in the following problems without using a calculator 】 1. A skier has just begun descending a 45 slope. Assuming the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.10, the skier’s acceleration is a=______ g. 2. (a) A geosynchronous satellite of the Earth is the one that stays above the same point on the equator of the Earth. The height above the Earth’s surface needed for a geosynchronous weather satellite is hs=_____ [In terms of rE]. [The Earth’s radius rE=6380 km]. (b) Assume the Earth is a perfect sphere, the difference between the values of g at the equator and at the poles due to the Earth’s rotation is g=_________ m/s2. 3. (a) A proton of mass 1.0 u traveling with a speed of 2104 m/s has an elastic head-on collision with a helium nucleus of mass 4.0 u initially at rest. The velocity of the proton after the collision is vP=_________ m/s. (b) If these two particles are observed to move off at 45, proton above the x-axis and helium below the x-axis. The velocity of the helium after the collision is vHe= _________ m/s. 4. A uniform thin rod of length L and mass M with its linear mass density varies linearly from =0 at the left end to =30 at the right end. Find the center of mass XCM=_________ L. 5. A non-uniform 1.0-kg stick can be balanced at a point 80 cm from one end. If it is pivoted about that end, it oscillates with a period of 3.14 s. The moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the stick through its center of mass is I=__________ kg-m2. 6. A copper wire 2 mm in diameter carries a 3.14-A current. The drift velocity of the free electrons is vd = ________ m/s. [The atomic mass of Cu is 63.5 u, so 63.5g of Cu contains 61023 free electrons. The mass density of Cu is 8.9103 kg/m3]. 7. An electron travels at 0.1c (c= speed of light) in a plane perpendicular to a 0.01-T uniform magnetic field. The cyclotron frequency is f=__________ Hz. 8. An optical coating of MgF2, whose index of refraction is n=1.4, is designed to eliminate reflected light at wavelengths centered at 560 nm when incident normally on glass for which n=1.5. The minimum thickness of this non-reflective coating is t=_______ nm. 國立彰化師範大學九十一學年度碩士班招生考試試題 系所:物理學系碩士班 ☆☆請在答案紙上作答☆☆ 科目:普通物理 共 2 頁,第 2 頁 二、 計算題: (每題 10 分, 共 40 分) 1. A projectile is launched at angle /4 from a cliff of height H above sea level. If it falls into the sea at a distance equal to 3H from the base of the cliff, then (a) what is the maximum height above the sea level? (b) what is the time of flight? 2. (a) A non-conducting thin circular disk of radius R has a uniform surface charge density (C/m2). Determine the potential V along the axis of the disk at a distance x from its center. (b) Using the result of (a), obtain the electric field E for an infinite plate with surface charge density (C/m2). 3. (a) Show that, for an ideal gas, CP-CV=R. (b) Show that, for an adiabatic quasi-static process of an ideal gas, PV is a constant, where =CP/CV. 4. Figure 1 shows the plane Cartesian coordinate system, the axes are labeled x and y, with the origin O and two points A(0,a),B(0,-a) along the y-axis. (a) If we put a charge q at point A, and a charge –q at point B, we have an electric dipole. Show that, in the far-field approximation, the resultant electric field falls off as the inverse cube of the distance along either the perpendicular bisector (x-axis) or the axis of the dipole (y-axis). (b) Figure 2 shows an electric dipole in the plane polar coordinate system (r,). Find the potential V(r,) at point C(r,) in the far-field approximation (i.e. r>>a). Then, use E r V 1 V and E to find the components of the electric field, and compare r r with the results of (a). y y C(r,θ) q(0,a) A A 0 B Figure 1. r θ x x 0 B -q(0,-a) Figure 2.