Chapter 3
... hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Nothing is created nothing is destroyed All stable ecosystems recycle matter and get energy from the sun ...
... hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Nothing is created nothing is destroyed All stable ecosystems recycle matter and get energy from the sun ...
Photosynthesis - mleonessciencepage
... What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? What are the colors of the visible light spectrum? In what cellular organelle does photosynthesis take place? Why is photosynthesis important? How is the process of photosynthesis in C4, C3, and CAM plants ...
... What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? What are the colors of the visible light spectrum? In what cellular organelle does photosynthesis take place? Why is photosynthesis important? How is the process of photosynthesis in C4, C3, and CAM plants ...
Question #1 Which organelle is responsible for cellular respiration?
... A) Plants can make all of their own nutrients and sugar, but animals must get them from other organisms. B) Plants cannot move, but animals can, so plants must get their nutrients from the soil. C) Plants make their own sugar, but animals must get it from other organisms. D) Plant cells are simp ...
... A) Plants can make all of their own nutrients and sugar, but animals must get them from other organisms. B) Plants cannot move, but animals can, so plants must get their nutrients from the soil. C) Plants make their own sugar, but animals must get it from other organisms. D) Plant cells are simp ...
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE: Energetics
... stomata thylakoid membrane; lumen grana (granum) stroma light reactions Calvin cycle NADP+ / NADPH ...
... stomata thylakoid membrane; lumen grana (granum) stroma light reactions Calvin cycle NADP+ / NADPH ...
Systems in Plants - RosedaleGrade10Science
... (pp. 136-139) A plant leaf is made up of a system of tissues, each with its own specific structure and function. The structure and location of the tissues are connected to their function. For photosynthesis, plants need to (1) absorb light, (2) obtain carbon dioxide and (3) obtain water. ...
... (pp. 136-139) A plant leaf is made up of a system of tissues, each with its own specific structure and function. The structure and location of the tissues are connected to their function. For photosynthesis, plants need to (1) absorb light, (2) obtain carbon dioxide and (3) obtain water. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. Which one of the following is not easily absorbed by plants? a. Nitrogen b. Potassium c. Calcium d. Iron 3. Oxygen evolved during photosynthesis is derived from a. Carbon di oxide b. Starch c. Water ...
... 2. Which one of the following is not easily absorbed by plants? a. Nitrogen b. Potassium c. Calcium d. Iron 3. Oxygen evolved during photosynthesis is derived from a. Carbon di oxide b. Starch c. Water ...
Lesson
... Photosynthesis Light Response Curve at Two Different CO2 Concentrations • More CO2 binds to Rubisco • Eventually all active sites are occupied – enzyme is saturated ...
... Photosynthesis Light Response Curve at Two Different CO2 Concentrations • More CO2 binds to Rubisco • Eventually all active sites are occupied – enzyme is saturated ...
Exam II Sample (1710).doc
... low carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. b. arid climates. c. ATP production at low proton gradients. d. fix carbon as a 3 carbon acid. e. carry out the light reaction in the dark. ...
... low carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. b. arid climates. c. ATP production at low proton gradients. d. fix carbon as a 3 carbon acid. e. carry out the light reaction in the dark. ...
Photosynthesis
... 2. Where does photosynthesis occur? ______________________________________________ 3. What are chloroplasts and where are they found? ___________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4. What are the two main functions of chloroplasts? ____ ...
... 2. Where does photosynthesis occur? ______________________________________________ 3. What are chloroplasts and where are they found? ___________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4. What are the two main functions of chloroplasts? ____ ...
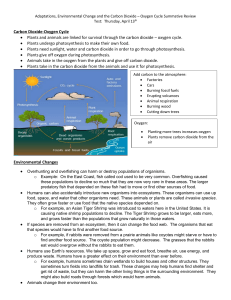
Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle • Plants and animals are linked for
... predatory fish that depended on these fish had to move or find other sources of food. Humans can also accidentally introduce new organisms into ecosystems. These organisms can use up food, space, and water that other organisms need. These animals or plants are called invasive species. They often gro ...
... predatory fish that depended on these fish had to move or find other sources of food. Humans can also accidentally introduce new organisms into ecosystems. These organisms can use up food, space, and water that other organisms need. These animals or plants are called invasive species. They often gro ...
Cell Functions Test Review
... Cell Membrane: determines what goes in/out of cell Mitochondria: provides energy for the cell Vacuole: stores water, waste, and other materials for the cell ...
... Cell Membrane: determines what goes in/out of cell Mitochondria: provides energy for the cell Vacuole: stores water, waste, and other materials for the cell ...
Botany
... forests, range lands, wilderness areas *Public health: solve pollution problems, some plant species are sensitive to pollutants ...
... forests, range lands, wilderness areas *Public health: solve pollution problems, some plant species are sensitive to pollutants ...
Blank Jeopardy
... Photosynthesis- food synthesized, carbon dioxide taken in, oxygen given off, occurs only in chloroplasts. ...
... Photosynthesis- food synthesized, carbon dioxide taken in, oxygen given off, occurs only in chloroplasts. ...
1 - contentextra
... breaking down the carbohydrate glucose; however, other organic compounds are commonly broken down by respiration. 11 Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of autotrophic cells. The process of photosynthesis involves light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Thylakoids have photosystems th ...
... breaking down the carbohydrate glucose; however, other organic compounds are commonly broken down by respiration. 11 Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of autotrophic cells. The process of photosynthesis involves light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Thylakoids have photosystems th ...
Porifera and Cnidaria Review Sheet/Practice Questions
... 1. Cellular respiration takes glucose from the food we eat and converts it to cellular energy molecules called ___ATP__________. 2. The process of cellular respiration takes place in the __mitochondria_______ and ___cytoplasm_______ of the cell? 4. ___Aerobic__________ respiration uses oxygen, while ...
... 1. Cellular respiration takes glucose from the food we eat and converts it to cellular energy molecules called ___ATP__________. 2. The process of cellular respiration takes place in the __mitochondria_______ and ___cytoplasm_______ of the cell? 4. ___Aerobic__________ respiration uses oxygen, while ...
WHAT IS PHOTOSYNTHESIS?
... The “plastoquinone” (PQ) accepts two protons H + located into the stroma to form plastoquinola (PC), while simultaneously pumping H + ions from the stroma toward the thylakoids using the energy of the photons of light released during the transportation as that electrons exchange energy to the final ...
... The “plastoquinone” (PQ) accepts two protons H + located into the stroma to form plastoquinola (PC), while simultaneously pumping H + ions from the stroma toward the thylakoids using the energy of the photons of light released during the transportation as that electrons exchange energy to the final ...
Ecology Study Guide part 3
... 12. Explains why plants grow toward light 13. Explains why plants only grow in certain seasons 14. Close association between organisms like fungus and algae or termites and gut bacteria 15. Blue-green algae 16. Organism in a food chain or ecosystem whose presence greatly influences species diversity ...
... 12. Explains why plants grow toward light 13. Explains why plants only grow in certain seasons 14. Close association between organisms like fungus and algae or termites and gut bacteria 15. Blue-green algae 16. Organism in a food chain or ecosystem whose presence greatly influences species diversity ...
Lesson
... ▫ Addition of CO2 to RuBP (carboxylation) Photosynthesis ▫ Addition of O2 to RuBP (oxidation) Photorespiration ...
... ▫ Addition of CO2 to RuBP (carboxylation) Photosynthesis ▫ Addition of O2 to RuBP (oxidation) Photorespiration ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Vocabulary File
... 1) Energy = the ability to do work 2) ATP = (adenosine triphosphate); energy storing molecule 3) ADP = adenosine diphosphate 4) Photosynthesis = the process that provides energy for almost all life 5) Autotroph = organisms that make their own food 6) Chlorophyll = green pigment in chloroplasts that ...
... 1) Energy = the ability to do work 2) ATP = (adenosine triphosphate); energy storing molecule 3) ADP = adenosine diphosphate 4) Photosynthesis = the process that provides energy for almost all life 5) Autotroph = organisms that make their own food 6) Chlorophyll = green pigment in chloroplasts that ...
Photosynthesis occurs in 2 sets of main reactions in the chloroplast
... from the surrounding environment when energy of a critical wavelength is nearby; c) emission of electrons from a metal when struck by any wavelength of light; d) emission of electrons stored in the daytime when stomata are open at night; e) release of NADPH and ATP energy during the Calvin Cycvle wh ...
... from the surrounding environment when energy of a critical wavelength is nearby; c) emission of electrons from a metal when struck by any wavelength of light; d) emission of electrons stored in the daytime when stomata are open at night; e) release of NADPH and ATP energy during the Calvin Cycvle wh ...
Photosynthesis Worksheet
... 2 The process by which plants and some bacteria use the energy from sunlight to produce sugar. (14) ...
... 2 The process by which plants and some bacteria use the energy from sunlight to produce sugar. (14) ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.