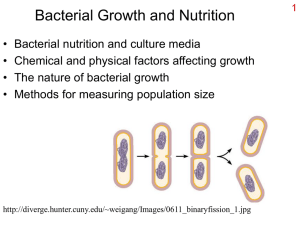
The Respiratory System
... • Why do astronauts wear space suits and carry oxygen when they go out in space? ...
... • Why do astronauts wear space suits and carry oxygen when they go out in space? ...
Chapter 9 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... metabolism • anaerobic respiration – energy source oxidized and degraded using molecules other than oxygen as exogenous electron acceptors – can yield large amount of energy (depending on reduction potential of energy source and electron acceptor), primarily by electron transport activity ...
... metabolism • anaerobic respiration – energy source oxidized and degraded using molecules other than oxygen as exogenous electron acceptors – can yield large amount of energy (depending on reduction potential of energy source and electron acceptor), primarily by electron transport activity ...
Review Material for Plant form and function
... potato tuber is (are) – diffusion due to concentration differences and bulk flow due to pressure differences. – pressure flow through the phloem. – active transport due to the hydrolysis of ATP and ion transport into the tuber cells. – determined by the structure and function of the tonoplast of the ...
... potato tuber is (are) – diffusion due to concentration differences and bulk flow due to pressure differences. – pressure flow through the phloem. – active transport due to the hydrolysis of ATP and ion transport into the tuber cells. – determined by the structure and function of the tonoplast of the ...
PP-Alveolar gas exchange Notes
... Waste molecule-need to rid the body of the gas Diffusion: Alveoli have a high concentration of oxygen Blood capillaries have a low concentration of oxygen Blood capillaries have a high concentration of carbon dioxide Alveolus have a low concentration of carbon dioxide As a result: Oxygen will di ...
... Waste molecule-need to rid the body of the gas Diffusion: Alveoli have a high concentration of oxygen Blood capillaries have a low concentration of oxygen Blood capillaries have a high concentration of carbon dioxide Alveolus have a low concentration of carbon dioxide As a result: Oxygen will di ...
Ecology
... the organisms in an ecosystem that belong to the same species Ex. Mice living in a meadow or pine trees in a forest or HUMANS Species are a group of organisms that can mate to produce offspring that can produce more offspring Ex. Brown pelican or human ...
... the organisms in an ecosystem that belong to the same species Ex. Mice living in a meadow or pine trees in a forest or HUMANS Species are a group of organisms that can mate to produce offspring that can produce more offspring Ex. Brown pelican or human ...
Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration – The ingredients for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. CO2 is obtained from the air by a plant’s leaves. H2O is obtained from the damp soil by a plant’s roots. ...
... Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration – The ingredients for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. CO2 is obtained from the air by a plant’s leaves. H2O is obtained from the damp soil by a plant’s roots. ...
Flip Folder 4 KEY - Madison County Schools
... 1. Free E of the electrons is used to actively transport H+ ions (a.k.a. called protons) into the inner thylakoid space The H+ ion concentration [H+] goes up inside the space. This causes the pH to decrease and become more acidic. The [H+] goes down in the stroma. The stroma becomes more basic. As t ...
... 1. Free E of the electrons is used to actively transport H+ ions (a.k.a. called protons) into the inner thylakoid space The H+ ion concentration [H+] goes up inside the space. This causes the pH to decrease and become more acidic. The [H+] goes down in the stroma. The stroma becomes more basic. As t ...
Plant Classification
... cell where photosynthesis will take place. 6. ________________________________ is a material the plant takes up through its roots and stems. 7. During photosynthesis, ________________________________ is a waste product released by the plant into the air. 8. Plants produce more glucose than they need ...
... cell where photosynthesis will take place. 6. ________________________________ is a material the plant takes up through its roots and stems. 7. During photosynthesis, ________________________________ is a waste product released by the plant into the air. 8. Plants produce more glucose than they need ...
Final Exam – Ecology Review
... NAME THE STEP IN A BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLE: ____________________ Process in which nitrogen gas from the atmosphere is converted into ammonia by bacteria that live in the soil and on the roots of plants called legumes ____________________ Process in which soil bacteria convert nitrogen compounds in soi ...
... NAME THE STEP IN A BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLE: ____________________ Process in which nitrogen gas from the atmosphere is converted into ammonia by bacteria that live in the soil and on the roots of plants called legumes ____________________ Process in which soil bacteria convert nitrogen compounds in soi ...
Notes for Ecology unit - Liberty Union High School District
... fuels, more CO2 is released each year this may result in global warming since CO2 traps heat (remember the ...
... fuels, more CO2 is released each year this may result in global warming since CO2 traps heat (remember the ...
alocalecosystempartone
... Salinity – Different soils have different salinity levels and only particular organisms thrive in certain salinity levels. Plants must have adaptations that enable them to cope with the different levels of salinity. ...
... Salinity – Different soils have different salinity levels and only particular organisms thrive in certain salinity levels. Plants must have adaptations that enable them to cope with the different levels of salinity. ...
Circle the correct underlined term(s)
... PLANTS STUDY GUIDE Topics: I. Plant Organs What are the three main organs in a plant? Roots, Stems, Leaves Leaf What is a leaf? A basic plant organ attached to the stem that serves as the site for photosynthesis. What is transpiration? The loss of water in a plant What is photosynthesis? (in detail! ...
... PLANTS STUDY GUIDE Topics: I. Plant Organs What are the three main organs in a plant? Roots, Stems, Leaves Leaf What is a leaf? A basic plant organ attached to the stem that serves as the site for photosynthesis. What is transpiration? The loss of water in a plant What is photosynthesis? (in detail! ...
Humes Biology Chapter 3 Biochemistry Carbon Compounds
... Composed of a long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain Wax can be found on the outside of plants to prevent water loss especially through leaves Can also be found in your ears where it prevents microorganisms from entering the ear canal o Steroids Composed of four fused carbon ri ...
... Composed of a long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain Wax can be found on the outside of plants to prevent water loss especially through leaves Can also be found in your ears where it prevents microorganisms from entering the ear canal o Steroids Composed of four fused carbon ri ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Research is conducted using three basic approaches: 1) Observing- The first step in asking ecological questions. 2) Experimenting- Used to test hypotheses. ...
... Research is conducted using three basic approaches: 1) Observing- The first step in asking ecological questions. 2) Experimenting- Used to test hypotheses. ...
bio100--eastside-owens valley-lect 1--f09-
... THE CENTRAL IMPORTANCE OF PLANTS • Plants cannot move (animals can). – Thus they are reflective of the physical conditions at a ...
... THE CENTRAL IMPORTANCE OF PLANTS • Plants cannot move (animals can). – Thus they are reflective of the physical conditions at a ...
An Overview of Plants Section 2 Seedless Plants
... An Overview of Plants A. Plant cells 1. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have cell walls, which provide structure and protection. 2. Most plant cells contain the green pigment chlorophyll. a. Photosynthesis—process where plants use chlorophyll to make food b. Chlorophyll is found in a cell structure ...
... An Overview of Plants A. Plant cells 1. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have cell walls, which provide structure and protection. 2. Most plant cells contain the green pigment chlorophyll. a. Photosynthesis—process where plants use chlorophyll to make food b. Chlorophyll is found in a cell structure ...
Question - Cloudfront.net
... Question: How do organisms affect one another’s survival? Answer: No organism can live in isolation. Organisms are interdependent and rely on each other for things like food and ...
... Question: How do organisms affect one another’s survival? Answer: No organism can live in isolation. Organisms are interdependent and rely on each other for things like food and ...
Unit 3 Notes
... – Levels of carbon dioxide + oxygen in blood: • Carbon dioxide concentrations monitored by pH • Oxygen concentrations monitored by chemoreceptors in ...
... – Levels of carbon dioxide + oxygen in blood: • Carbon dioxide concentrations monitored by pH • Oxygen concentrations monitored by chemoreceptors in ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... from neutral, etc. change enzymes so the enzyme is unable to work. Questions: 16. What subunits make up proteins? ...
... from neutral, etc. change enzymes so the enzyme is unable to work. Questions: 16. What subunits make up proteins? ...
File
... • Our biosphere is the inhabited portion of our planet made up of three parts: – Atmosphere – Hydrosphere – Geosphere ...
... • Our biosphere is the inhabited portion of our planet made up of three parts: – Atmosphere – Hydrosphere – Geosphere ...
Transport, Food Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants
... area of the root for water absorption. 3. Do not have a cuticle. Absorption into the roots takes place by osmosis. ...
... area of the root for water absorption. 3. Do not have a cuticle. Absorption into the roots takes place by osmosis. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.