native species
... trophic level. Pyramids (Diagrams) that show the transfer of: (pg. 72 and 73 in text) • Energy • Biomass – amount of living matter at each trophic level • Population Size – relative # of organisms at each trophic level ...
... trophic level. Pyramids (Diagrams) that show the transfer of: (pg. 72 and 73 in text) • Energy • Biomass – amount of living matter at each trophic level • Population Size – relative # of organisms at each trophic level ...
Sustainability of Ecosystems Science 10 Test Review Ecologist
... 15. _____ T _____ During a thunderstorm, the energy released by lightning helps form nitrates. 16. _____ F _____ The only reactants required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. 17. _____ F _____ Amino acids are needed to produce genetic material. 18. ______ T _____Coal deposits resulted ...
... 15. _____ T _____ During a thunderstorm, the energy released by lightning helps form nitrates. 16. _____ F _____ The only reactants required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. 17. _____ F _____ Amino acids are needed to produce genetic material. 18. ______ T _____Coal deposits resulted ...
SC09 Unit Worksheets
... 13. Name and describe the location, climate, physical features, and the plant and animal adaptations of the temperate grassland biome found in Canada. C TEMPERATE GRASSLAND - Location: Called prairies, they are found above 23.5 degrees north latitude. - Climate: Temperate Grasslands get 25 to 100 c ...
... 13. Name and describe the location, climate, physical features, and the plant and animal adaptations of the temperate grassland biome found in Canada. C TEMPERATE GRASSLAND - Location: Called prairies, they are found above 23.5 degrees north latitude. - Climate: Temperate Grasslands get 25 to 100 c ...
Ecology Test Review
... Competition: occurs when two or more organisms need a limited resource (food, water, shelter). It can occur within a species or between organisms that are differing species. Cooperation : organisms working together Mutualism – A symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit. Commens ...
... Competition: occurs when two or more organisms need a limited resource (food, water, shelter). It can occur within a species or between organisms that are differing species. Cooperation : organisms working together Mutualism – A symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit. Commens ...
The Respiratory System
... • The respiratory system is related to the cardiovascular system because it exchanges the oxygen and carbon dioxide that the blood transports around the body ...
... • The respiratory system is related to the cardiovascular system because it exchanges the oxygen and carbon dioxide that the blood transports around the body ...
Topic 2 Molecular Biology
... • Biochemistry is a branch of organic chemistry dealing with _________ ___________. • All living organisms are made of molecules that can be classified into one of four types. • Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins or nucleic acids ...
... • Biochemistry is a branch of organic chemistry dealing with _________ ___________. • All living organisms are made of molecules that can be classified into one of four types. • Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins or nucleic acids ...
COVALENT BOND - hovanscience
... • Base = pH above 7 (lower H+ than pure water) • Acid = pH below 7 (higher H+ than pure water) • Buffer – weak acids or bases that can prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH – Example: bicarbonate ...
... • Base = pH above 7 (lower H+ than pure water) • Acid = pH below 7 (higher H+ than pure water) • Buffer – weak acids or bases that can prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH – Example: bicarbonate ...
Respiratory System
... Breathing • Breathing- (aka ventilation), The process through which the respiratory system moves air into and out of the lungs. • In contrast, Respiration refers to cellular respiration, a complex metabolic activity during which the energy needed to support life activities is released. • During resp ...
... Breathing • Breathing- (aka ventilation), The process through which the respiratory system moves air into and out of the lungs. • In contrast, Respiration refers to cellular respiration, a complex metabolic activity during which the energy needed to support life activities is released. • During resp ...
Nitrogen Cycle
... this point forth. Plants and algae can assimilate ammonia and ammonium directly for the biosynthesis. The remaining bulk of decomposed byproducts is utilized by bacteria in a process called nitrification. Some are used by heterotroph for further assimilation of organic carbon. Some are fixed by clay ...
... this point forth. Plants and algae can assimilate ammonia and ammonium directly for the biosynthesis. The remaining bulk of decomposed byproducts is utilized by bacteria in a process called nitrification. Some are used by heterotroph for further assimilation of organic carbon. Some are fixed by clay ...
Cycles of Matter in the Biosphere
... Carbon is found in all living organisms on Earth The most common exchange of Carbon is between plants and animals though there are Four Main Ways Carbon is recycled in the ...
... Carbon is found in all living organisms on Earth The most common exchange of Carbon is between plants and animals though there are Four Main Ways Carbon is recycled in the ...
Intro to Biology & Biochemistry
... - the basic building blocks for the body - they contain the elements C, H, O, N, & sometimes S- they are made of monomers known as amino acids - polypeptides are long chains of amino acids - proteins are held ...
... - the basic building blocks for the body - they contain the elements C, H, O, N, & sometimes S- they are made of monomers known as amino acids - polypeptides are long chains of amino acids - proteins are held ...
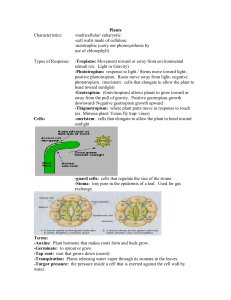
Plants
... Xylem-a transport subsystem containing key cells called tracheids. This system carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Tracheids are hollow cells with thick cell walls that resist pressure (example- drinking straw). Phloem-transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates pro ...
... Xylem-a transport subsystem containing key cells called tracheids. This system carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Tracheids are hollow cells with thick cell walls that resist pressure (example- drinking straw). Phloem-transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates pro ...
Loomis EOC Practice part 2 EOCpracticePart2
... will be more question about species interactions (symbiosis, etc) as well as food webs, bioamplification, and energy pyramids. There should be questions from CH 15 (resources) and CH 16 (engineering design process) and of course, complex systems. Bottom line, pay attention to BULLETS in extended res ...
... will be more question about species interactions (symbiosis, etc) as well as food webs, bioamplification, and energy pyramids. There should be questions from CH 15 (resources) and CH 16 (engineering design process) and of course, complex systems. Bottom line, pay attention to BULLETS in extended res ...
Key Terms * Copy into your journal
... an ecosystem? • Plants use Carbon dioxide from the air to create food. • When that plant is eaten, the stored carbon is broken down and is now in the animal’s system. • The animal breathes out carbon dioxide and it is released back into the atmosphere. • If the animal dies, the carbon is broken down ...
... an ecosystem? • Plants use Carbon dioxide from the air to create food. • When that plant is eaten, the stored carbon is broken down and is now in the animal’s system. • The animal breathes out carbon dioxide and it is released back into the atmosphere. • If the animal dies, the carbon is broken down ...
Post-Test Plants January 25, 2014
... a. To protect and distribute the zygote. b. To entice animals to eat the plant. c. To be fertilized by other plants. d. To store water for the mother plant. ...
... a. To protect and distribute the zygote. b. To entice animals to eat the plant. c. To be fertilized by other plants. d. To store water for the mother plant. ...
Exam I Sample Questions
... Sufficient energy must be added to break hydrogen bonding between neighboring water molecules before its state can change from liquid to gas Sufficient energy must be added to redistribute electrons from the oxygen molecule to the hydrogen molecules of the water molecules before its state can change ...
... Sufficient energy must be added to break hydrogen bonding between neighboring water molecules before its state can change from liquid to gas Sufficient energy must be added to redistribute electrons from the oxygen molecule to the hydrogen molecules of the water molecules before its state can change ...
1 - theozone
... spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. b. c. d. ...
... spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. b. c. d. ...
Biochemical Compounds
... all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms Carbon can covalently bond with many other elements because it has four valence electrons Carbon can form chains or rings by bonding with other carbon atoms ...
... all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms Carbon can covalently bond with many other elements because it has four valence electrons Carbon can form chains or rings by bonding with other carbon atoms ...
1 - Revsworld
... spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. b. c. d. ...
... spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. b. c. d. ...
Metabolic pathways are
... ii) the nature of the chemical reaction. iii) most names end in “-ase” Common Enzymes Involved in Metabolism: Kinase: transfers a phosphate group from ATP to another compound (e.g. glucose kinase). Phosphatase: Removes a phosphate group from a substrate, no ATP/ADP required (e.g. phosphoglucose phos ...
... ii) the nature of the chemical reaction. iii) most names end in “-ase” Common Enzymes Involved in Metabolism: Kinase: transfers a phosphate group from ATP to another compound (e.g. glucose kinase). Phosphatase: Removes a phosphate group from a substrate, no ATP/ADP required (e.g. phosphoglucose phos ...
Lesson plan MULTIKEY
... Chemical reactions within cells drive all activities associated with life. During chemical reactions, atoms of the reactants (starting materials) are rearranged to form the products (ending materials). In human cells chemical reactions make new products and release energy. At any moment, thousands o ...
... Chemical reactions within cells drive all activities associated with life. During chemical reactions, atoms of the reactants (starting materials) are rearranged to form the products (ending materials). In human cells chemical reactions make new products and release energy. At any moment, thousands o ...
Saturday Review – Biology
... ____ 62. On a hot summer day, a road crew worker perspires and then feels thirsty as her body temperature increases. This response is an example of a. releasing enzymes. c. assimilation proteins. b. decreasing respiration. d. maintaining homeostasis. ...
... ____ 62. On a hot summer day, a road crew worker perspires and then feels thirsty as her body temperature increases. This response is an example of a. releasing enzymes. c. assimilation proteins. b. decreasing respiration. d. maintaining homeostasis. ...
Science Chapter 7 Notes - msgreenshomepage
... 1. In any food web, energy is lost each time one organism eats another. Because of this, there have to be many more plants than there are plant-eaters. There are more ...
... 1. In any food web, energy is lost each time one organism eats another. Because of this, there have to be many more plants than there are plant-eaters. There are more ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.