Cellular Respiration
... This is the final pathway of aerobic respiration. It occurS in the mitochondria. The pathway removes electrons and protons from the NADH and FADH2 molecules. FAD is Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide. It is an electron carrier like NADH. FADH2 is the reduced fonn that carries the electrons and protons. . E ...
... This is the final pathway of aerobic respiration. It occurS in the mitochondria. The pathway removes electrons and protons from the NADH and FADH2 molecules. FAD is Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide. It is an electron carrier like NADH. FADH2 is the reduced fonn that carries the electrons and protons. . E ...
Horticulture I- Unit B 3.00 Plant Physiology
... •_______________________________-breathing pores •_______________________________-show where terminal buds have been located •_______________________________-show where leaves were attached •_______________________________-bud on the end of a stem •_________________________________________-bud on si ...
... •_______________________________-breathing pores •_______________________________-show where terminal buds have been located •_______________________________-show where leaves were attached •_______________________________-bud on the end of a stem •_________________________________________-bud on si ...
Sample question
... Similarly the grasshopper has a gastric caecum which may contain these bacteria for the same reason. Humans don’t need to digest cellulose so their equivalent (appendix) is very small and doesn’t house bacteria. ...
... Similarly the grasshopper has a gastric caecum which may contain these bacteria for the same reason. Humans don’t need to digest cellulose so their equivalent (appendix) is very small and doesn’t house bacteria. ...
Vascular tissue
... leaves; flower parts in sets of 2, 4, or 5; netted / branching veins on leaves ...
... leaves; flower parts in sets of 2, 4, or 5; netted / branching veins on leaves ...
File
... Read through the list of objectives we have covered. These are what you need to know for your quiz. Read through them. If you can answer the statement, check it off. If not, this is an area you need to study or come in and ask me some questions. Be sure to read your science daily reviews and your vo ...
... Read through the list of objectives we have covered. These are what you need to know for your quiz. Read through them. If you can answer the statement, check it off. If not, this is an area you need to study or come in and ask me some questions. Be sure to read your science daily reviews and your vo ...
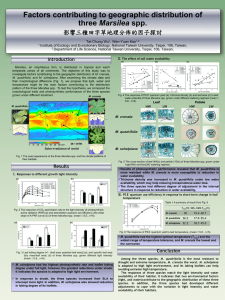
Factors contribuctied to gregraphic distribution of three Marsilea spp
... Marsilea, an amphibious fern, is distributed in tropical and warm temperate zones of all continents. The objective of this study was to investigate factors contributing to the geographic distribution of M. crenata, M. quadrifolia, and M. schelpiana. After examining the climate data and their morphol ...
... Marsilea, an amphibious fern, is distributed in tropical and warm temperate zones of all continents. The objective of this study was to investigate factors contributing to the geographic distribution of M. crenata, M. quadrifolia, and M. schelpiana. After examining the climate data and their morphol ...
Biology – Module 2 – Patterns in Nature
... respect to: o the chemical composition of their diet o the functions of the structures involved The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and its associated organs. The alimentary canal is a long tube running from the mouth of to the anus where the ingested food is broken down into small ...
... respect to: o the chemical composition of their diet o the functions of the structures involved The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and its associated organs. The alimentary canal is a long tube running from the mouth of to the anus where the ingested food is broken down into small ...
Science Department Fourth Primary General Revision Unit one 1
... A lot of animals depend mainly on plants to get their food. Plants supply animals with the required energy for survival. For example, we see cows and sheep feed on the plants, and birds feed on the seeds of some plants. How do plants manufacture their food? Plants manufacture their food Plant cells ...
... A lot of animals depend mainly on plants to get their food. Plants supply animals with the required energy for survival. For example, we see cows and sheep feed on the plants, and birds feed on the seeds of some plants. How do plants manufacture their food? Plants manufacture their food Plant cells ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... a. Provide structural units found in ____ and in the cell membrane b. Provide the major _____ source for the body. c. Each gram of carbohydrate provides ____ Kcalories. d. Only energy source for ____ and nerve cells. e. Blood sugar is known as _______. B. Lipids (Fats) 1. Structure of Lipids a. Lipi ...
... a. Provide structural units found in ____ and in the cell membrane b. Provide the major _____ source for the body. c. Each gram of carbohydrate provides ____ Kcalories. d. Only energy source for ____ and nerve cells. e. Blood sugar is known as _______. B. Lipids (Fats) 1. Structure of Lipids a. Lipi ...
Environmental Microbiology – Seminar 31.10
... 2) What happens if there is no O2 in the body? In other words: no NAD+ available and Glycolysis process stops. Without oxygen humans die quickly. In muscles, however, oxygen is often used up and then the cells gain energy by substrate level phosphorylation in glycolysis and get rid of their electron ...
... 2) What happens if there is no O2 in the body? In other words: no NAD+ available and Glycolysis process stops. Without oxygen humans die quickly. In muscles, however, oxygen is often used up and then the cells gain energy by substrate level phosphorylation in glycolysis and get rid of their electron ...
Paleo Lecture 1 - Tarleton State University
... 54. Mixtures of methane, ammonia, hydrogen and water vapor (or nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor) in the presence of electricity or ultraviolet light leads to the production of A.nucleic acids B.organic phosphorous compounds C.amino acids D.it may lead to any of the above 55. ? is a by-produc ...
... 54. Mixtures of methane, ammonia, hydrogen and water vapor (or nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor) in the presence of electricity or ultraviolet light leads to the production of A.nucleic acids B.organic phosphorous compounds C.amino acids D.it may lead to any of the above 55. ? is a by-produc ...
The effects of interaction of biotic and abiotic factors
... global carbon (C) cycle (McGuire et al. 2009; Lafleur et al. 2012) since northern soils account for approximately 50% of the estimated global below-ground organic C (Tarnocai et al. 2009). In particular, climate changes may turn cold biomes from sinks to sources depending on the balance between Gros ...
... global carbon (C) cycle (McGuire et al. 2009; Lafleur et al. 2012) since northern soils account for approximately 50% of the estimated global below-ground organic C (Tarnocai et al. 2009). In particular, climate changes may turn cold biomes from sinks to sources depending on the balance between Gros ...
Plants
... nutrients for the plants • Hold the plant to the ground • Store extra food for the plant. Plant food is starch (a polysaccharide) ...
... nutrients for the plants • Hold the plant to the ground • Store extra food for the plant. Plant food is starch (a polysaccharide) ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions plants are grown in can be changed to promote growth. ...
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions plants are grown in can be changed to promote growth. ...
answers - Biology Resources
... conditions of moisture and temperature but placed in daylight for the same period of time. At the end of this period the numbers of seeds which germinated in each case would be counted and compared. 14 Figure 1: A-plumule, will form the plant's shoot; B-radicle, will form the plant's first root; C- ...
... conditions of moisture and temperature but placed in daylight for the same period of time. At the end of this period the numbers of seeds which germinated in each case would be counted and compared. 14 Figure 1: A-plumule, will form the plant's shoot; B-radicle, will form the plant's first root; C- ...
here
... which will produce new cells of both allowing for the plant to thicken. They transport the fluids and nutrients from the root to the leaf Meristem is undifferentiated cells which give rise to various organs - vascular tissue, flowers, leaves. They are filled with cytoplasm and few organelles In wood ...
... which will produce new cells of both allowing for the plant to thicken. They transport the fluids and nutrients from the root to the leaf Meristem is undifferentiated cells which give rise to various organs - vascular tissue, flowers, leaves. They are filled with cytoplasm and few organelles In wood ...
Document
... b. High levels of fermentation products will build up in their bodies c. They will no longer be able to produce adequate amounts of ATP d. They will no longer be able to absorb water and will become dehydrated ...
... b. High levels of fermentation products will build up in their bodies c. They will no longer be able to produce adequate amounts of ATP d. They will no longer be able to absorb water and will become dehydrated ...
VCE426_913 - VTechWorks
... a plant uses to make its food. A pigment (coloring) called chlorophyll, which gives leaves their green color, is used to collect this solar energy. Some plants, like red cabbage, have leaves of another color, but if you look closely you will see green mixed in with with other colors. When light stri ...
... a plant uses to make its food. A pigment (coloring) called chlorophyll, which gives leaves their green color, is used to collect this solar energy. Some plants, like red cabbage, have leaves of another color, but if you look closely you will see green mixed in with with other colors. When light stri ...
AP PPT - Respiratory
... • Describe the structure and functions of the organs of the respiratory system • Trace the movement of air from the nostrils to the alveoli • Describe the role of pulmonary surfactants • Explain how respiratory muscles affect thoracic volume • List three conditions that make the alveoli wellsuited f ...
... • Describe the structure and functions of the organs of the respiratory system • Trace the movement of air from the nostrils to the alveoli • Describe the role of pulmonary surfactants • Explain how respiratory muscles affect thoracic volume • List three conditions that make the alveoli wellsuited f ...
Mitochondrial Respiration
... involves energy capture through incorporation of carbon into small sugars, which are reduced by energy from photosynthetic electron transport. The citric acid cycle involves energy release through loss of carbon from small organic acids which are oxidized, producing electrons to be used in mitochond ...
... involves energy capture through incorporation of carbon into small sugars, which are reduced by energy from photosynthetic electron transport. The citric acid cycle involves energy release through loss of carbon from small organic acids which are oxidized, producing electrons to be used in mitochond ...
File
... • Because the respiratory system only has one entrance and exit point, anything blocking the pathway will interrupt gas exchange (choke). • Since oxygen cannot reach the alveoli, no oxygen can go into the blood. • If no oxygen gets into the blood, the body cell will not be able to perform cellular r ...
... • Because the respiratory system only has one entrance and exit point, anything blocking the pathway will interrupt gas exchange (choke). • Since oxygen cannot reach the alveoli, no oxygen can go into the blood. • If no oxygen gets into the blood, the body cell will not be able to perform cellular r ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.