fermentation
... 1. No oxygen is required for fermentation. Aerobic respiration is typically the first path pyruvate will take because it is far more efficient in terms of energy capture than the other methods (capturing (40% of the original energy in glucose versus the 2% that fermentation captures). However, aero ...
... 1. No oxygen is required for fermentation. Aerobic respiration is typically the first path pyruvate will take because it is far more efficient in terms of energy capture than the other methods (capturing (40% of the original energy in glucose versus the 2% that fermentation captures). However, aero ...
The Krebs Cycle - Advanced
... dramatic changes during the history of earth’s atmosphere. Correlating these clues with the fossil record leads to two major conclusions: that early life evolved in the absence of oxygen, and that oxygen first appeared between 2 and 3 billion years ago ( Figure 1.1) because of photosynthesis by the ...
... dramatic changes during the history of earth’s atmosphere. Correlating these clues with the fossil record leads to two major conclusions: that early life evolved in the absence of oxygen, and that oxygen first appeared between 2 and 3 billion years ago ( Figure 1.1) because of photosynthesis by the ...
Slide 1
... Some plants are short-day plants, some are long-day plants, others are intermediate-day plants ...
... Some plants are short-day plants, some are long-day plants, others are intermediate-day plants ...
Chapter 1
... There are several classes of consumers, depending on their food source – Primary consumers (herbivores): Feed directly on plants or other producers e.g. - zooplankton (copepods, cladocerans etc.) – Secondary consumers (primary carnivores) feed on primary consumers. e.g ...
... There are several classes of consumers, depending on their food source – Primary consumers (herbivores): Feed directly on plants or other producers e.g. - zooplankton (copepods, cladocerans etc.) – Secondary consumers (primary carnivores) feed on primary consumers. e.g ...
Chapter 9
... Decomposition involves respiration: the release of the energy fixed by photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O. Decomposition involves several processes: fragmentation, ingestion, egestion, and concentration. All heterotrophs are decomposers to some extent, but the concept of decomposers is reserved for those o ...
... Decomposition involves respiration: the release of the energy fixed by photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O. Decomposition involves several processes: fragmentation, ingestion, egestion, and concentration. All heterotrophs are decomposers to some extent, but the concept of decomposers is reserved for those o ...
Ecology Slide 3
... the sun to the Earth • Most solar energy reaching Earth is reflected or absorbed • Only about 1% of total energy is available for photosynthesis • Photosynthetic organisms capture only about 3% of this amount ...
... the sun to the Earth • Most solar energy reaching Earth is reflected or absorbed • Only about 1% of total energy is available for photosynthesis • Photosynthetic organisms capture only about 3% of this amount ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... of oxygen consumption. Studies on simple animals often use a respirometer. Respirometers measure the change in gas volume in a closed system. Any change is due to the respiratory activity of the study organisms. Potassium hydroxide or soda lime is used to absorb the carbon dioxide produced, meaning ...
... of oxygen consumption. Studies on simple animals often use a respirometer. Respirometers measure the change in gas volume in a closed system. Any change is due to the respiratory activity of the study organisms. Potassium hydroxide or soda lime is used to absorb the carbon dioxide produced, meaning ...
08_Cellular respiration ppt
... Two electrons and one hydrogen ion are accepted by NAD+ resulting two NADH Four ATP produced by substrate-level phosphorylation Net gain of two ATP Both G3Ps converted to pyruvates ...
... Two electrons and one hydrogen ion are accepted by NAD+ resulting two NADH Four ATP produced by substrate-level phosphorylation Net gain of two ATP Both G3Ps converted to pyruvates ...
all notes from this document will be shown in class
... decomposers with energy to run their metabolism. Energy and matter can also move from one ecosystem to another. This movement is done through processes like seed dispersal, animal migration, leaching, and erosion.A biome is a major ecosystem type that can be found in different regions of the planet ...
... decomposers with energy to run their metabolism. Energy and matter can also move from one ecosystem to another. This movement is done through processes like seed dispersal, animal migration, leaching, and erosion.A biome is a major ecosystem type that can be found in different regions of the planet ...
File
... 3. Insert the plastic straw into the other balloon. Wrap the rubber band around the neck of the balloon, securing the straw in place. ...
... 3. Insert the plastic straw into the other balloon. Wrap the rubber band around the neck of the balloon, securing the straw in place. ...
1. Explain how a hormone may cause its effect on
... 23. Using photoperiodism as an example, explain how an integrated control system can regulate a plant process such as flowering. • Photoperiodism is a series of complicated systems working together • Phytochromes detect the amount & quality of light to determine if flowering will happen • Plant hor ...
... 23. Using photoperiodism as an example, explain how an integrated control system can regulate a plant process such as flowering. • Photoperiodism is a series of complicated systems working together • Phytochromes detect the amount & quality of light to determine if flowering will happen • Plant hor ...
Which of the following molecules is most likely to be used in a
... Note to students: The answers to these questions are detailed as this is considered an open book assignment. Use this key as a worksheet for final exam and you can simplify the answers in your own words, if you need to! Generation of Biochemical Energy and Krebs cycle: 1. Distinguish between cyclic ...
... Note to students: The answers to these questions are detailed as this is considered an open book assignment. Use this key as a worksheet for final exam and you can simplify the answers in your own words, if you need to! Generation of Biochemical Energy and Krebs cycle: 1. Distinguish between cyclic ...
Respiratory system 1
... • Respiration is the circulation on gases around the body. • The supply of gases is delivered through the process of breathing.(Respiration) ...
... • Respiration is the circulation on gases around the body. • The supply of gases is delivered through the process of breathing.(Respiration) ...
Chemical Reactions (Part One)
... Eggs contain a protein called albumen. The protein molecules are long chains of amino acids folded into a ball shape. When eggs are heated, some of the proteins break apart and the molecules unfold. These molecules then join to other nearby protein molecules until they are all linked in a network. 1 ...
... Eggs contain a protein called albumen. The protein molecules are long chains of amino acids folded into a ball shape. When eggs are heated, some of the proteins break apart and the molecules unfold. These molecules then join to other nearby protein molecules until they are all linked in a network. 1 ...
Respiratory System
... • The lower end of the trachea divides into two bronchi (tubes) that carry air into the lungs. One bronchus goes to the left lung, the other to the right lung. • Bronchioles: The smallest branches of the bronchi ...
... • The lower end of the trachea divides into two bronchi (tubes) that carry air into the lungs. One bronchus goes to the left lung, the other to the right lung. • Bronchioles: The smallest branches of the bronchi ...
Resp Notes
... facilitate diffusion by “carrying” oxygen across the cell membranes ﴾no energy required﴿. ...
... facilitate diffusion by “carrying” oxygen across the cell membranes ﴾no energy required﴿. ...
Electron Transport Chain Questions
... 9. What is the purpose of NAD+? What type of reaction is NAD+ involved in? The purpose of NAD+ is to serve as an electron carrier. As bonds are broken in the molecule when it is oxidized (loses electrons and H+ ion), NAD+ collects the energy in the form of electrons and becomes reduced to NADH (oxid ...
... 9. What is the purpose of NAD+? What type of reaction is NAD+ involved in? The purpose of NAD+ is to serve as an electron carrier. As bonds are broken in the molecule when it is oxidized (loses electrons and H+ ion), NAD+ collects the energy in the form of electrons and becomes reduced to NADH (oxid ...
External factors and plant growth – Chapter 28
... Tensional integrity is structural integrity created by interactive tension between structure components Disruption of integrity increases calcium levels Thigmotropism Response to touch Tendrils Circadian rhythms Regular 24-hour cycles in plant function Biological clocks Rhythms continue ...
... Tensional integrity is structural integrity created by interactive tension between structure components Disruption of integrity increases calcium levels Thigmotropism Response to touch Tendrils Circadian rhythms Regular 24-hour cycles in plant function Biological clocks Rhythms continue ...
File
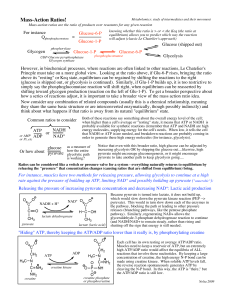
... energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction. For example, the burning of wood is a chemical reaction (see Figure 2.51). Cellulose and other substances in the wood combine ...
... energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction. For example, the burning of wood is a chemical reaction (see Figure 2.51). Cellulose and other substances in the wood combine ...
electron transport chain
... -are oxidations – loss of electrons -are also dehydrogenations lost electrons are accompanied by hydrogen what is actually lost is a hydrogen atom (1 electron, 1 proton). • A hydrogen atom is equivalent to a hydrogen ion plus an electron H = H+ + e-electrons carry energy from one molecule to another ...
... -are oxidations – loss of electrons -are also dehydrogenations lost electrons are accompanied by hydrogen what is actually lost is a hydrogen atom (1 electron, 1 proton). • A hydrogen atom is equivalent to a hydrogen ion plus an electron H = H+ + e-electrons carry energy from one molecule to another ...
Gloxinia Production
... nitrogen in the ammonium form because these have resulted in foliar disorders. Twisted, cupped, or curled leaves with a general deep blue-green color are often symptoms ofexcess nitrogen or high ammonium. Watch for boron deficiency during periods of high light in the summer. Crown leaves will be def ...
... nitrogen in the ammonium form because these have resulted in foliar disorders. Twisted, cupped, or curled leaves with a general deep blue-green color are often symptoms ofexcess nitrogen or high ammonium. Watch for boron deficiency during periods of high light in the summer. Crown leaves will be def ...
From Seed to Shining Seed
... its energy by breaking down glucose through a process called respiration. Respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis. (See the illustration Respiration and Photosynthesis on page 122.) Plants continuously transport water to the leaves from the roots. Leaves release water vapor and other gases thro ...
... its energy by breaking down glucose through a process called respiration. Respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis. (See the illustration Respiration and Photosynthesis on page 122.) Plants continuously transport water to the leaves from the roots. Leaves release water vapor and other gases thro ...
Cellular Respiration Worksheet and Answers
... 13. Under which condition would you expect the mitochondrial proton gradient to be highest and therefore ATP synthesis to proceed? a. Pyruvate (present) oxygen (present) ATP levels (high) b. Pyruvate (present) oxygen (present) ATP ...
... 13. Under which condition would you expect the mitochondrial proton gradient to be highest and therefore ATP synthesis to proceed? a. Pyruvate (present) oxygen (present) ATP levels (high) b. Pyruvate (present) oxygen (present) ATP ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.