Aerobic Energy Systems
... VO2 max is the maximum amount of O2 that the body can consume and use. A higher VO2 max means a higher level of aerobic fitness. If exercise intensity is submaximal (below VO2 max) then O2 consumption reaches a ‘steady state.’ – O2 consumption matches O2 required. VO2 max can be assessed by measurin ...
... VO2 max is the maximum amount of O2 that the body can consume and use. A higher VO2 max means a higher level of aerobic fitness. If exercise intensity is submaximal (below VO2 max) then O2 consumption reaches a ‘steady state.’ – O2 consumption matches O2 required. VO2 max can be assessed by measurin ...
[B] There are two classes of flowering plants, Monocotyledons and
... numerous joining cross veins so that, as with the dicotyledon, mesophyll cells are always close to a vein. ...
... numerous joining cross veins so that, as with the dicotyledon, mesophyll cells are always close to a vein. ...
Lab 4: Non Tracehophytes and Seedless Tracheophytes
... Plants are generally defined as multicellular, photosynthetic eukaryotes. Plants cells have cell walls composed of cellulose, and store surplus carbohydrates as starch. They utilize two photosystems in photosynthesis with two forms of chlorophyll (a and b).This list of characteristics is not mutuall ...
... Plants are generally defined as multicellular, photosynthetic eukaryotes. Plants cells have cell walls composed of cellulose, and store surplus carbohydrates as starch. They utilize two photosystems in photosynthesis with two forms of chlorophyll (a and b).This list of characteristics is not mutuall ...
Oecologia (Bcrl.) 45, 331-340 (1980)
... chloroplasts were isolated in a solution containing 0.35 M NaCl, lOmg/ml Bovine Serum Albumin, 1% PVP-40 in 0.1 M Tricine, pH 7.8. The final chloroplast solution was made up in a 1:10 diluted mixture of the above buffer. An aliquot of this solution 2) Carbon Fixation containing from 15-50 ug of chlo ...
... chloroplasts were isolated in a solution containing 0.35 M NaCl, lOmg/ml Bovine Serum Albumin, 1% PVP-40 in 0.1 M Tricine, pH 7.8. The final chloroplast solution was made up in a 1:10 diluted mixture of the above buffer. An aliquot of this solution 2) Carbon Fixation containing from 15-50 ug of chlo ...
Strange Plants - Pearson SuccessNet
... All carnivorous, or meat-eating, plants grow in places where the soil lacks some nutrients they need to grow. To get these nutrients, they feed on the flesh of insects and other small animals. The Venus’s flytrap is called an active meateating plant because its leaves actually move to trap flies. Fl ...
... All carnivorous, or meat-eating, plants grow in places where the soil lacks some nutrients they need to grow. To get these nutrients, they feed on the flesh of insects and other small animals. The Venus’s flytrap is called an active meateating plant because its leaves actually move to trap flies. Fl ...
The Energy of Life The living cell Is a miniature factory where
... Bind to another part of an enzyme, changing the function A noncompetitive inhibitor binds to the enzyme away from the active site, altering the conformation of the enzyme so that its ...
... Bind to another part of an enzyme, changing the function A noncompetitive inhibitor binds to the enzyme away from the active site, altering the conformation of the enzyme so that its ...
AP Biology Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... without oxygen. It only releases a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis: the first step of breaking down glucose—it splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3C each) ...
... without oxygen. It only releases a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis: the first step of breaking down glucose—it splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3C each) ...
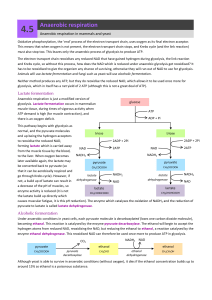
Anaerobic respiration
... has to be reoxidised to give the organism any chance of surviving, otherwise they will run out of NAD to use for glycolysis. Animals will use lactate fermentation and fungi such as yeast will use alcoholic fermentation. Neither method produces any ATP, but they do reoxidise the reduced NAD, which al ...
... has to be reoxidised to give the organism any chance of surviving, otherwise they will run out of NAD to use for glycolysis. Animals will use lactate fermentation and fungi such as yeast will use alcoholic fermentation. Neither method produces any ATP, but they do reoxidise the reduced NAD, which al ...
File
... molecules which transfer specific ion across the membrane. These proteins are sometimes called pumps. They can have a dual role, e.g. the sodium/potassium pump actively pumps sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, both against their own concentration gradient. ...
... molecules which transfer specific ion across the membrane. These proteins are sometimes called pumps. They can have a dual role, e.g. the sodium/potassium pump actively pumps sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, both against their own concentration gradient. ...
Metabolism - College of the Canyons
... 2 FAD + 2 H2 2 FADH2 • Carbon atoms of glucose have all been carried away as CO2 and exhaled • Energy lost as heat, stored in 2 ATP, 8 reduced NADH, 2 FADH2 molecules of the matrix reactions and 2 NADH from glycolysis • Citric acid cycle is a source of substances for synthesis of fats and nonessen ...
... 2 FAD + 2 H2 2 FADH2 • Carbon atoms of glucose have all been carried away as CO2 and exhaled • Energy lost as heat, stored in 2 ATP, 8 reduced NADH, 2 FADH2 molecules of the matrix reactions and 2 NADH from glycolysis • Citric acid cycle is a source of substances for synthesis of fats and nonessen ...
Assessment Schedule – 2011
... produces glucose sugar and oxygen gas. When aphids suck the sap from roses, the growth of plants is reduced because new leaves are damaged or eaten. Without more leaves, the plant cannot carry out photosynthesis effectively. Fungal diseases flourish most during warm, humid weather. Spring and autumn ...
... produces glucose sugar and oxygen gas. When aphids suck the sap from roses, the growth of plants is reduced because new leaves are damaged or eaten. Without more leaves, the plant cannot carry out photosynthesis effectively. Fungal diseases flourish most during warm, humid weather. Spring and autumn ...
Lecture_10_F11
... Cellular Respiration: the big picture • process in which cells consume O2 and produce CO2 ...
... Cellular Respiration: the big picture • process in which cells consume O2 and produce CO2 ...
Ch 25 Powerpoint
... and break down pyruvic acid molecules: H atoms of pyruvic acid are removed by coenzymes and are primary source of energy gain C and O atoms are removed and released as CO2 in the process of decarboxylation ...
... and break down pyruvic acid molecules: H atoms of pyruvic acid are removed by coenzymes and are primary source of energy gain C and O atoms are removed and released as CO2 in the process of decarboxylation ...
Plants & The Colonization of Land
... Instead, these plants transport water from cell-to-cell by osmosis Vascular Plants Have specialized tissues to transport water and nutrients in plants Xylem – carries water upward from roots Phloem – carries nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis ...
... Instead, these plants transport water from cell-to-cell by osmosis Vascular Plants Have specialized tissues to transport water and nutrients in plants Xylem – carries water upward from roots Phloem – carries nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis ...
Plants & The Colonization of Land
... Instead, these plants transport water from cell-to-cell by osmosis Vascular Plants Have specialized tissues to transport water and nutrients in plants Xylem – carries water upward from roots Phloem – carries nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis ...
... Instead, these plants transport water from cell-to-cell by osmosis Vascular Plants Have specialized tissues to transport water and nutrients in plants Xylem – carries water upward from roots Phloem – carries nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis ...
Lesson 4 - Plant Processes - Hitchcock
... reflects more green light than it reflects other colors of light. As a result, most plants look green. ...
... reflects more green light than it reflects other colors of light. As a result, most plants look green. ...
Cellular Respiration - UNT's College of Education
... To review the "big picture" of metabolism, aiding students in understanding the relationship among glycolysis, the Kreb's cycle, and the ETC. See the diagram for the simulation layout. ...
... To review the "big picture" of metabolism, aiding students in understanding the relationship among glycolysis, the Kreb's cycle, and the ETC. See the diagram for the simulation layout. ...
Three–dimensional Modelling of dc Arc Discharges for Carbon Nanostructure production
... Keywords: arc discharge, carbon nanotubes, graphene, modeling, computational fluid dynamics 1. Introduction Carbon nanostructures, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoribbons, have unique properties that have motivated many researchers to attempt their integration into advanced new devices. Po ...
... Keywords: arc discharge, carbon nanotubes, graphene, modeling, computational fluid dynamics 1. Introduction Carbon nanostructures, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoribbons, have unique properties that have motivated many researchers to attempt their integration into advanced new devices. Po ...
EOC Biology Prep Reporting Category 5 Interdependence within
... Metabolism produces nitrogenous compounds that must be excreted from the body. These compounds can be excreted as different types of waste products. Some characteristics of each type of waste are shown in the tables below. ...
... Metabolism produces nitrogenous compounds that must be excreted from the body. These compounds can be excreted as different types of waste products. Some characteristics of each type of waste are shown in the tables below. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.

![[B] There are two classes of flowering plants, Monocotyledons and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008149765_1-fc8c97c2a4d1c1fef9c3adc6730fba20-300x300.png)