Multi-Transistor Circuits: Current Mirror and Differential Pair Phys 3610/6610 Lab 20 Student: TA:
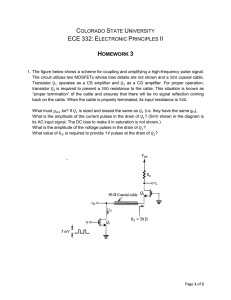
... Phys 3610/6610 Lab 20 ...
... Phys 3610/6610 Lab 20 ...
BEX100 – Basic Electricity
... transistors, (PNP, NPN types) and explain how they operate Understand what is meant by “Amplifier Current Gain” of a transistor Interpret wiring schematics containing transistors Identify the various application uses for transistors Understand the basic construction of an SCR and how it functions ...
... transistors, (PNP, NPN types) and explain how they operate Understand what is meant by “Amplifier Current Gain” of a transistor Interpret wiring schematics containing transistors Identify the various application uses for transistors Understand the basic construction of an SCR and how it functions ...
Transistors, Logic Gates and Karnaugh Maps
... Introduction to Digital Systems (J.Palmer and D. Perlman) ...
... Introduction to Digital Systems (J.Palmer and D. Perlman) ...
Introduction:
... The transistor is a main building block of all modern electronic systems.It is a three terminal device whose output current, voltage and/ or power are controlled by its input current. In digital computer electronics , the transistor is used as a high speed electronic switch that is capable of switch ...
... The transistor is a main building block of all modern electronic systems.It is a three terminal device whose output current, voltage and/ or power are controlled by its input current. In digital computer electronics , the transistor is used as a high speed electronic switch that is capable of switch ...
pdf
... Figure 7-2: APS-2 pixel layout. The four large rectangles make up the CDS capacitor C2 . The reset and source follower transistors use H-gates, while the current source and row-select switches use straight gates. ...
... Figure 7-2: APS-2 pixel layout. The four large rectangles make up the CDS capacitor C2 . The reset and source follower transistors use H-gates, while the current source and row-select switches use straight gates. ...
EE 3161 – Semiconductor Devices
... must be accompanied by a doctor’s excuse. If an exam is missed with such an excuse, we will just make the final worth more to cover the lost exam. Emails: At the moment the class enrollment looks like it will be about 80 students. With this large of a class size, I honestly don’t think I will be abl ...
... must be accompanied by a doctor’s excuse. If an exam is missed with such an excuse, we will just make the final worth more to cover the lost exam. Emails: At the moment the class enrollment looks like it will be about 80 students. With this large of a class size, I honestly don’t think I will be abl ...
Chapter 24: Electronics
... Digital signals are also easier to store, process, and reproduce than analog signals. ...
... Digital signals are also easier to store, process, and reproduce than analog signals. ...
Physics First Ch 24 ppt
... Digital signals are also easier to store, process, and reproduce than analog signals. ...
... Digital signals are also easier to store, process, and reproduce than analog signals. ...
Transistors
... Hearing Aids were the first commercial application of the new solid state invention ...
... Hearing Aids were the first commercial application of the new solid state invention ...
Drivetrain
... it high current gain (written β or hFE), and takes up less space than using two discrete transistors in the same configuration. The use of two separate transistors in an actual circuit is still very common, even though integrated packaged devices are available. This configuration was invented by eng ...
... it high current gain (written β or hFE), and takes up less space than using two discrete transistors in the same configuration. The use of two separate transistors in an actual circuit is still very common, even though integrated packaged devices are available. This configuration was invented by eng ...
U00d9#U2026#U00d8#U00b4#U00d8#U00b1#U00d9
... or digital (uses a display much like a digital clock). Integrated circuits have made digital logic so inexpensive that an electronic timer is now less expensive than many mechanical and electromechanical timers. Individual timers are implemented as a simple single-chip computer system, similar to a ...
... or digital (uses a display much like a digital clock). Integrated circuits have made digital logic so inexpensive that an electronic timer is now less expensive than many mechanical and electromechanical timers. Individual timers are implemented as a simple single-chip computer system, similar to a ...
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS (BJTS)
... to a conducting plate, which is insulated from the silicon by a layer of non conducting oxide or a layer of polycrystalline silicon (poly silicon) Depletion-mode n-channel MOSFET is a unipolar transistor because only one kind ("polarity") of electric charge is involved in making it ...
... to a conducting plate, which is insulated from the silicon by a layer of non conducting oxide or a layer of polycrystalline silicon (poly silicon) Depletion-mode n-channel MOSFET is a unipolar transistor because only one kind ("polarity") of electric charge is involved in making it ...
Semiconductor Devices II
... At their most basic level, transistors may seem simple. But their development actually required many years of painstaking research. Before transistors, computers relied on slow, inefficient vacuum tubes and mechanical switches to process information. In 1958, engineers (one of them Intel co-founder ...
... At their most basic level, transistors may seem simple. But their development actually required many years of painstaking research. Before transistors, computers relied on slow, inefficient vacuum tubes and mechanical switches to process information. In 1958, engineers (one of them Intel co-founder ...
Lecture#6 Transistor Biasing Circuit (Q point and dc load line)
... The DC Operating point For a transistor circuit to amplify it must be properly biased with dc voltages. The dc operating point between saturation and cutoff is called the Q-point. The goal is to set the Q-point such that that it does not go into saturation or cutoff when an a ac signal is applied. ...
... The DC Operating point For a transistor circuit to amplify it must be properly biased with dc voltages. The dc operating point between saturation and cutoff is called the Q-point. The goal is to set the Q-point such that that it does not go into saturation or cutoff when an a ac signal is applied. ...
4 – The Power BJT 3
... blocking must be negative and the device must be kept in quasi-saturation to minimize the stored charges. The delay time is denoted by td , corresponding to the time to discharge the capacitance of base–emitter junction, which can be reduced with a larger current base with high slope. Storage time ( ...
... blocking must be negative and the device must be kept in quasi-saturation to minimize the stored charges. The delay time is denoted by td , corresponding to the time to discharge the capacitance of base–emitter junction, which can be reduced with a larger current base with high slope. Storage time ( ...
Transistor
.jpg?width=300)
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its development in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics, and the inventors were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.