Armstrong 521/525 output transistor replacement
... MJ2955 will suffice ( it is a better spec than the old Germanium AL102 ). A few resistors have to be replaced on the power amplifier printed circuit card, these are in the bias circuitry for the output transistors. Note, both output transistors have to be replaced for MJ2955's even if only one AL102 ...
... MJ2955 will suffice ( it is a better spec than the old Germanium AL102 ). A few resistors have to be replaced on the power amplifier printed circuit card, these are in the bias circuitry for the output transistors. Note, both output transistors have to be replaced for MJ2955's even if only one AL102 ...
transistor
... There are two input terminals for the signal to be amplified and two output terminals for the connecting the load and a means of supplying power to the amplifier. ...
... There are two input terminals for the signal to be amplified and two output terminals for the connecting the load and a means of supplying power to the amplifier. ...
Methodology PRINT
... There were many complex components used for this project. These components helped complete the final product. Materials such as aluminum plates, bread boards, the Basic Stamp, and much more were used. But the most important of all were the microphones, transistors, LM386 and ADC0831. An Omni-directi ...
... There were many complex components used for this project. These components helped complete the final product. Materials such as aluminum plates, bread boards, the Basic Stamp, and much more were used. But the most important of all were the microphones, transistors, LM386 and ADC0831. An Omni-directi ...
From analog to digital circuits
... clamped to one of the power rails by a conductive (on) device, while the other device serves as a load of effectively infinite resistance (off). This leads to static properties that approximate those of the ideal inverter. - The PMOS devices is slower (lower mobility of holes) so it has to be larger ...
... clamped to one of the power rails by a conductive (on) device, while the other device serves as a load of effectively infinite resistance (off). This leads to static properties that approximate those of the ideal inverter. - The PMOS devices is slower (lower mobility of holes) so it has to be larger ...
A transistor inverter (NOT gate)
... A transistor inverter (NOT gate) Inverters (NOT gates) are available on logic ICs but if you only require one inverter it is usually better to use this circuit. The output signal (voltage) is the inverse of the input signal: ...
... A transistor inverter (NOT gate) Inverters (NOT gates) are available on logic ICs but if you only require one inverter it is usually better to use this circuit. The output signal (voltage) is the inverse of the input signal: ...
Physics of a BJT
... Depletion region shrinks due to charges from the battery. The electric field is weaker. Majority carrier can cross via diffusion; Greater diffusion current. Current flows from P side to N side ...
... Depletion region shrinks due to charges from the battery. The electric field is weaker. Majority carrier can cross via diffusion; Greater diffusion current. Current flows from P side to N side ...
971 Quiz 01
... transformer output voltage 10V. The right side figure shows the Zener diode v i characteristics. ...
... transformer output voltage 10V. The right side figure shows the Zener diode v i characteristics. ...
Linear Systems NPN Transistor
... 1. Absolute Maximum ratings are limiting values above which serviceability may be impaired 2. The reverse base‐to‐emitter voltage must never exceed 6.2 volts; the reverse base‐to‐emitter current must never exceed 10µA. ...
... 1. Absolute Maximum ratings are limiting values above which serviceability may be impaired 2. The reverse base‐to‐emitter voltage must never exceed 6.2 volts; the reverse base‐to‐emitter current must never exceed 10µA. ...
Bipolar Junction Transistors and Field Effect Transistor Amplifiers
... VBE, will give a sinusoidal collector current, Ic, superimposed on the DC current Ic at the Qpoint. Depending upon the configuration of the resistors in the collector, the emitter, and the load, there will be an ideal Q-point for maximum distortion-free output signal amplitude. Determining these res ...
... VBE, will give a sinusoidal collector current, Ic, superimposed on the DC current Ic at the Qpoint. Depending upon the configuration of the resistors in the collector, the emitter, and the load, there will be an ideal Q-point for maximum distortion-free output signal amplitude. Determining these res ...
FM Transmitter
... This stage amplifies the RF signal. A Zetex ZTX320 RF transistor was used to do this efficiently. L2 and the 10p capacitor in parallel with it are designed to reduce harmonics from the circuit. ...
... This stage amplifies the RF signal. A Zetex ZTX320 RF transistor was used to do this efficiently. L2 and the 10p capacitor in parallel with it are designed to reduce harmonics from the circuit. ...
Bipolar Transistor
... A transistor is basically a three terminal semiconductor device that may be used to provide a number of functions. Its chief applications are use as a switch or as an amplifier. The three terminals of a bipolar transistor are labelled base, emitter and collector (see Figure 1.1). A small change of c ...
... A transistor is basically a three terminal semiconductor device that may be used to provide a number of functions. Its chief applications are use as a switch or as an amplifier. The three terminals of a bipolar transistor are labelled base, emitter and collector (see Figure 1.1). A small change of c ...
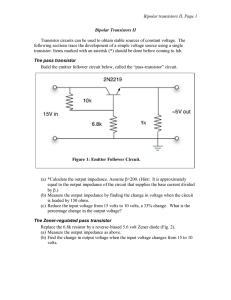
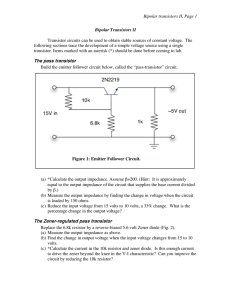
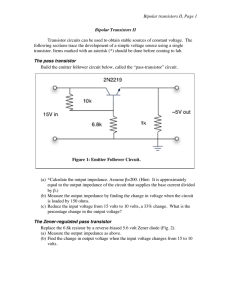
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Present the completed power supply to your instructor. Plot V vs. I for your supply by loading it. Choose several load resistors from 2k to 100. As the current increases do you note any qualitative change in the curve? If yes, comment on possible reasons. ...
... Present the completed power supply to your instructor. Plot V vs. I for your supply by loading it. Choose several load resistors from 2k to 100. As the current increases do you note any qualitative change in the curve? If yes, comment on possible reasons. ...
List advantages and disadvantages of an np
... List advantages and disadvantages of an np-CMOS circuit. What is Domino Logic? Why is the clock feed through become problem and why is it occurring? What is the charge sharing and why is it occurring? Calculate the final output voltage of the two capacitors in parallel, 5pF and 2pF. The 5pF capacito ...
... List advantages and disadvantages of an np-CMOS circuit. What is Domino Logic? Why is the clock feed through become problem and why is it occurring? What is the charge sharing and why is it occurring? Calculate the final output voltage of the two capacitors in parallel, 5pF and 2pF. The 5pF capacito ...
4991_Chapter_10_Fall..
... Cutoff Region – Both junctions reversebiased – Very little base or collector current Active Linear Region – BE junction forward biased, CB junction reverse-biased – ...
... Cutoff Region – Both junctions reversebiased – Very little base or collector current Active Linear Region – BE junction forward biased, CB junction reverse-biased – ...
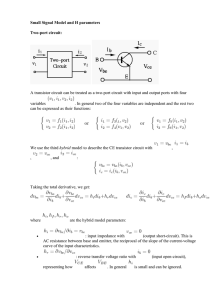
Small Signal Model and H parameters
... A transistor circuit can be treated as a two-port circuit with input and output ports with four variables . In general two of the four variables are independent and the rest two can be expressed as their functions: ...
... A transistor circuit can be treated as a two-port circuit with input and output ports with four variables . In general two of the four variables are independent and the rest two can be expressed as their functions: ...
Transistors
... Three-terminal semiconductor device – Control current or voltage between two of the terminals by applying a current or voltage to the third terminal ...
... Three-terminal semiconductor device – Control current or voltage between two of the terminals by applying a current or voltage to the third terminal ...
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... On a piece of perforated board solder together the following circuit: ...
... On a piece of perforated board solder together the following circuit: ...
TRANSISTORS AND THYRISTORS
... • When turned on (triggered), they become low-resistance current paths and remain, although the trigger is removed, until the current is reduced to a certain level or until they are turned off ...
... • When turned on (triggered), they become low-resistance current paths and remain, although the trigger is removed, until the current is reduced to a certain level or until they are turned off ...
The Transistor - labsanywhere.net
... If the base is thin, electrons from the emitter are swept though the base to the collector. Electrons in the collector then respond to the positive voltage and flow out of the ...
... If the base is thin, electrons from the emitter are swept though the base to the collector. Electrons in the collector then respond to the positive voltage and flow out of the ...
Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
... Thus, the peak-to-peak value of ac component of VCE = 4 V, and peak-to-peak value of vin = 0.8 V Thus the gain is 5, but with a negative sign, as seen from Fig. 4.13. Confirm that when the base voltage VB is higher the o/p voltage is lower. ...
... Thus, the peak-to-peak value of ac component of VCE = 4 V, and peak-to-peak value of vin = 0.8 V Thus the gain is 5, but with a negative sign, as seen from Fig. 4.13. Confirm that when the base voltage VB is higher the o/p voltage is lower. ...
mosfet jfet
... • A transistor is a 3 terminal electronic device made of semiconductor material. • Transistors have many uses, including amplification, switching, voltage regulation, and the modulation of signals ...
... • A transistor is a 3 terminal electronic device made of semiconductor material. • Transistors have many uses, including amplification, switching, voltage regulation, and the modulation of signals ...
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... The rectangular box refers to the full-wave rectifier WL02F. and “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer The output should be about 5 volts. ...
... The rectangular box refers to the full-wave rectifier WL02F. and “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer The output should be about 5 volts. ...
Transistor
.jpg?width=300)
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its development in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics, and the inventors were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.