lecture1:ac analysis
... The base current eq. is not linear and can’t be written as ac current superimposed on dc quiescent value. If vbe << VT, we can expand the exponential term in a Taylor series, keeping only linear term which lead to small signal approximation. ...
... The base current eq. is not linear and can’t be written as ac current superimposed on dc quiescent value. If vbe << VT, we can expand the exponential term in a Taylor series, keeping only linear term which lead to small signal approximation. ...
1 Static Characteristics I
... This is also a logic inverting action. In saturation, the base of the transistor is said to be overdriven. That is to say more current is fed into the base than is required to produce the maximum current that can flow in the collector. Normally, 4 to 5 times the current needed to bring the collector ...
... This is also a logic inverting action. In saturation, the base of the transistor is said to be overdriven. That is to say more current is fed into the base than is required to produce the maximum current that can flow in the collector. Normally, 4 to 5 times the current needed to bring the collector ...
3 The MOS Transistor Inverter Dynamic Characteristics
... of the output voltage is shown in Fig. 3.2. Initially the output voltage will be at the supply voltage, VDD, with the capacitance fully charged. If an input voltage of Vi = VDD is applied to the gate of the transistor, then this means that initially the transistor operates with VGS = VDD and with VD ...
... of the output voltage is shown in Fig. 3.2. Initially the output voltage will be at the supply voltage, VDD, with the capacitance fully charged. If an input voltage of Vi = VDD is applied to the gate of the transistor, then this means that initially the transistor operates with VGS = VDD and with VD ...
Electronics8_SLOaddendum050211
... common-emitter amplifier. Scored by the correct ID of the elements shown of a commonemitter amplifier: 14 to 17 elements are ...
... common-emitter amplifier. Scored by the correct ID of the elements shown of a commonemitter amplifier: 14 to 17 elements are ...
ZXM66P03N8 30V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET
... ZXM66P03N8 30V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET ...
... ZXM66P03N8 30V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET ...
Electric Current
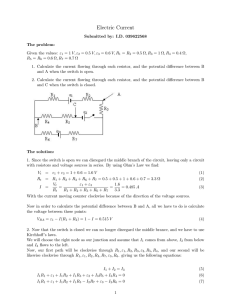
... Electric Current Submitted by: I.D. 039622568 The problem: Given the values: ε1 = 1 V, ε2 = 0.5 V, ε3 = 0.6 V, R1 = R2 = 0.5 Ω, R3 = 1 Ω, R4 = 0.4 Ω, R5 = R6 = 0.6 Ω, R7 = 0.7 Ω 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is op ...
... Electric Current Submitted by: I.D. 039622568 The problem: Given the values: ε1 = 1 V, ε2 = 0.5 V, ε3 = 0.6 V, R1 = R2 = 0.5 Ω, R3 = 1 Ω, R4 = 0.4 Ω, R5 = R6 = 0.6 Ω, R7 = 0.7 Ω 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is op ...
SST505 - Micross Components
... Peak Operating Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . POV = 50V 1. Absolute maximum ratings are limiting values above which serviceability may be impaired. 2. Pulsed, t = 2ms. Maximum VF where IF < 1.1IF(max). 3. Pulsed, t = 2ms. Continuous currents may vary. 4. Pulsed, t = 2ms. ...
... Peak Operating Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . POV = 50V 1. Absolute maximum ratings are limiting values above which serviceability may be impaired. 2. Pulsed, t = 2ms. Maximum VF where IF < 1.1IF(max). 3. Pulsed, t = 2ms. Continuous currents may vary. 4. Pulsed, t = 2ms. ...
Semiconductor Electronics, Materials, Devices and Sample Circuits
... b, c. The angle between three crystallographic axis are called interfacial angles represented by α, β and γ. The primitives and interfacial angles constitute the lattice parameters of a unit cell. [The cubic crystal may be of the form, simple cubic (sc) lattice, the body centred cubic (bee) lattice, ...
... b, c. The angle between three crystallographic axis are called interfacial angles represented by α, β and γ. The primitives and interfacial angles constitute the lattice parameters of a unit cell. [The cubic crystal may be of the form, simple cubic (sc) lattice, the body centred cubic (bee) lattice, ...
Gen2 SupIRBuck™ Family
... The second generation of SupIRBuck™ family of integrated point-ofload (POL) voltage regulators features IR’s latest advantages in control IC, MOSFETs and package integration technologies to deliver up to 12A output current in a low-profile, thermally enhanced 5x6 mm Power-QFN package. The four Gen2 ...
... The second generation of SupIRBuck™ family of integrated point-ofload (POL) voltage regulators features IR’s latest advantages in control IC, MOSFETs and package integration technologies to deliver up to 12A output current in a low-profile, thermally enhanced 5x6 mm Power-QFN package. The four Gen2 ...
Electronic signal converters Micropace™ LMI
... Electronic signal converters Micropace™ LMI Micropace™ Range •The Micropace™ line of rugged, low cost control modules provide you with the ability to proportionally adjust the output of any LMI AA7/AA9/B7/B9/C7/C9 metering pump. •Adjustment can be made by multiplying (MP-500-M), dividing (MP-400-D) ...
... Electronic signal converters Micropace™ LMI Micropace™ Range •The Micropace™ line of rugged, low cost control modules provide you with the ability to proportionally adjust the output of any LMI AA7/AA9/B7/B9/C7/C9 metering pump. •Adjustment can be made by multiplying (MP-500-M), dividing (MP-400-D) ...
Gilbert cell - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... The cells invented by Barrie Gilbert, as described by the schematics noted as "Gilbert", have two additional diodes. These diodes log the input current in such a way that the exponential characteristics of the following transistors result in an, ideally, perfect multiplication of the input currents. ...
... The cells invented by Barrie Gilbert, as described by the schematics noted as "Gilbert", have two additional diodes. These diodes log the input current in such a way that the exponential characteristics of the following transistors result in an, ideally, perfect multiplication of the input currents. ...
Objective bits
... 3). The order of voltage required for accelerating the electron beam deflect and sweep is of the order of kv 4). Triggering of the signal in CRO is done to get true representation of input signal 5). The type of electron emission that takes place in a CRT is thermionic emission 6). Scale markings p ...
... 3). The order of voltage required for accelerating the electron beam deflect and sweep is of the order of kv 4). Triggering of the signal in CRO is done to get true representation of input signal 5). The type of electron emission that takes place in a CRT is thermionic emission 6). Scale markings p ...
Current Sensing in Pass Transistor
... becoming dominant factors in the design of integrated circuits [6]. Traditional design methodologies tend to concentrate more on active power and often overlook standby or leakage power. However, as transistors scale, it is predicted that leakage power will at some point dominate the overall power c ...
... becoming dominant factors in the design of integrated circuits [6]. Traditional design methodologies tend to concentrate more on active power and often overlook standby or leakage power. However, as transistors scale, it is predicted that leakage power will at some point dominate the overall power c ...
Active Pixel Sensor Circuit
... isolation of SF output from the pixel output – Higher bias current: readout needs to be a smaller time after ...
... isolation of SF output from the pixel output – Higher bias current: readout needs to be a smaller time after ...
Transistor
.jpg?width=300)
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its development in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics, and the inventors were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.