ENERGY Physiology Function:workàlive -grows(mitosis)
... molecule down into 3-carbonm molecules called pyruvate -process is an ancient one-all organisms from simple bacteria to humans perform it the same way -yields 2 ATP molecules for every one glucose molecule broken down -yields 2 NADH per glucose molecule Aerobic Cellular reaction Oxygen-required=ae ...
... molecule down into 3-carbonm molecules called pyruvate -process is an ancient one-all organisms from simple bacteria to humans perform it the same way -yields 2 ATP molecules for every one glucose molecule broken down -yields 2 NADH per glucose molecule Aerobic Cellular reaction Oxygen-required=ae ...
Elite Fuel® White Papers ©
... Methylcobalamin has multiple supportive roles in the body, including red blood cell formation, nervous system health, homocysteine and folate metabolism, melatonin synthesis, and more. Coenzyme B12 or adenosylcobalami ...
... Methylcobalamin has multiple supportive roles in the body, including red blood cell formation, nervous system health, homocysteine and folate metabolism, melatonin synthesis, and more. Coenzyme B12 or adenosylcobalami ...
L-Carnitine in human metabolism
... Finally the acyl-CoA is conveyed to the betaoxidation and fragmented in chains containing two Carbons (acetyl-CoA), which subsequently enter in the Krebs cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, with the final result of energy production (ATP). ...
... Finally the acyl-CoA is conveyed to the betaoxidation and fragmented in chains containing two Carbons (acetyl-CoA), which subsequently enter in the Krebs cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, with the final result of energy production (ATP). ...
Microbial Metabolism
... joins with Oxaloacetic Acid (4C) to make Citric Acid (6C) Citric acid is oxidized releasing CO2 , free H+, & e- and forming ketoglutaric acid (5C) Free e- reduce the energy carriers NAD+ to NADH and FAD+ to FADH2 Ketoglutaric acid is also oxidized releasing more CO2 , free H+, & eThe cycle continues ...
... joins with Oxaloacetic Acid (4C) to make Citric Acid (6C) Citric acid is oxidized releasing CO2 , free H+, & e- and forming ketoglutaric acid (5C) Free e- reduce the energy carriers NAD+ to NADH and FAD+ to FADH2 Ketoglutaric acid is also oxidized releasing more CO2 , free H+, & eThe cycle continues ...
Metabolic Processes
... How do the large number of folds of the inner mitochondrion membrane assist in this process? How is this folding related to specific energy requirements of the ...
... How do the large number of folds of the inner mitochondrion membrane assist in this process? How is this folding related to specific energy requirements of the ...
Lecture Chpt. 08 Metabol
... • Some chemical reactions release energy – exergonic – breaking polymers – hydrolysis = catabolism ...
... • Some chemical reactions release energy – exergonic – breaking polymers – hydrolysis = catabolism ...
Guidelines for the Investigation of Hyperammonaemia
... other metabolic disorders should prompt early contact with the regional metabolic centre to coordinate more specialised investigations and clinical management (Table 4). These specialised investigations are best undertaken at the tertiary care facility to which the child is transferred for clinical ...
... other metabolic disorders should prompt early contact with the regional metabolic centre to coordinate more specialised investigations and clinical management (Table 4). These specialised investigations are best undertaken at the tertiary care facility to which the child is transferred for clinical ...
metabolism and function of carbohydrates
... 4. Heteropolysaccarides. Representatives of glycosaminoglycans (hyaluronic acid, heparin, keratan sulphate, dermatan sulphate, chondroitin sulphate), monomers, bonds, properties and significance. Glycosaminoglycans as component of proteoglycans, role of proteoglycans. 5. Oligosaccarides of glycoprot ...
... 4. Heteropolysaccarides. Representatives of glycosaminoglycans (hyaluronic acid, heparin, keratan sulphate, dermatan sulphate, chondroitin sulphate), monomers, bonds, properties and significance. Glycosaminoglycans as component of proteoglycans, role of proteoglycans. 5. Oligosaccarides of glycoprot ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... range, due to accumulation of fat – in men more then 25%, in wumen more tha 30% of total body weight • Obesity is considered as chronic disease which can result in multiorgan damage manifeted as complications of obesity • Obesity is the result of influence of many pathogenic mechanisms ...
... range, due to accumulation of fat – in men more then 25%, in wumen more tha 30% of total body weight • Obesity is considered as chronic disease which can result in multiorgan damage manifeted as complications of obesity • Obesity is the result of influence of many pathogenic mechanisms ...
Muscle cells generate force by shortening their length via chemical
... unable to sustain twitch due to limited ability to make large amounts of ATP once glycogen reserves have been used up. You want FastGlycolytic to run a 100 yard dash! ...
... unable to sustain twitch due to limited ability to make large amounts of ATP once glycogen reserves have been used up. You want FastGlycolytic to run a 100 yard dash! ...
- Angelo State University
... energy-rich molecules of ATP. – The whole purpose of the catabolic pathway is to convert the chemical energy in foods into molecules of ATP, which carries energy to parts of the cell where energy is needed. – The common catabolic pathway and the ways in which carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins prov ...
... energy-rich molecules of ATP. – The whole purpose of the catabolic pathway is to convert the chemical energy in foods into molecules of ATP, which carries energy to parts of the cell where energy is needed. – The common catabolic pathway and the ways in which carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins prov ...
b-oxidation - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Acyl-CoAs are converted to acyl-carnitines by carnitine acyltransferase. • A translocator then imports Acyl carnitine into the matrix while simultaneously exporting free carnitine to the cytosol • Acyl-carnitine is then converted back to acylCoA in the matrix ...
... • Acyl-CoAs are converted to acyl-carnitines by carnitine acyltransferase. • A translocator then imports Acyl carnitine into the matrix while simultaneously exporting free carnitine to the cytosol • Acyl-carnitine is then converted back to acylCoA in the matrix ...
Chapter 5 Active Lecture Questions
... Apoenzymes are inactive by themselves and must be activated by ...
... Apoenzymes are inactive by themselves and must be activated by ...
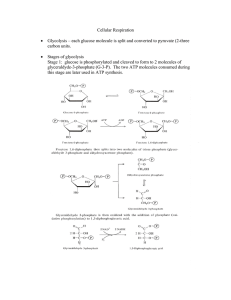
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
... are produced. ATP are consumed in the formation of Glucose-6-phosphate from glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
... are produced. ATP are consumed in the formation of Glucose-6-phosphate from glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
CH`s 8 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for control. If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down. Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in the catabolic pathway. REV ...
... Feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for control. If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down. Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in the catabolic pathway. REV ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.