Theory_2004
... In the early post-absorbtive period, the brain uses about 120g of glucose per day Fatty acids are released once all body glycogen stores have been used up Although we store most of our energy as fat, we cannot convert fatty acids into carbohydrate Net gluconeogenesis is possible from part of triacyl ...
... In the early post-absorbtive period, the brain uses about 120g of glucose per day Fatty acids are released once all body glycogen stores have been used up Although we store most of our energy as fat, we cannot convert fatty acids into carbohydrate Net gluconeogenesis is possible from part of triacyl ...
Keshara Senanayake Ms.Reep AP BIOLOGY Chapter 6
... >since ATP formation if not spontaneous free energy is spent to make it occur catabolic pathways (like cellular respiration) give energy for endergonic process of making ATP (ATP cycle is like a revolving door through which energy passes during its transfer from catabolic to anabolic pathways) sp ...
... >since ATP formation if not spontaneous free energy is spent to make it occur catabolic pathways (like cellular respiration) give energy for endergonic process of making ATP (ATP cycle is like a revolving door through which energy passes during its transfer from catabolic to anabolic pathways) sp ...
Cellular respiration
... How does cell respiration compare to Photosynthesis? C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... How does cell respiration compare to Photosynthesis? C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
How Cells Harvest Energy
... Respiration During respiration, electrons are shuttled through electron carriers to a final electron acceptor. aerobic respiration: final electron receptor is oxygen (O2) anaerobic respiration: final electron acceptor is an inorganic molecule (not O2) fermentation: final electron acceptor is an org ...
... Respiration During respiration, electrons are shuttled through electron carriers to a final electron acceptor. aerobic respiration: final electron receptor is oxygen (O2) anaerobic respiration: final electron acceptor is an inorganic molecule (not O2) fermentation: final electron acceptor is an org ...
Concept 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational
... • Most metabolic enzymes can catalyze a reaction in both the forward and reverse direction. – The actual direction depends on the relative concentrations of products and reactants. – Enzymes catalyze reactions in the direction of ...
... • Most metabolic enzymes can catalyze a reaction in both the forward and reverse direction. – The actual direction depends on the relative concentrations of products and reactants. – Enzymes catalyze reactions in the direction of ...
Respiration Respiration Respiration
... The goal of respiration is to produce ATP. -energy is released from oxidation reaction in the form of electrons -electrons are shuttled by electron carriers (e.g. NAD+) to an electron transport chain -electron energy is converted to ATP at the electron transport chain ...
... The goal of respiration is to produce ATP. -energy is released from oxidation reaction in the form of electrons -electrons are shuttled by electron carriers (e.g. NAD+) to an electron transport chain -electron energy is converted to ATP at the electron transport chain ...
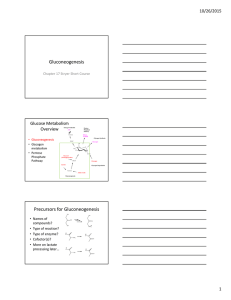
Gluconeogenesis Precursors for Gluconeogenesis
... – Costs ATP to make driving force for next reaction – First step in biosynthesis of glucose and many other molecules • Related to which amino acid? ...
... – Costs ATP to make driving force for next reaction – First step in biosynthesis of glucose and many other molecules • Related to which amino acid? ...
Cell Respiration State that oxidation involves the loss of electrons
... In the Krebs cycle and glycolysis, pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed from the respiratory substrates. Oxidised NAD is converted into reduced NAD, except in the Krebs cycle, where FAD is reduced instead. Hydrogen atoms or their electrons are transported along a series of carriers in the final stage ...
... In the Krebs cycle and glycolysis, pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed from the respiratory substrates. Oxidised NAD is converted into reduced NAD, except in the Krebs cycle, where FAD is reduced instead. Hydrogen atoms or their electrons are transported along a series of carriers in the final stage ...
C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 6 CO 2 + H 2 O + ATP
... What is the chemical or pigment that traps light energy, it is also found in the thylakoid membrane? ...
... What is the chemical or pigment that traps light energy, it is also found in the thylakoid membrane? ...
Mock Exam 2 BY 123 - Cusic Supplemental Instruction
... c. Entropy of a system may increase as long as the total entropy of the universe increases. d. Both A and B e. All of the above 1. Conservation of Energy - Energy cannot be created or destroyed. 2. Free energy is declining. Things in nature go towards disorder or randomness or an increase in Entropy ...
... c. Entropy of a system may increase as long as the total entropy of the universe increases. d. Both A and B e. All of the above 1. Conservation of Energy - Energy cannot be created or destroyed. 2. Free energy is declining. Things in nature go towards disorder or randomness or an increase in Entropy ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
... If it turns yellow you have a monosaccharide, if it turns yellow you have a disaccharide, if it turns purple you have a polysaccharide ...
... If it turns yellow you have a monosaccharide, if it turns yellow you have a disaccharide, if it turns purple you have a polysaccharide ...
AS Biology - TavistockCollegeScience
... oils at room temperature, normally found in plants Animal fats have a higher melting point and are generally solid at room temperature due to saturated fatty acids ...
... oils at room temperature, normally found in plants Animal fats have a higher melting point and are generally solid at room temperature due to saturated fatty acids ...
(CH2) 2 - CHM152-SP10
... component of the name indicates whether there is a ketone group or an aldehyde group attached to it. If there is a ketone group attached then the name will begin with the prefix “keto” and if there is an aldehyde group attached to it then the name will begin with the prefix “aldo.” The second compon ...
... component of the name indicates whether there is a ketone group or an aldehyde group attached to it. If there is a ketone group attached then the name will begin with the prefix “keto” and if there is an aldehyde group attached to it then the name will begin with the prefix “aldo.” The second compon ...
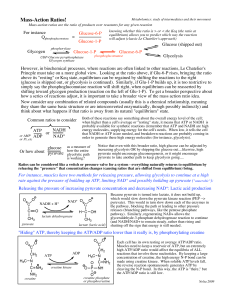
Mass-Action Ratios!
... above its "resting" or Keq state, equilibrium can be regained by shifting the reactions to the right (glucose is shipped out, or glycolysis is continued). Similarly, if Glu-1-P builds up, it is too restrictive to simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be re ...
... above its "resting" or Keq state, equilibrium can be regained by shifting the reactions to the right (glucose is shipped out, or glycolysis is continued). Similarly, if Glu-1-P builds up, it is too restrictive to simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be re ...
GLYCOLYSIS
... GLYCOLYSIS: The anaerobic breakdown of glucose This chart outlines the steps in the biochemical pathway called glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells GLUCOSE ...
... GLYCOLYSIS: The anaerobic breakdown of glucose This chart outlines the steps in the biochemical pathway called glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells GLUCOSE ...
Science 3 - Module 6 - Study Guide For the Oral Exam: You should
... Can you explain how photosynthesis follows the law of conservation of mass and law of conservation energy? How do plants store glucose for later use? ...
... Can you explain how photosynthesis follows the law of conservation of mass and law of conservation energy? How do plants store glucose for later use? ...
08_DetailLectOut_jkAR
... The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. The first law is also known as the principle of conservation of energy. Plants do not produce energy; they transform light energy to chemical energy. ...
... The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. The first law is also known as the principle of conservation of energy. Plants do not produce energy; they transform light energy to chemical energy. ...
File
... Can you explain how photosynthesis follows the law of conservation of mass and law of conservation energy? How do plants store glucose for later use? ...
... Can you explain how photosynthesis follows the law of conservation of mass and law of conservation energy? How do plants store glucose for later use? ...
All About Pdf - B
... because they are intimately involved in cellular energy metabolism, namely the glycolytic, Krebs cycle and pentose pathways. The B vitamins act as cofactors in converting carbohydrates into glucose which the body burns to produce energy. For example, the process of glycolysis which converts energy s ...
... because they are intimately involved in cellular energy metabolism, namely the glycolytic, Krebs cycle and pentose pathways. The B vitamins act as cofactors in converting carbohydrates into glucose which the body burns to produce energy. For example, the process of glycolysis which converts energy s ...
Recovery Following Exercise
... •Within this component, the very first amount of oxygen consumed is used to resaturate myoglobin with oxygen. •The rest of the oxygen is required to produce sufficient energy from aerobic respiration to restore the muscle ATP and phosphocreatine stores •It takes a short amount of time (2-3 mins) for ...
... •Within this component, the very first amount of oxygen consumed is used to resaturate myoglobin with oxygen. •The rest of the oxygen is required to produce sufficient energy from aerobic respiration to restore the muscle ATP and phosphocreatine stores •It takes a short amount of time (2-3 mins) for ...
Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency presenting as acute hypercapnic respiratory failure CASE STUDY
... acutely ill patient is the determination of the urinary dicarboxylic acids. The pattern in the patient was compatible with a fatty acid b-oxidation defect. The blood acylcarnitine pattern subsequently helps to differentiate the subtype of boxidation defect. In the present case, the serum and urine b ...
... acutely ill patient is the determination of the urinary dicarboxylic acids. The pattern in the patient was compatible with a fatty acid b-oxidation defect. The blood acylcarnitine pattern subsequently helps to differentiate the subtype of boxidation defect. In the present case, the serum and urine b ...
Anabolism
... • Energy is the capacity to change something; it is the ability to do work • Common forms of energy: • Heat • Light • Sound • Electrical energy • Mechanical energy • Chemical energy ...
... • Energy is the capacity to change something; it is the ability to do work • Common forms of energy: • Heat • Light • Sound • Electrical energy • Mechanical energy • Chemical energy ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.