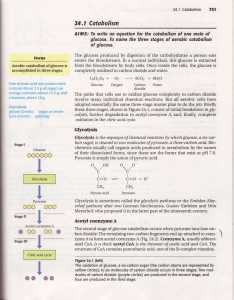
File - Serrano High School AP Biology
... Free energy is a portion of a system’s energy that can perform work when the temperature is uniform throughout the system. The quantity of free energy in a system is G. G is made up of 3 components: H = total energy of a system, S = entropy, and T = temperature in Kelvin. If there is an increase in ...
... Free energy is a portion of a system’s energy that can perform work when the temperature is uniform throughout the system. The quantity of free energy in a system is G. G is made up of 3 components: H = total energy of a system, S = entropy, and T = temperature in Kelvin. If there is an increase in ...
Chapter 6
... In the process, pyruvic acid is reduced to either lactic acid or ethanol or another organic molecule. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... In the process, pyruvic acid is reduced to either lactic acid or ethanol or another organic molecule. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Flux-balance Analysis - Systems Biology Research Group
... In regions where the α value is negative, there is dual limitation of the substrates. Based on the absolute value of α , the substrate with a greater contribution toward obtaining the objective (here considered to be biomass production) can be identified. If the absolute value of α is greater than u ...
... In regions where the α value is negative, there is dual limitation of the substrates. Based on the absolute value of α , the substrate with a greater contribution toward obtaining the objective (here considered to be biomass production) can be identified. If the absolute value of α is greater than u ...
Metabolism and Glycolysis
... formation of CH3—CO~CoA links glycolysis to FAT synthesis and entry to the TCA or Krebs's cycle. ...
... formation of CH3—CO~CoA links glycolysis to FAT synthesis and entry to the TCA or Krebs's cycle. ...
Lipogenesis (2014)
... Carrier of acyl/acetyl groups between mitochondria and cytosol H-carrier NB: the synthesis of TAG occurs mainly in liver and mammary glands but it is stored mainly in adipose tissue and muscles ...
... Carrier of acyl/acetyl groups between mitochondria and cytosol H-carrier NB: the synthesis of TAG occurs mainly in liver and mammary glands but it is stored mainly in adipose tissue and muscles ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... feature governing phase separation is electrical asymmetry, usually noted by such parameters as dialectic constant, electronegativity, or polarizability. The primary rule of phase separation under these circumstances is that oil and water do not mix. Oils are dominated by quite symmetric C–H bonds a ...
... feature governing phase separation is electrical asymmetry, usually noted by such parameters as dialectic constant, electronegativity, or polarizability. The primary rule of phase separation under these circumstances is that oil and water do not mix. Oils are dominated by quite symmetric C–H bonds a ...
Oxidative phosphorylation.
... Even the preceding reaction must overcome the activation energy necessary to “ignite” the glucose. The sugar, in reality, is burned (oxidized) slowly, not in one explosive step. Actually, this is a good thing since a spontaneous burst (release) of energy would proceed so quickly that little time wou ...
... Even the preceding reaction must overcome the activation energy necessary to “ignite” the glucose. The sugar, in reality, is burned (oxidized) slowly, not in one explosive step. Actually, this is a good thing since a spontaneous burst (release) of energy would proceed so quickly that little time wou ...
2. Large-scale Metabolic Reconstruction
... We adopted a gene-centric organization of metabolic information, in which each of the known metabolic genes is be mapped to one or many reactions. The core of the GSM was generated using the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) genes database for M. musculus (Release 46) [8]. The gene–reac ...
... We adopted a gene-centric organization of metabolic information, in which each of the known metabolic genes is be mapped to one or many reactions. The core of the GSM was generated using the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) genes database for M. musculus (Release 46) [8]. The gene–reac ...
What is Cellular Respiration?
... usable energy in the form of ATP than any anaerobic pathway. Nevertheless, the anaerobic pathways are important and are the sole source of ATP for many anaerobic bacteria. Eukaryotic cells also resort to anaerobic pathways if their oxygen supply is low. For example, when muscle cells are working ver ...
... usable energy in the form of ATP than any anaerobic pathway. Nevertheless, the anaerobic pathways are important and are the sole source of ATP for many anaerobic bacteria. Eukaryotic cells also resort to anaerobic pathways if their oxygen supply is low. For example, when muscle cells are working ver ...
Review #3 Chapters 9 – 10
... All of the following statements about photosynthesis are true EXCEPT a. The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH b. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar c. Photosystem I contains P700 chlorophyll a molecules at the reaction cente ...
... All of the following statements about photosynthesis are true EXCEPT a. The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH b. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar c. Photosystem I contains P700 chlorophyll a molecules at the reaction cente ...
ATP GENERATION The energy captured within ATP can then be
... released from the ATP hydrolysis reaction (large −_G) is coupled to the synthesis reaction (large +_G). In this way, the cell can progressively create order. Electron transport system (ETS) ...
... released from the ATP hydrolysis reaction (large −_G) is coupled to the synthesis reaction (large +_G). In this way, the cell can progressively create order. Electron transport system (ETS) ...
Chemical Energy Production
... • At rest – skeletal muscle uses fatty acid metabolism to provide energy – blood glucose is reserved primarily for brain ...
... • At rest – skeletal muscle uses fatty acid metabolism to provide energy – blood glucose is reserved primarily for brain ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY - Georgia Institute of Technology
... SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY More on Glycogen Control Citric Acid Cycle ...
... SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY More on Glycogen Control Citric Acid Cycle ...
H &
... The names and structures of some of the intermediate compounds in metabolism are complex. You do not need to memorize them, but they wi[ be used in the text to make it easierto followwhat is happening. Remembei also that all the steps ofthese reactions are catalyzedby enzyrnes. The phosphoryl group ...
... The names and structures of some of the intermediate compounds in metabolism are complex. You do not need to memorize them, but they wi[ be used in the text to make it easierto followwhat is happening. Remembei also that all the steps ofthese reactions are catalyzedby enzyrnes. The phosphoryl group ...
chapter outline - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... 3. Completion of degradation accompanied by the generation of many ATP molecules C. Many of the catabolic pathways can also be used for synthesis (anabolic) reactions and are termed amphibolic; reducing power is used to convert precursor metabolites into macromolecules III. Aerobic Respiration - com ...
... 3. Completion of degradation accompanied by the generation of many ATP molecules C. Many of the catabolic pathways can also be used for synthesis (anabolic) reactions and are termed amphibolic; reducing power is used to convert precursor metabolites into macromolecules III. Aerobic Respiration - com ...
Consortium for Educational Communication
... break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process as they break high-energy bonds. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell gains useful energy to fuel cellular activity. Chemically, cellular respiration is considered an exothermic redox reaction. The overall reaction is brok ...
... break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process as they break high-energy bonds. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell gains useful energy to fuel cellular activity. Chemically, cellular respiration is considered an exothermic redox reaction. The overall reaction is brok ...
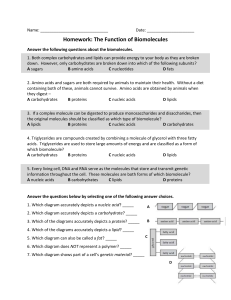
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B nucleic acids and lipids C carbohydrates and lipids D nucleic acids and proteins 13. Which set of biomole ...
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B nucleic acids and lipids C carbohydrates and lipids D nucleic acids and proteins 13. Which set of biomole ...
Energy and Life
... The electron transport chain consists of enzymes in four complexes held in fixed positions and the two coenzymes that carry electrons from one complex to the next. Enzymes of the electron transport chain are imbedded in the inner membrane of mitochondria. Ultimately, water will be produced from thes ...
... The electron transport chain consists of enzymes in four complexes held in fixed positions and the two coenzymes that carry electrons from one complex to the next. Enzymes of the electron transport chain are imbedded in the inner membrane of mitochondria. Ultimately, water will be produced from thes ...
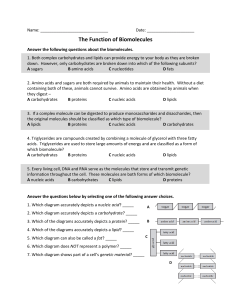
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways
... Metabolism is the collection of enzymecatalyzed reactions that convert substrates that are external to the cell into various internal products. ...
... Metabolism is the collection of enzymecatalyzed reactions that convert substrates that are external to the cell into various internal products. ...
chapt 6
... In the process, pyruvic acid is reduced to either lactic acid or ethanol or another organic molecule. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... In the process, pyruvic acid is reduced to either lactic acid or ethanol or another organic molecule. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.