Amino acid lecture(1) by Prof.Dr.Moaed Al
... However, transamination or oxidative deamination is not the first reaction in catabolism of eight amino acids: Serine and threonine are deaminated by dehydration, and histidine undergoes deamination by desaturation. The five remaining amino acids are deaminated later on, after partial transformation ...
... However, transamination or oxidative deamination is not the first reaction in catabolism of eight amino acids: Serine and threonine are deaminated by dehydration, and histidine undergoes deamination by desaturation. The five remaining amino acids are deaminated later on, after partial transformation ...
Jeopardy 2
... What is the energy tally from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid during the Krebs cycle? A: What is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP? ...
... What is the energy tally from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid during the Krebs cycle? A: What is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP? ...
(,umoles/g. fresh wt./min. at 250)
... changing from a standard diet to a low-carbohydrate diet the enzyme activity fell to about onethird, and on a high-carbohydrate (sucrose-casein) diet it rose more than threefold. Thus the difference in enzyme activity between diets low and high in carbohydrate was about tenfold. It is very probable, ...
... changing from a standard diet to a low-carbohydrate diet the enzyme activity fell to about onethird, and on a high-carbohydrate (sucrose-casein) diet it rose more than threefold. Thus the difference in enzyme activity between diets low and high in carbohydrate was about tenfold. It is very probable, ...
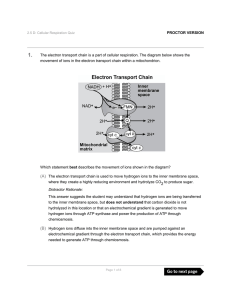
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... amino acids requires oxygen to generate ATP and that only glucose can continue to be catabolized when oxygen supply is limited, which may result in more ATP generated from glucose when blood oxygen levels are low. ...
... amino acids requires oxygen to generate ATP and that only glucose can continue to be catabolized when oxygen supply is limited, which may result in more ATP generated from glucose when blood oxygen levels are low. ...
19 Oxidative Phosphorylation-Electron Transport A
... then be donated to Cyctochrome b/c will then follow the same route of electron transport and proton pumping as NADH. That means there is one less proton being pumped out of the matrix and into Inter membrane space when FADH2 donates the proton. That equates to one less ATP molecule being made. So wh ...
... then be donated to Cyctochrome b/c will then follow the same route of electron transport and proton pumping as NADH. That means there is one less proton being pumped out of the matrix and into Inter membrane space when FADH2 donates the proton. That equates to one less ATP molecule being made. So wh ...
Synthesis and Degradation of Lipids
... o DHP acyltransferase in ER and peroxisomes Glyceroneogenesis in liver Partial gluconeogenesis from oxalacetate ...
... o DHP acyltransferase in ER and peroxisomes Glyceroneogenesis in liver Partial gluconeogenesis from oxalacetate ...
AMINOACID METABOLISM
... The aminoacids undergo certain common reactions like TRANSAMINATION followed by DEAMINATION for the liberation of Ammonia. The amino group of aa is utilized for the formation of UREA. The carbon skeleton of aa is first converted to ketoacids which meet one or more of the following fates: ...
... The aminoacids undergo certain common reactions like TRANSAMINATION followed by DEAMINATION for the liberation of Ammonia. The amino group of aa is utilized for the formation of UREA. The carbon skeleton of aa is first converted to ketoacids which meet one or more of the following fates: ...
Cell Respiration
... For each molecule of glucose degraded to carbon dioxide and water by respiration, the cell makes up to 38 ATP, each with 7.3 kcal/mol of free energy. ...
... For each molecule of glucose degraded to carbon dioxide and water by respiration, the cell makes up to 38 ATP, each with 7.3 kcal/mol of free energy. ...
chapter 9 cellular respiration: harvesting chemical energy
... For each molecule of glucose degraded to carbon dioxide and water by respiration, the cell makes up to 38 ATP, each with 7.3 kcal/mol of free energy. ...
... For each molecule of glucose degraded to carbon dioxide and water by respiration, the cell makes up to 38 ATP, each with 7.3 kcal/mol of free energy. ...
cellular-respiration 1
... 1. Despite a low yield of two ATP molecules, fermentation provides a quick burst of ATP energy for muscular activity. 2. Fermentation products are toxic to cells. a. When blood cannot remove all lactate from muscles, lactate changes pH and causes muscles to fatigue. b. The individual is in oxygen de ...
... 1. Despite a low yield of two ATP molecules, fermentation provides a quick burst of ATP energy for muscular activity. 2. Fermentation products are toxic to cells. a. When blood cannot remove all lactate from muscles, lactate changes pH and causes muscles to fatigue. b. The individual is in oxygen de ...
Strength Training - Mr. Nettles Health and Physical Education Classes
... Ectomorph’s must make sure that they increase their calorie intake as well as include a strength training routine to see an increase in muscle mass and body weight. Endomorph’s must make sure they watch their calorie intake as well as get plenty of Aerobic Exercise & always incorporate a strength ...
... Ectomorph’s must make sure that they increase their calorie intake as well as include a strength training routine to see an increase in muscle mass and body weight. Endomorph’s must make sure they watch their calorie intake as well as get plenty of Aerobic Exercise & always incorporate a strength ...
Alcoholic fermentation
... …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to ETHANAL (…..C), releasing …………….. . The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase then ……………….. ETHANAL to ETHANOL (…..C), at the same time ………………… NADH back to ……………. . CH3CHO + NADH ...
... …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to ETHANAL (…..C), releasing …………….. . The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase then ……………….. ETHANAL to ETHANOL (…..C), at the same time ………………… NADH back to ……………. . CH3CHO + NADH ...
GLOBAL WARMING - Agronomy Courses
... GREENHOUSE GAS PRODUCTION IN LIVESTOCK • Methane – Produced by anerobic fermentation of carbohydrates in the rumen, large intestine, or stored manure – Produced by Methanogenic archea • Methanogenic archea are associated with cellulolytic bacteria and protozoa – Methane producing mechanisms • Aceta ...
... GREENHOUSE GAS PRODUCTION IN LIVESTOCK • Methane – Produced by anerobic fermentation of carbohydrates in the rumen, large intestine, or stored manure – Produced by Methanogenic archea • Methanogenic archea are associated with cellulolytic bacteria and protozoa – Methane producing mechanisms • Aceta ...
ENERGY-PRODUCING ABILITY OF BACTERIA
... Without energy, there would be no life on this planet. Most biological energy comes in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a moiety where the energy is stored in the phosphodiester bonds. This biomolecule is the one that is used as the universal energy currency in both prokaryotic and eukaryot ...
... Without energy, there would be no life on this planet. Most biological energy comes in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a moiety where the energy is stored in the phosphodiester bonds. This biomolecule is the one that is used as the universal energy currency in both prokaryotic and eukaryot ...
Eicosanoid Synthesis
... hydrophobic channel by which arachidonic acid enters the cyclooxygenase active site. ...
... hydrophobic channel by which arachidonic acid enters the cyclooxygenase active site. ...
Cellular Respiration
... synthase complexes, which capture the energy to make ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... synthase complexes, which capture the energy to make ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules TEKS 9A
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
The Effects of Beta-alanine Supplementation on the Aging Population
... (Carnosyn (TM)) supplementation in elderly subjects (60-80 years): effects on muscle carnosine content and physical capacity. Amino Acids, 43(1), 49-56. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1190-x 4. Culbertson, J. Y., Kreider, R. B., Greenwood, M., & Cooke, M. (2010). Effects of Beta-Alanine on Muscle Carnosine ...
... (Carnosyn (TM)) supplementation in elderly subjects (60-80 years): effects on muscle carnosine content and physical capacity. Amino Acids, 43(1), 49-56. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1190-x 4. Culbertson, J. Y., Kreider, R. B., Greenwood, M., & Cooke, M. (2010). Effects of Beta-Alanine on Muscle Carnosine ...
Digestible carbohydrates
... pentoses but is utilizable by glucose and galactose if their lumenal concentration is favorable. Absorption is derived by concentration gradient of sugar in the intestinal lumen, i.e., sugars passes from high concentration in lumen to lower concentration in mucosal cells then to blood. It utilizes a ...
... pentoses but is utilizable by glucose and galactose if their lumenal concentration is favorable. Absorption is derived by concentration gradient of sugar in the intestinal lumen, i.e., sugars passes from high concentration in lumen to lower concentration in mucosal cells then to blood. It utilizes a ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.