BIOC*4520 - University of Guelph
... constants, coupled reactions and redox reactions in biochemical processes. ...
... constants, coupled reactions and redox reactions in biochemical processes. ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations
... Common structure: phosphate group, base, and a five-carbon sugar. Sugar is either DNA or RNA. Bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine (DNA), and uracil (RNA). Nucleotides link together to build nucleic acids. ...
... Common structure: phosphate group, base, and a five-carbon sugar. Sugar is either DNA or RNA. Bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine (DNA), and uracil (RNA). Nucleotides link together to build nucleic acids. ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
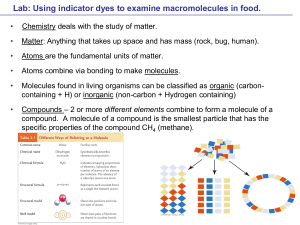
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
Transcription and Translation Made Easy
... Do all point mutations cause disruption to the protein? Explain your answer. No, because there may be several base combinations that create the same amino acid. When DNA is added or deleted, what happens to each of the codes on the mRNA strand and what is this type of mutation called? According to i ...
... Do all point mutations cause disruption to the protein? Explain your answer. No, because there may be several base combinations that create the same amino acid. When DNA is added or deleted, what happens to each of the codes on the mRNA strand and what is this type of mutation called? According to i ...
worksheet 12-3
... c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases the newly formed polypeptide and the mRNA molecule. 18. What is an anticodon? ...
... c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases the newly formed polypeptide and the mRNA molecule. 18. What is an anticodon? ...
Chem 371-001 - Loyola University Chicago
... and final will count 200 as mentioned previously. Exam dates cannot be moved ahead of schedule for individuals either. All emergencies, such us severe weather, medical emergency or family death etc. will need written proof for special consideration. In-semester travel for non-emergency reasons, such ...
... and final will count 200 as mentioned previously. Exam dates cannot be moved ahead of schedule for individuals either. All emergencies, such us severe weather, medical emergency or family death etc. will need written proof for special consideration. In-semester travel for non-emergency reasons, such ...
Lecture 27
... Form monomeric units of nucleic acids-storage and expression of genetic information. Nucleoside triphosphates (i.e., ATP, GTP) are compounds that store energy from energy releasing pathways (glycolysis, electron transport) and are use to supply energy for energyrequiring reactions in the cell. Most ...
... Form monomeric units of nucleic acids-storage and expression of genetic information. Nucleoside triphosphates (i.e., ATP, GTP) are compounds that store energy from energy releasing pathways (glycolysis, electron transport) and are use to supply energy for energyrequiring reactions in the cell. Most ...
RNA - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... _____ 9. made x-ray defraction pictures that helped determine the shape of DNA _____ 10. Determined the double helix structure of DNA _____ 11. won a Noble Prize for work using x-ray crystallography to help determine DNA’s structure _____ 12. used r and s strains of bacteria to determine that DNA is ...
... _____ 9. made x-ray defraction pictures that helped determine the shape of DNA _____ 10. Determined the double helix structure of DNA _____ 11. won a Noble Prize for work using x-ray crystallography to help determine DNA’s structure _____ 12. used r and s strains of bacteria to determine that DNA is ...
Medical Biochemistry at a Glance. 3rd Edition. At a Glance Brochure
... Preface to the third edition 7 Acknowledgements to the third edition 7 Figure key 8 SI/mass unit conversions 9 Part 1 Acids, bases and pH 1 Acids, bases and hydrogen ions (protons) 10 2 Understanding pH 12 3 Production and removal of protons into and from the blood 14 4 Metabolic alkalosis and metab ...
... Preface to the third edition 7 Acknowledgements to the third edition 7 Figure key 8 SI/mass unit conversions 9 Part 1 Acids, bases and pH 1 Acids, bases and hydrogen ions (protons) 10 2 Understanding pH 12 3 Production and removal of protons into and from the blood 14 4 Metabolic alkalosis and metab ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Why are triacylglycerols able to provide more energy than carbohydrates (gram for gram)? A) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates. B) The carbohydrates contain f ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Why are triacylglycerols able to provide more energy than carbohydrates (gram for gram)? A) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates. B) The carbohydrates contain f ...
Answers
... 29. Active site. It is theorized that enzymes work on only one set of substrates and are specific to a reaction. They are not used up in the reaction (meaning they exist in the same form before and after the reaction) but act as ushers so they proceed faster and more controlled. The active site of ...
... 29. Active site. It is theorized that enzymes work on only one set of substrates and are specific to a reaction. They are not used up in the reaction (meaning they exist in the same form before and after the reaction) but act as ushers so they proceed faster and more controlled. The active site of ...
Biomolecule PPT
... Polysaccharides: Starches and sugars examples of carbohydrates that are used by living things as a source of energy. Examples: Cellulose - plants make it for cell walls Starch - (long chain of glucose) ...
... Polysaccharides: Starches and sugars examples of carbohydrates that are used by living things as a source of energy. Examples: Cellulose - plants make it for cell walls Starch - (long chain of glucose) ...
8/27/08 Transcript I
... In its best form during fatty acid biosynthesis Simply means the product of one enzyme catalyzed reaction is furnished to another enzyme. It doesn’t diffuse into the bulk solution, it is furnished nanometers away from the active site. You go from one active site to another active site without ...
... In its best form during fatty acid biosynthesis Simply means the product of one enzyme catalyzed reaction is furnished to another enzyme. It doesn’t diffuse into the bulk solution, it is furnished nanometers away from the active site. You go from one active site to another active site without ...
AS and A2 Biology resource
... Comparative Anatomy of the Gastro-Intestinal Tract Purpose A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic sp ...
... Comparative Anatomy of the Gastro-Intestinal Tract Purpose A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic sp ...
The Building Blocks Teacher Key
... incomplete proteins. Meat contains all of the amino acids, and is therefore a complete protein. The combination of rice and beans contains all of the amino acids; this combination is considered a complementary protein. ...
... incomplete proteins. Meat contains all of the amino acids, and is therefore a complete protein. The combination of rice and beans contains all of the amino acids; this combination is considered a complementary protein. ...
practice note taking
... What type of molecule is formed when there is an uneven sharing of electrons in a covalent bond (water was the example given)? What are the building blocks of protein? An attraction between substances of the same kind ...
... What type of molecule is formed when there is an uneven sharing of electrons in a covalent bond (water was the example given)? What are the building blocks of protein? An attraction between substances of the same kind ...
In Class Review for Test 3
... Answer: A 3 nucleotide sequence of mRNA that “tells” tRNA what amino acid to bring to the ribosome ...
... Answer: A 3 nucleotide sequence of mRNA that “tells” tRNA what amino acid to bring to the ribosome ...
Mutated
... 1. Which type of mutations had the biggest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 2. Which type of mutations had the smallest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 3. Which examples would you predict to have the biggest effects on a trait? WHY? 4. Which examples would you predict to have the smallest e ...
... 1. Which type of mutations had the biggest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 2. Which type of mutations had the smallest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 3. Which examples would you predict to have the biggest effects on a trait? WHY? 4. Which examples would you predict to have the smallest e ...
Introduction_to_Enzymes (1)
... • Everyone should -explain why enzymes are necessary for life -state that enzymes are made of protein • Most people will -understand that an enzyme is a biological catalyst • Some people might -be able to write out word equations for enzyme reactions ...
... • Everyone should -explain why enzymes are necessary for life -state that enzymes are made of protein • Most people will -understand that an enzyme is a biological catalyst • Some people might -be able to write out word equations for enzyme reactions ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.