
Amino acids and proteins
... much of the water. All groups capable of forming a hydrogen bond MUST, hence Hbonding in the backbone (C=O to N-H) by way of helices and sheets is an efficient way of ensuring maximum H-bonding. Sidechains can either accept (as in C=O) or donate (as in N-H, or OH) an H-bond. The capacity of proteins ...
... much of the water. All groups capable of forming a hydrogen bond MUST, hence Hbonding in the backbone (C=O to N-H) by way of helices and sheets is an efficient way of ensuring maximum H-bonding. Sidechains can either accept (as in C=O) or donate (as in N-H, or OH) an H-bond. The capacity of proteins ...
Amino acids and protein (lec. 2%2c 2015)
... so can forms hydrogen bond with H2O. In those amino acids, R may contain: 1- OH group : as in serine, threonine and tyrosine 2- SH group : as in cysteine 3- amide group: as in glutamine and aspargine 4- NH2 group or nitrogen act as a base (basic amino acids ): as lysine, arginine and histidine 5- CO ...
... so can forms hydrogen bond with H2O. In those amino acids, R may contain: 1- OH group : as in serine, threonine and tyrosine 2- SH group : as in cysteine 3- amide group: as in glutamine and aspargine 4- NH2 group or nitrogen act as a base (basic amino acids ): as lysine, arginine and histidine 5- CO ...
Chapter 5 – Homework
... 1. Explain how enzymes speed up chemical reactions in terms of changes in activation energy. ½ pt – They lower the activation energy required for the reaction to take place. 2. Contrast and compare cofactors versus coenzymes. ½ pt - Cofactors are inorganic helpers to enzymes such as Fe. Cu, Zn ½ pt ...
... 1. Explain how enzymes speed up chemical reactions in terms of changes in activation energy. ½ pt – They lower the activation energy required for the reaction to take place. 2. Contrast and compare cofactors versus coenzymes. ½ pt - Cofactors are inorganic helpers to enzymes such as Fe. Cu, Zn ½ pt ...
Why plants need nutrients
... Nitrogen atoms are needed to make amino acids and proteins (including enzymes) and other important biological molecules. Nitrogen promotes green, leafy growth and the formation of stems. Crops with high nitrogen demands include grasses and leafy vegetables such as lettuce, spinach and cabbage. The a ...
... Nitrogen atoms are needed to make amino acids and proteins (including enzymes) and other important biological molecules. Nitrogen promotes green, leafy growth and the formation of stems. Crops with high nitrogen demands include grasses and leafy vegetables such as lettuce, spinach and cabbage. The a ...
Restriction Enzymes - Seattle Central College
... of the DNA at specific nucleotide. • They are member of the class of nucleases. Endonucleases cleave nucleic acid at internal positions, while exonucleases progressively digest from the ends of the nucleic acid molecules. • The three dimensional structure of the restriction enzyme allows it to fit p ...
... of the DNA at specific nucleotide. • They are member of the class of nucleases. Endonucleases cleave nucleic acid at internal positions, while exonucleases progressively digest from the ends of the nucleic acid molecules. • The three dimensional structure of the restriction enzyme allows it to fit p ...
Fill in the Captions AP Lesson #26 Are our diets only glucose? How
... proteins → → → → → amino acids ...
... proteins → → → → → amino acids ...
Purine nucleotide synthesis De novo
... obtained from nucleic acid breakdown (from nucleic acid turnover or from the diet) • During de novo synthesis new bases are synthesized purine nucleotides are constructed a few atoms at a time on a ribose-based structure the framework for pyrimidine bases is first synthesized and is then attache ...
... obtained from nucleic acid breakdown (from nucleic acid turnover or from the diet) • During de novo synthesis new bases are synthesized purine nucleotides are constructed a few atoms at a time on a ribose-based structure the framework for pyrimidine bases is first synthesized and is then attache ...
Document
... mRNA and 16SrRNA interaction. There is SD sequence ( RBS , ribosome binding site ) 8-13 nt upstream of the initiation codon in prokaryotic mRNA which base-pairs with a complementary sequence near the 3’ end of 16SrRNA. ...
... mRNA and 16SrRNA interaction. There is SD sequence ( RBS , ribosome binding site ) 8-13 nt upstream of the initiation codon in prokaryotic mRNA which base-pairs with a complementary sequence near the 3’ end of 16SrRNA. ...
Purine metabolism - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
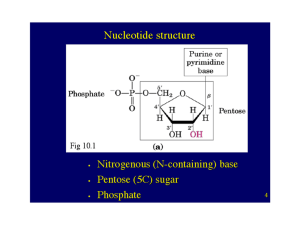
... Nucleotides are linked by 5’ to 3’ phosphodiester bonds to generate DNA and RNA ...
... Nucleotides are linked by 5’ to 3’ phosphodiester bonds to generate DNA and RNA ...
PROTEINS – STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (DR. TRAISH)
... 2. Convention: amino terminus on the left (N-terminal), COOH terminus on the right (C-terminal) ii. Secondary Structure 1. Local folding of amino acids in primary sequence into a specific arrangement 2. Different regions of the polypeptide can be different conformations – doesn’t have to be all one ...
... 2. Convention: amino terminus on the left (N-terminal), COOH terminus on the right (C-terminal) ii. Secondary Structure 1. Local folding of amino acids in primary sequence into a specific arrangement 2. Different regions of the polypeptide can be different conformations – doesn’t have to be all one ...
Introduction to Protein Structure
... case, the charged molecule needs to be hidden away from the outside of the protein into a hydrophobic pocket inside the protein. Because the binding site of the molecule must be near the surface of the protein, the binding must cause a change in conformation of the protein such that the bound molecu ...
... case, the charged molecule needs to be hidden away from the outside of the protein into a hydrophobic pocket inside the protein. Because the binding site of the molecule must be near the surface of the protein, the binding must cause a change in conformation of the protein such that the bound molecu ...
of a protein
... they also use as a unit of molecular weight of biomacromolecules the Dalton (after John Dalton [1766-1844] who suggested for the unit of atomic mass the weight of an H atom in 1803; since 1961 we use 12C as a basis of atomic weight especially due to the discovery of ...
... they also use as a unit of molecular weight of biomacromolecules the Dalton (after John Dalton [1766-1844] who suggested for the unit of atomic mass the weight of an H atom in 1803; since 1961 we use 12C as a basis of atomic weight especially due to the discovery of ...
Dentistry college - first class Medical biology
... contrast prokaryotic cells store their DNA only in cytoplasm . ...
... contrast prokaryotic cells store their DNA only in cytoplasm . ...
yes - Learnblock
... For a cellular reaction to reach equilibrium the product must be continually used by the cell elsewhere opposite. if used then equilibrium never attained ...
... For a cellular reaction to reach equilibrium the product must be continually used by the cell elsewhere opposite. if used then equilibrium never attained ...
myosinTeacher.pdf
... Question 13 - pg 7 Using all the information you have so far – list at least two possible explanations for the difference between survival curves with the different mutations. 1. Mutations leading to a change in charge have the most profound affect on the function of myosin. 2. Mutations located in ...
... Question 13 - pg 7 Using all the information you have so far – list at least two possible explanations for the difference between survival curves with the different mutations. 1. Mutations leading to a change in charge have the most profound affect on the function of myosin. 2. Mutations located in ...
Lecture Slides
... 4) Higher O2 levels allowed new type of heterotrophy. Aerobic respiration - “burn” organic matter with O 2 (Eubacteria, Eukarya) C6 H12O6 (Glucose; e- dnr) + 6O2 (e- acptr) 6CO2 + 6H2 O + 36 ATP Much more efficient than fermentation. Leaves no energy-rich waste (e.g., ethanol). Self-sustaining eco ...
... 4) Higher O2 levels allowed new type of heterotrophy. Aerobic respiration - “burn” organic matter with O 2 (Eubacteria, Eukarya) C6 H12O6 (Glucose; e- dnr) + 6O2 (e- acptr) 6CO2 + 6H2 O + 36 ATP Much more efficient than fermentation. Leaves no energy-rich waste (e.g., ethanol). Self-sustaining eco ...
Amino acids [qualitative tests]
... Objectives: -general information about amino acids. -qualitative tests of amino acids. ...
... Objectives: -general information about amino acids. -qualitative tests of amino acids. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.



















![Amino acids [qualitative tests]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282328_1-c8bb4ef27caebe478c13494a7af59cc2-300x300.png)


