3. BIOMOLECULES I. CARBOHYDRATES
... 11. 11. THE METABOLIC PROCESSES II. LIPID METABOLISM ............................................ 1. 11.1. Biosynthesis of lipids ................................................................................................. 1.1. 11. 1. 1. Biosynthesis of triglicerides ........................... ...
... 11. 11. THE METABOLIC PROCESSES II. LIPID METABOLISM ............................................ 1. 11.1. Biosynthesis of lipids ................................................................................................. 1.1. 11. 1. 1. Biosynthesis of triglicerides ........................... ...
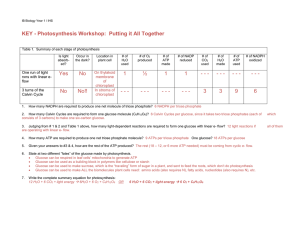
Chapt 2-9 Practice Problem Answers
... Activity 2.1 Question 1: Many students don’t understand that nutrients for plants are inorganic and most nutrients for animals (heterotrophs) are organic. Questions 2 and 3: Most students know how to balance a chemical equation. Fewer understand the relationship between molecules of a substance and ...
... Activity 2.1 Question 1: Many students don’t understand that nutrients for plants are inorganic and most nutrients for animals (heterotrophs) are organic. Questions 2 and 3: Most students know how to balance a chemical equation. Fewer understand the relationship between molecules of a substance and ...
Alterations of the PPP2R1B gene located at 11q23 in human
... termed a HEAT (Huntington elongation A subunit TOR) motif.8 9 The HEAT repeat motif is characterised by a pair of antiparallel á helices (termed A and B) that are stacked in a consecutive array to generate a regular repetitive protein architecture, reflecting the internal repeats of the protein sequ ...
... termed a HEAT (Huntington elongation A subunit TOR) motif.8 9 The HEAT repeat motif is characterised by a pair of antiparallel á helices (termed A and B) that are stacked in a consecutive array to generate a regular repetitive protein architecture, reflecting the internal repeats of the protein sequ ...
Lipid Oxidation - anslab.iastate.edu
... • Oxygen is the most important factor on the development of lipid oxidation • Ground state oxygen is itself a radical, with two unpaired electrons each located in a * antibonding orbital • Ground state oxygen has its outermost pair of electrons parallel spins: does not allow them to react with most ...
... • Oxygen is the most important factor on the development of lipid oxidation • Ground state oxygen is itself a radical, with two unpaired electrons each located in a * antibonding orbital • Ground state oxygen has its outermost pair of electrons parallel spins: does not allow them to react with most ...
Two fatty acid ∆9-desaturase genes, ole1 and ole2
... Genes encoding two distinct fatty acid ∆9-desaturases were isolated from strains of the oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina. Two genomic sequences, ∆9-1 and ∆9-2, each containing a single intron, were cloned from strain CBS 528.72 while one cDNA clone, LM9, was isolated from strain CBS 210.32. The ...
... Genes encoding two distinct fatty acid ∆9-desaturases were isolated from strains of the oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina. Two genomic sequences, ∆9-1 and ∆9-2, each containing a single intron, were cloned from strain CBS 528.72 while one cDNA clone, LM9, was isolated from strain CBS 210.32. The ...
What is natural immunity?
... homologous if they can be said to have shared an ancestor • Genes or proteins are either homologs or they are not- there is no such thing as percent homology. There is percent identity or similarity of the sequences ...
... homologous if they can be said to have shared an ancestor • Genes or proteins are either homologs or they are not- there is no such thing as percent homology. There is percent identity or similarity of the sequences ...
origins debate intro
... a D-ribose), a nucleobase (in RNA, the bases can be either (ribose in RNA) (deoxyribose in DNA) adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or uracil (U); in DNA, thymine (T) takes the place of uracil; other bases such as inosine exist but are not commonly found in living systems), and a phosphate group ...
... a D-ribose), a nucleobase (in RNA, the bases can be either (ribose in RNA) (deoxyribose in DNA) adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or uracil (U); in DNA, thymine (T) takes the place of uracil; other bases such as inosine exist but are not commonly found in living systems), and a phosphate group ...
PDF
... according to the above-described alternation of the two systems. The changes of the above-mentioned enzyme systems affect the energy level in the pupa. Both the amount of the fraction ATP + ADP as of AMP varies along a U-shaped curve. During metamorphosis first a decomposition and later a rebuilding ...
... according to the above-described alternation of the two systems. The changes of the above-mentioned enzyme systems affect the energy level in the pupa. Both the amount of the fraction ATP + ADP as of AMP varies along a U-shaped curve. During metamorphosis first a decomposition and later a rebuilding ...
Lab 5: Proteins and the small molecules that love them
... cannot have it’s pH altered without having deleterious consequences for many other processes and the temperature inside each cell is carefully maintained in many organisms. However catalysts are available – usually in the form of enzymes. In this course, you have already been introduced to several e ...
... cannot have it’s pH altered without having deleterious consequences for many other processes and the temperature inside each cell is carefully maintained in many organisms. However catalysts are available – usually in the form of enzymes. In this course, you have already been introduced to several e ...
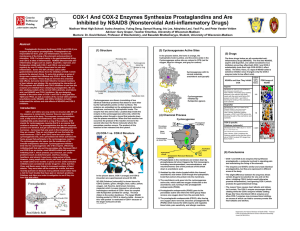
COX-1 And COX-2 Enzymes Synthesize Prostaglandins and Are
... different parts of the body. The enzymes convert arachidonic acid, a fatty acid in cell membranes, into prostaglandins, modified fatty acids attached to a ring of five carbons. COX stands for cyclooxygenase meaning that it is an enzyme that oxidizes a substrate. The prostaglandins that the two enzym ...
... different parts of the body. The enzymes convert arachidonic acid, a fatty acid in cell membranes, into prostaglandins, modified fatty acids attached to a ring of five carbons. COX stands for cyclooxygenase meaning that it is an enzyme that oxidizes a substrate. The prostaglandins that the two enzym ...
Renal tubular reabsorption
... • “Uphill” transport of one substance is linked to “downhill” transport of another substance • Carrier must be occupied by both substances (or be unoccupied) to be mobile in the membrane • Saturable (has a Vmax) • Demonstrates specificity and affinity of carrier for substance transported • “Uphill” ...
... • “Uphill” transport of one substance is linked to “downhill” transport of another substance • Carrier must be occupied by both substances (or be unoccupied) to be mobile in the membrane • Saturable (has a Vmax) • Demonstrates specificity and affinity of carrier for substance transported • “Uphill” ...
Topic 1: Statistical analysis (2 hours)
... Explain how the structure and properties of phospholipids help to properties of phospholipids help to maintain the maintain the structure of cell membranes (9) structure of cell membranes. phospholipid structure hydrophobic tail / hydrophilic head; head made from glycerol and phosphate; tail made fr ...
... Explain how the structure and properties of phospholipids help to properties of phospholipids help to maintain the maintain the structure of cell membranes (9) structure of cell membranes. phospholipid structure hydrophobic tail / hydrophilic head; head made from glycerol and phosphate; tail made fr ...
Hepatic Failure: Role for biochemists and nutrition experts
... and neur otr ans mitter s . (3) Ammonia metabolis m pr imar ily occur s in the hepatic tis s ue and s econdar ily in the mus cle tis s ue. Due to mus cle was ting in HF, ammonia metabolis m in the mus cle is diminis hed and ex ces s ammonia cr os s es the blood- br ain bar r ier . T he ammonia thus ...
... and neur otr ans mitter s . (3) Ammonia metabolis m pr imar ily occur s in the hepatic tis s ue and s econdar ily in the mus cle tis s ue. Due to mus cle was ting in HF, ammonia metabolis m in the mus cle is diminis hed and ex ces s ammonia cr os s es the blood- br ain bar r ier . T he ammonia thus ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.