Movsumov I.S., Garayev E.A. STUDYING OF CHEMICAL
... The influence of addition of amino acids before the drying of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus L.) on the composition of aroma compounds was studied by the capillary gas chromatography and chromatography – mass spectrometry methods. It was found that concentration of carbonyls and heterocyclic volatile c ...
... The influence of addition of amino acids before the drying of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus L.) on the composition of aroma compounds was studied by the capillary gas chromatography and chromatography – mass spectrometry methods. It was found that concentration of carbonyls and heterocyclic volatile c ...
Chemistry 160:581 – Biochemistry - Syllabus for Fall 2014 Monday
... A strong prior preparation in organic chemistry and some preparation in physical chemistry are useful pre-requisites. This one-semester course introduces the structural aspects of the four major classes of biopolymers: nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, with a significant emphasis on ...
... A strong prior preparation in organic chemistry and some preparation in physical chemistry are useful pre-requisites. This one-semester course introduces the structural aspects of the four major classes of biopolymers: nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, with a significant emphasis on ...
Aptamers as Drugs. PDF
... chemistry and binding interactions. For instance, Famulok and his colleagues found that certain DNA polymerases are able to tolerate chemically modified nucleotides29. They were able to enzymatically incorporate a variety of different functional groups, i.e. acidic, basic, or lipophilic, into a grow ...
... chemistry and binding interactions. For instance, Famulok and his colleagues found that certain DNA polymerases are able to tolerate chemically modified nucleotides29. They were able to enzymatically incorporate a variety of different functional groups, i.e. acidic, basic, or lipophilic, into a grow ...
The Microbiological Degradation of Aromatic Compounds
... Department of Biochemistry and Soil Science, University College of North Wales, Bangor The breakdown of aromatic compounds by ring cleavage is an essential biochemical step in Nature's 'carbon' cycle and is performed by several kinds of microorganism. Bacteria are the most versatile in this respect, ...
... Department of Biochemistry and Soil Science, University College of North Wales, Bangor The breakdown of aromatic compounds by ring cleavage is an essential biochemical step in Nature's 'carbon' cycle and is performed by several kinds of microorganism. Bacteria are the most versatile in this respect, ...
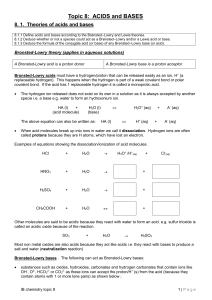
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... Lewis bases: electron pair donors A Lewis base is a reactant which during a reaction donates an electron pair; common Lewis bases are: nitrogen compounds (e.g. ammonia), water and the hydroxide ion as they have a great tendency, because of their lone pairs, to donate these electron pairs to Le ...
... Lewis bases: electron pair donors A Lewis base is a reactant which during a reaction donates an electron pair; common Lewis bases are: nitrogen compounds (e.g. ammonia), water and the hydroxide ion as they have a great tendency, because of their lone pairs, to donate these electron pairs to Le ...
Super secondary structure (Motif)
... that is ~25° off the axis of the helix. •Similarly, every 3rd residue forms a ridge (± 3n ridge) that is ~45° off the axis of the helix •Between two adjacent ridges lies a groove •Helix packing occurs when the ridge of one helix fits within the groove of another helix ...
... that is ~25° off the axis of the helix. •Similarly, every 3rd residue forms a ridge (± 3n ridge) that is ~45° off the axis of the helix •Between two adjacent ridges lies a groove •Helix packing occurs when the ridge of one helix fits within the groove of another helix ...
SUBUNITS FROM REDUCED .AND S
... by weight of the dry chloroplasts (Kupke 1962). The function of this large amount of protein is that of an essential enzyme in the fixation of carbon dioxide by ribulose-l,5-diphosphate to produce phosphoglyceric acid. As in the case of other enzyme systcms, e.g. aspartate transcarbamylase (Gerhart ...
... by weight of the dry chloroplasts (Kupke 1962). The function of this large amount of protein is that of an essential enzyme in the fixation of carbon dioxide by ribulose-l,5-diphosphate to produce phosphoglyceric acid. As in the case of other enzyme systcms, e.g. aspartate transcarbamylase (Gerhart ...
Slide 1
... a variety of species of snake, some species would bind predictably to the antibody whereas others would not.2 ...
... a variety of species of snake, some species would bind predictably to the antibody whereas others would not.2 ...
What is transcription
... condition, activating factor is required for initiation. For example, Lac promoter Plac requires cAMP receptor protein (CRP ) ...
... condition, activating factor is required for initiation. For example, Lac promoter Plac requires cAMP receptor protein (CRP ) ...
Primary Sequence of Ovomucoid Messenger RNA
... code for these two proteins offer an attractive model system for the study of coordinate expression of unlinked genes in a steroid-hormone target tissue. We have previously reported that the ovomucoid gene has a complex structure containing seven intervening sequences (9, 21) . Messenger RNA sequenc ...
... code for these two proteins offer an attractive model system for the study of coordinate expression of unlinked genes in a steroid-hormone target tissue. We have previously reported that the ovomucoid gene has a complex structure containing seven intervening sequences (9, 21) . Messenger RNA sequenc ...
Bile
... Bile acids are derivatives of cholesterol synthesized in the hepatocyte. It has various components like water, cholesterol, bile pigments, anions of the bile acids, phospholipids, bicarbonate and other ions. Cholesterol is converted into the cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acids, which are then con ...
... Bile acids are derivatives of cholesterol synthesized in the hepatocyte. It has various components like water, cholesterol, bile pigments, anions of the bile acids, phospholipids, bicarbonate and other ions. Cholesterol is converted into the cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acids, which are then con ...
Organic Chemistry Notes Student
... A. Carbohydrates - ______________________________________ Monosaccharides are the simplest ______________________. • The carbohydrate monomers are ___________________ • A monosaccharide has a formula that is a multiple of CH2O ______________________ ...
... A. Carbohydrates - ______________________________________ Monosaccharides are the simplest ______________________. • The carbohydrate monomers are ___________________ • A monosaccharide has a formula that is a multiple of CH2O ______________________ ...
Full contents - Scion Publishing
... Box 7.4 The specificity of substrate binding......................................... 00 7.2.2 Factors influencing the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction........................................................................................ 00 Box 7.5 Exploiting thermostable enzymes in ...
... Box 7.4 The specificity of substrate binding......................................... 00 7.2.2 Factors influencing the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction........................................................................................ 00 Box 7.5 Exploiting thermostable enzymes in ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) an alternate site for production of urea in the kidney B) transport of important enzymes for gluconeogenesis C) an indirect means for muscle to eliminate nitrogen and replenish its energy supply D) a cycle for the direct synthesis of carbohydrates in muscle Answer: C Page Ref: Section 17-7 60) A ...
... A) an alternate site for production of urea in the kidney B) transport of important enzymes for gluconeogenesis C) an indirect means for muscle to eliminate nitrogen and replenish its energy supply D) a cycle for the direct synthesis of carbohydrates in muscle Answer: C Page Ref: Section 17-7 60) A ...
CH_16_4_Levels_Protein_Structure
... basic and acidic amino acids. For example, the ionized R group of arginine, which has a positive charge, can form a salt bridge (ionic bond) with the R group in aspartic acid, which has a negative charge. 4. Hydrogen bonds form between H of a polar R group and the O or N of another amino acid. For e ...
... basic and acidic amino acids. For example, the ionized R group of arginine, which has a positive charge, can form a salt bridge (ionic bond) with the R group in aspartic acid, which has a negative charge. 4. Hydrogen bonds form between H of a polar R group and the O or N of another amino acid. For e ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
... oxidative phosphorylation. 4. Can also be used for gluconeogenesis to form G6P 5. 1 molecule of G6P can be converted via 6 cycles of PPP and gluconeogenesis to 6 CO2 molecules and generate 12 NADPH molecules. 6. Flux through PPP (rate of NADPH production) is controlled by the glucose-6-phosphate deh ...
... oxidative phosphorylation. 4. Can also be used for gluconeogenesis to form G6P 5. 1 molecule of G6P can be converted via 6 cycles of PPP and gluconeogenesis to 6 CO2 molecules and generate 12 NADPH molecules. 6. Flux through PPP (rate of NADPH production) is controlled by the glucose-6-phosphate deh ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.