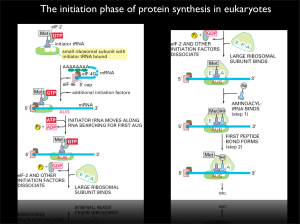
The initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotes
... Figure 7 The binding of the 4E-BPs to eIF4E is regulated by phosphorylation. The 4E-BPs and eIF4Gs compete for a common binding site on eIF4E. Various stimuli increase the phosphorylation of the 4E-BPs. Hyperphosphorylated 4E-BPs have a relatively low affinity for eIF4E. Conversely, a decrease in 4E ...
... Figure 7 The binding of the 4E-BPs to eIF4E is regulated by phosphorylation. The 4E-BPs and eIF4Gs compete for a common binding site on eIF4E. Various stimuli increase the phosphorylation of the 4E-BPs. Hyperphosphorylated 4E-BPs have a relatively low affinity for eIF4E. Conversely, a decrease in 4E ...
Document
... • ALT values are significantly increased in cases of hepatitis and moderately increased in cirrhosis, liver tumors, obstructive ...
... • ALT values are significantly increased in cases of hepatitis and moderately increased in cirrhosis, liver tumors, obstructive ...
role of aldehyde oxidase and keto
... transcriptome of knockout demonstrates overall downregulation of direct retinoiddependent genes as well as perturbations in pathways controlling lipid homeostasis and cellular secretion, particularly in sexually immature animals. Humans have been shown to have the AOX enzymes although little is know ...
... transcriptome of knockout demonstrates overall downregulation of direct retinoiddependent genes as well as perturbations in pathways controlling lipid homeostasis and cellular secretion, particularly in sexually immature animals. Humans have been shown to have the AOX enzymes although little is know ...
Isolation of Vibrio harveyi Acyl Carrier Protein and the fabG, acpP
... and other complex molecules in a variety of organisms. The prototypic ACP from Escherichia coli is a 9-kDa acidic protein (pI, 4.1) of 77 amino acids which carries fatty acids as thioester intermediates attached to a phosphopantetheine prosthetic group at Ser-36 (17, 31). In addition to its major fu ...
... and other complex molecules in a variety of organisms. The prototypic ACP from Escherichia coli is a 9-kDa acidic protein (pI, 4.1) of 77 amino acids which carries fatty acids as thioester intermediates attached to a phosphopantetheine prosthetic group at Ser-36 (17, 31). In addition to its major fu ...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Metabolic engineering of for production
... ‘classical’ strain improvement [i.e. the use of nontargeted mutagenesis, combined with high-throughput analysis to select for better-performing mutants (Vinci & Byng, 1999)]. While classical strain improvement continues to be of great importance in industrial biotechnology, it is increasingly being ...
... ‘classical’ strain improvement [i.e. the use of nontargeted mutagenesis, combined with high-throughput analysis to select for better-performing mutants (Vinci & Byng, 1999)]. While classical strain improvement continues to be of great importance in industrial biotechnology, it is increasingly being ...
Free aromatic amino acids in egg yolk show antioxidant properties
... methods significantly reduced (p < 0.05) the antioxidant values. Ferulic acid was detected in trace amounts and no other phenolic compounds were found. However, tryptophan and tyrosine were found to be two main contributors to the antioxidant property of egg yolk. The contents of total free amino aci ...
... methods significantly reduced (p < 0.05) the antioxidant values. Ferulic acid was detected in trace amounts and no other phenolic compounds were found. However, tryptophan and tyrosine were found to be two main contributors to the antioxidant property of egg yolk. The contents of total free amino aci ...
Over-expression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in hybrid
... polymerized into more complex macromolecules. Studies have shown that altered carbon partitioning can manifest changes in the chemical composition of plants by the altered regulation of genes involved in the synthesis of lignin or cellulose (Li et al., 2003; Canam et al., 2006). Despite these findin ...
... polymerized into more complex macromolecules. Studies have shown that altered carbon partitioning can manifest changes in the chemical composition of plants by the altered regulation of genes involved in the synthesis of lignin or cellulose (Li et al., 2003; Canam et al., 2006). Despite these findin ...
Exploring Yeast as a Cell Factory for the Production of Carboxylic
... PHB formation, especially in the absence of oxygen, a condition that is desirable in industry since it reduces the need for aeration, and therefore the overall process cost. ix ...
... PHB formation, especially in the absence of oxygen, a condition that is desirable in industry since it reduces the need for aeration, and therefore the overall process cost. ix ...
Isolation of All Soluble Tryptic Peptides from the α Polypeptide
... Column Chromatography of the Soluble Tryptic Peptides on Dowex 1 x 2 500 ml of dry resin (Dowex 1 x 2, 200-400 mesh, Cl-form, Dow Chemical Company) was suspended in three volumes of deionized water. The suspension, after stirred, was allowed to stand for an hour and then the fine particles discarded ...
... Column Chromatography of the Soluble Tryptic Peptides on Dowex 1 x 2 500 ml of dry resin (Dowex 1 x 2, 200-400 mesh, Cl-form, Dow Chemical Company) was suspended in three volumes of deionized water. The suspension, after stirred, was allowed to stand for an hour and then the fine particles discarded ...
A futile metabolic cycle activated in adipocytes by - Zen-Bio
... In adipocytes, GyK promotes storage of FA by increasing TG synthesis from precursors that are either imported or recycled within the cell. The latter pathway is uniquely dependent upon expression of GyK. However, induction of adipocyte GyK to physiologically significant levels is noteworthy because ...
... In adipocytes, GyK promotes storage of FA by increasing TG synthesis from precursors that are either imported or recycled within the cell. The latter pathway is uniquely dependent upon expression of GyK. However, induction of adipocyte GyK to physiologically significant levels is noteworthy because ...
Protein hydrolysates in sports nutrition
... reference to sports nutrition. The effects of protein hydrolysate ingestion on blood amino acid levels, muscle protein anabolism, body composition, exercise performance and muscle glycogen resynthesis are discussed. ...
... reference to sports nutrition. The effects of protein hydrolysate ingestion on blood amino acid levels, muscle protein anabolism, body composition, exercise performance and muscle glycogen resynthesis are discussed. ...
Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, Second Edition
... © 2012 Delmar Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied, duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. ...
... © 2012 Delmar Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied, duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. ...
Acetobactev diazotrophicus sp. nov., a Nitrogen
... are microaerobic dinitrogen fixers which grow on N, as a sole nitrogen source in semisolid media and after initial growth with starter nitrogen in liquid media; they grow well in liquid media with combined nitrogen sources. Nitrate is not reduced, and N, fixation occurs at high nitrate concentration ...
... are microaerobic dinitrogen fixers which grow on N, as a sole nitrogen source in semisolid media and after initial growth with starter nitrogen in liquid media; they grow well in liquid media with combined nitrogen sources. Nitrate is not reduced, and N, fixation occurs at high nitrate concentration ...
Mechanistic insights into pancreatic beta
... Elevated glucose levels augment the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in islet cells, which induce oxidative stress. ROS is produced following oxidative phosphorylation of glucose in mitochondria. Since beta-cells have very low levels of antioxidant enzymes, they are particularly vulnerabl ...
... Elevated glucose levels augment the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in islet cells, which induce oxidative stress. ROS is produced following oxidative phosphorylation of glucose in mitochondria. Since beta-cells have very low levels of antioxidant enzymes, they are particularly vulnerabl ...
Fundamental Challenges in Mechanistic Enzymology: Progress
... General Historical Overview of Understanding Enzymatic Rate Enhancements. Very early ideas about how ...
... General Historical Overview of Understanding Enzymatic Rate Enhancements. Very early ideas about how ...
2016A Guerreiro Microbial Cell
... mM for S. cerevisiae [6-8]. Depending on the acid concentration, acetic acid may induce a PCD either with an apoptotic or a necrotic phenotype [6-8]. In S. cerevisiae, acetic acid - induced PCD with an apoptotic phenotype is known to be mediated by mitochondria, an organelle that fulfills crucial fu ...
... mM for S. cerevisiae [6-8]. Depending on the acid concentration, acetic acid may induce a PCD either with an apoptotic or a necrotic phenotype [6-8]. In S. cerevisiae, acetic acid - induced PCD with an apoptotic phenotype is known to be mediated by mitochondria, an organelle that fulfills crucial fu ...
Enzymes with Molecular Tunnels - Department of Biochemistry | UW
... changes that occur upon substrate binding include a rigid body rotation of the R-subunit with respect to the β-subunit and movements of the β-subunit in the region defined by Gly 93 to Gly 189. The net effect of these conformational changes is to restrict access of the solvent to both the R- and β-s ...
... changes that occur upon substrate binding include a rigid body rotation of the R-subunit with respect to the β-subunit and movements of the β-subunit in the region defined by Gly 93 to Gly 189. The net effect of these conformational changes is to restrict access of the solvent to both the R- and β-s ...
Specificity of the Organic Acid Activation of
... is stimulated and stabilized by pyruvate (Zhang et al., 1996), it is obvious that pyruvate reacts directly with the AOX protein. In soybean, it has been shown that pyruvate generated intramitochondrially during oxidation of malate and succinate can also lead to activation of AOX (Day et al., 1994), ...
... is stimulated and stabilized by pyruvate (Zhang et al., 1996), it is obvious that pyruvate reacts directly with the AOX protein. In soybean, it has been shown that pyruvate generated intramitochondrially during oxidation of malate and succinate can also lead to activation of AOX (Day et al., 1994), ...
Facultative Anaerobiosis in the Invertebrates: Pathways and Control
... helminths studied to date, regardless of their oxygen requirements, be they aerobic or anaerobic, are capable of the complete oxidation of substrates to CO2 and water. All of those examined accumulate organic end-products. Since substrates are not completely metabolized, it would appear that termina ...
... helminths studied to date, regardless of their oxygen requirements, be they aerobic or anaerobic, are capable of the complete oxidation of substrates to CO2 and water. All of those examined accumulate organic end-products. Since substrates are not completely metabolized, it would appear that termina ...
The methylcitric acid pathway in Ralstonia eutropha
... used for the catabolism of this short-chain fatty acid, e.g. the acrylate pathway, the methylmalonyl-CoA pathway or the malonic semialdehyde-CoA pathway (Vagelos, 1959). In addition, the cyclic 2-methylcitric acid pathway has been identified as a new strategy for the breakdown of propionate in the y ...
... used for the catabolism of this short-chain fatty acid, e.g. the acrylate pathway, the methylmalonyl-CoA pathway or the malonic semialdehyde-CoA pathway (Vagelos, 1959). In addition, the cyclic 2-methylcitric acid pathway has been identified as a new strategy for the breakdown of propionate in the y ...
$doc.title
... All these past attempts to create novel-coloured flowers have focused on the manipulation of the flavonoid pigmentation pathways that exist in flowers (Elomaa and Holton, 1994; Forkmann and Martens, 2001). To create black flowers, for example, researchers tried to increase the concentrations of fl ...
... All these past attempts to create novel-coloured flowers have focused on the manipulation of the flavonoid pigmentation pathways that exist in flowers (Elomaa and Holton, 1994; Forkmann and Martens, 2001). To create black flowers, for example, researchers tried to increase the concentrations of fl ...
Learning Outcomes
... to deduce their properties (c) compare the bonding and structures of diamond and graphite in order to deduce their properties such as electrical conductivity, lubricating or cutting action (candidates will not be required to draw the structures) ...................................................... ...
... to deduce their properties (c) compare the bonding and structures of diamond and graphite in order to deduce their properties such as electrical conductivity, lubricating or cutting action (candidates will not be required to draw the structures) ...................................................... ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.