Lab Exercise 7 - Cellular Respiration
... Heat is produced in both fermentation and aerobic respiration because living cells are never 100% efficient in transforming energy from one usable form (like food molecules) to another usable form (like ATP). A certain amount of energy is always released in a form that cannot power reactions within ...
... Heat is produced in both fermentation and aerobic respiration because living cells are never 100% efficient in transforming energy from one usable form (like food molecules) to another usable form (like ATP). A certain amount of energy is always released in a form that cannot power reactions within ...
Chapter 1 - TeacherWeb
... Wobble effect at third position For both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes know initiation, elongation, and termination for transcription and translation Prokaryotic Transcription Initiation: Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the ...
... Wobble effect at third position For both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes know initiation, elongation, and termination for transcription and translation Prokaryotic Transcription Initiation: Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the ...
Unit 4: Cellular Energy Study Guide
... ATP is a high energy molecule composed of a ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three high energy phosphate groups. The energy in ATP is found in the bonds that connect each phosphate. Energy is released when a phosphate is broken off. ATP – 1 phosphate = ADP (adenosine diphosphate) ADP – 1 phosphate ...
... ATP is a high energy molecule composed of a ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three high energy phosphate groups. The energy in ATP is found in the bonds that connect each phosphate. Energy is released when a phosphate is broken off. ATP – 1 phosphate = ADP (adenosine diphosphate) ADP – 1 phosphate ...
Topics To Know For Chapter 6
... 12. Know the events of chemiosmosis discussed in class and where does it take place. - thylakoid membrane - ATP synthetase - thylakoid space - electron flow - pH 4 - photosystems I & II - H+ concentration 13. Know what makes the Calvin cycle work or operate. Describe the events taking place in the C ...
... 12. Know the events of chemiosmosis discussed in class and where does it take place. - thylakoid membrane - ATP synthetase - thylakoid space - electron flow - pH 4 - photosystems I & II - H+ concentration 13. Know what makes the Calvin cycle work or operate. Describe the events taking place in the C ...
BCHEM 254 – METABOLISM IN HEALTH AND DISEASES II Lecture
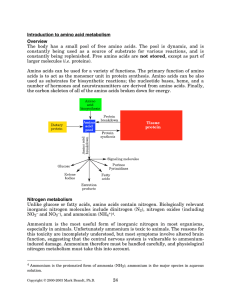
... Nitrogen Bases: There are two kinds of nitrogen-containing bases in nucleic acids: purines and pyrimidines. Purines consist of two fused nitrogen-containing rings with a total of nine ring atoms. Pyridmidines have only a six-membered nitrogencontaining ring. Purines and pyrimidines are "flat", hydr ...
... Nitrogen Bases: There are two kinds of nitrogen-containing bases in nucleic acids: purines and pyrimidines. Purines consist of two fused nitrogen-containing rings with a total of nine ring atoms. Pyridmidines have only a six-membered nitrogencontaining ring. Purines and pyrimidines are "flat", hydr ...
Supplementary Text 2: Extensions to the prototype model
... The prototype model1 was developed in order to integrate major pathway components with other pertinent information on sphingolipid metabolism. As typical in modeling, this model design was based on abstraction and simplification. In order to facilitate the direct experimental testing of model predic ...
... The prototype model1 was developed in order to integrate major pathway components with other pertinent information on sphingolipid metabolism. As typical in modeling, this model design was based on abstraction and simplification. In order to facilitate the direct experimental testing of model predic ...
Slide 1
... Why simulate a biomolecule? What is the current status? Biomolecular simulation: An example ...
... Why simulate a biomolecule? What is the current status? Biomolecular simulation: An example ...
1.Oxidative phosphorylation
... tissue is abundant in the newborn and in some adult mammals, and it is brown because of its high content of mitochondria. In humans, brown adipose tissue is abundant in infants, but it gradually diminishes and is barely detectable in adults. • UCP1 provides body heat during cold stress in the young ...
... tissue is abundant in the newborn and in some adult mammals, and it is brown because of its high content of mitochondria. In humans, brown adipose tissue is abundant in infants, but it gradually diminishes and is barely detectable in adults. • UCP1 provides body heat during cold stress in the young ...
Transcription - smithlhhsb121
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
A Practice Reactions Quiz -
... A) Write complete balanced equations for the following reactions. B) Label each reaction as either SYN, DEC, SR, DR, or COMB. C) Place a star next to any reaction which required knowledge of oxidation numbers. D) Finally, find the two reactions below which do not actually take place. Write “NR” and ...
... A) Write complete balanced equations for the following reactions. B) Label each reaction as either SYN, DEC, SR, DR, or COMB. C) Place a star next to any reaction which required knowledge of oxidation numbers. D) Finally, find the two reactions below which do not actually take place. Write “NR” and ...
Slide 1
... They are of 2 types DNA or RNA. DNA is made of nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. RNA is made of nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. GENE is a piece of DNA capable of forming a functional product either protein or RNA. 5. Every cell typically has thousands ...
... They are of 2 types DNA or RNA. DNA is made of nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. RNA is made of nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. GENE is a piece of DNA capable of forming a functional product either protein or RNA. 5. Every cell typically has thousands ...
6 Characteristics of Living Things
... living things have one or more cells. The cell is the building block of living things, and it is surrounded by a boundary. ...
... living things have one or more cells. The cell is the building block of living things, and it is surrounded by a boundary. ...
b-Oxidation of fatty acids
... of species or even kingdom. 4. A number of invariant arginine and lysine clusters can be found on the surface of the molecule. Cytochrome c has a dual function in the cell. Electron transport for ATP production AND the major cause of most programmed cell death (apoptosis) is initiated by the release ...
... of species or even kingdom. 4. A number of invariant arginine and lysine clusters can be found on the surface of the molecule. Cytochrome c has a dual function in the cell. Electron transport for ATP production AND the major cause of most programmed cell death (apoptosis) is initiated by the release ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Glutathione serves as a reductant; is conjugated to drugs to make them more water soluble (detoxification). Reduces peroxides formed during oxygen transport. The resulting oxidized form of GSH consists of two molecules disulfide bonded together (abbreviated GSSG). Is involved in amino acid transport ...
... Glutathione serves as a reductant; is conjugated to drugs to make them more water soluble (detoxification). Reduces peroxides formed during oxygen transport. The resulting oxidized form of GSH consists of two molecules disulfide bonded together (abbreviated GSSG). Is involved in amino acid transport ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
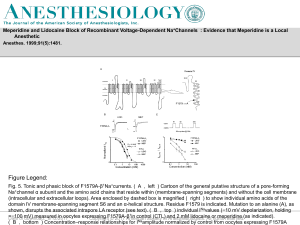
... Fig. 5. Tonic and phasic block of F1579A-β1Na+currents. ( A , left ) Cartoon of the general putative structure of a pore-forming Na+channel α subunit and the amino acid chains that reside within (membrane-spanning segments) and without the cell membrane (intracellular and extracellular loops). Area ...
... Fig. 5. Tonic and phasic block of F1579A-β1Na+currents. ( A , left ) Cartoon of the general putative structure of a pore-forming Na+channel α subunit and the amino acid chains that reside within (membrane-spanning segments) and without the cell membrane (intracellular and extracellular loops). Area ...
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
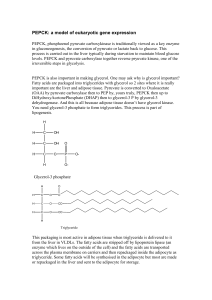
... PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose levels. PEPCK and pyruvate carboxylase together ...
... PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose levels. PEPCK and pyruvate carboxylase together ...
Fermentation Fermentation is an ancient mode of metabolism, and it
... and acetyl phosphate. As a fermentation pathway, it is employed mainly by the heterolactic acid bacteria, which include some species of Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc. In this pathway, glucose-phosphate is oxidized to 6-phosphogluconic acid, which becomes oxidized and decarboxylated to form pentose p ...
... and acetyl phosphate. As a fermentation pathway, it is employed mainly by the heterolactic acid bacteria, which include some species of Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc. In this pathway, glucose-phosphate is oxidized to 6-phosphogluconic acid, which becomes oxidized and decarboxylated to form pentose p ...
Active Transport Lab
... the consequences for amino acid transport. Similarly, you can alter the cellular (inside) or extracellular (outside of cells) levels of amino acids and investigate the effect on how cells use ATP. Because the amino acid transport channel is paired to the ATP-driven sodium/potassium pump, you will ho ...
... the consequences for amino acid transport. Similarly, you can alter the cellular (inside) or extracellular (outside of cells) levels of amino acids and investigate the effect on how cells use ATP. Because the amino acid transport channel is paired to the ATP-driven sodium/potassium pump, you will ho ...
L7c RESPIRATION Ch9 etc regulation
... build up of proton gradient just so H+ could flow through ATP synthase enzyme to build ATP ...
... build up of proton gradient just so H+ could flow through ATP synthase enzyme to build ATP ...
Cellular respiration 2
... After glycogen stores are used up the body begins to FAT break down ________ That’s why aerobic exercise must continue for longer than 20 minutes if you want to lose weight! Image from: http://blackmovie.us/movie/Fat.Albert/fat.albert.movie.jpg ...
... After glycogen stores are used up the body begins to FAT break down ________ That’s why aerobic exercise must continue for longer than 20 minutes if you want to lose weight! Image from: http://blackmovie.us/movie/Fat.Albert/fat.albert.movie.jpg ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.