Physical Models for Protein Folding and Drug Design
... Once the conformation of a protein is known, one can attempt at designing drugs to interact with the protein. Most of the targets of pharmaceutical drugs are enzymes, that is proteins whose task is to catalyze some reaction in the human body. Such drugs usually inhibit the associated enzyme by cappi ...
... Once the conformation of a protein is known, one can attempt at designing drugs to interact with the protein. Most of the targets of pharmaceutical drugs are enzymes, that is proteins whose task is to catalyze some reaction in the human body. Such drugs usually inhibit the associated enzyme by cappi ...
DOC
... food conversion (maximise protein deposition in the animal) and to maximise growth performance under culture conditions. Understanding the physiological basis of observed growth in terms of anabolic and catabolic processes will then enable informed decisions to be made on the modification of diets a ...
... food conversion (maximise protein deposition in the animal) and to maximise growth performance under culture conditions. Understanding the physiological basis of observed growth in terms of anabolic and catabolic processes will then enable informed decisions to be made on the modification of diets a ...
Role of Water soluble Vitamins in Food Industry
... The water-soluble vitamins, inactive in their so-called free states, must be activated to their coenzyme forms; addition of phosphate groups occurs in the activation of thiamin, riboflavin, and vitamin B6; a shift in structure activates biotin, and formation of a complex between the free vitamin and ...
... The water-soluble vitamins, inactive in their so-called free states, must be activated to their coenzyme forms; addition of phosphate groups occurs in the activation of thiamin, riboflavin, and vitamin B6; a shift in structure activates biotin, and formation of a complex between the free vitamin and ...
Glycolic Acid Labeling During Photosynthesis
... significant compared to the biosynthesis of glycolic acid from CO, one might expect a significantly higher ratio of tritium to :'C in glycolic acid than in other intermediates of the photosynthetic carbol redutction cycle, after a short period of photosynthesis with both tracers. Also, one would exp ...
... significant compared to the biosynthesis of glycolic acid from CO, one might expect a significantly higher ratio of tritium to :'C in glycolic acid than in other intermediates of the photosynthetic carbol redutction cycle, after a short period of photosynthesis with both tracers. Also, one would exp ...
Differential effects of heptanoate and hexanoate on myocardial citric
... adjusted to give interventricular venous oxygen saturation of 35– 45%. A continuous infusion of [U-14C]glucose (0.2 Ci/min) was initiated 30 min before ischemia into the proximal end of the coronary perfusion line at a rate of 0.1 ml/min. Regional myocardial ischemiareperfusion was induced in the L ...
... adjusted to give interventricular venous oxygen saturation of 35– 45%. A continuous infusion of [U-14C]glucose (0.2 Ci/min) was initiated 30 min before ischemia into the proximal end of the coronary perfusion line at a rate of 0.1 ml/min. Regional myocardial ischemiareperfusion was induced in the L ...
Kinetics - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Group complementation - the ability to recognize specific regions of the substrate to align reactants with catalytic site. Based on non-covalent molecular interactions. Lock and key vs. induced fit - both occur. Induced fit takes place when binding of one part of the substrate to the enzyme alters t ...
... Group complementation - the ability to recognize specific regions of the substrate to align reactants with catalytic site. Based on non-covalent molecular interactions. Lock and key vs. induced fit - both occur. Induced fit takes place when binding of one part of the substrate to the enzyme alters t ...
Predicting enzyme targets for cancer drugs by profiling
... different cells. This is the reaction representation method what we call reaction profiling. By this method, we can construct the flux similarity between the reactions and then further use the machine learning methods to analyze their properties in the metabolic network. A promising approach in drug ...
... different cells. This is the reaction representation method what we call reaction profiling. By this method, we can construct the flux similarity between the reactions and then further use the machine learning methods to analyze their properties in the metabolic network. A promising approach in drug ...
Control of cytoplasmic pH under anoxic
... pH and membrane potential. Since ion-selective microelectrodes pick up a mixed electrical signal, which consists of both the membrane potential difference and the free ion concentration, a separate microelectrode which measures the membrane potential, had to be inserted into the same cell. In some c ...
... pH and membrane potential. Since ion-selective microelectrodes pick up a mixed electrical signal, which consists of both the membrane potential difference and the free ion concentration, a separate microelectrode which measures the membrane potential, had to be inserted into the same cell. In some c ...
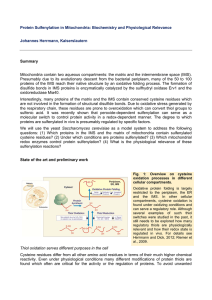
Protein Sulfenylation in Mitochondria: Biochemistry and
... In some cellular compartments such as in the bacterial periplasm, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the intermembrane space of mitochondria (IMS), dedicated machineries exist which introduce stable disulfide bonds into newly synthesized proteins. In this case, thiol oxidation can significantly cont ...
... In some cellular compartments such as in the bacterial periplasm, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the intermembrane space of mitochondria (IMS), dedicated machineries exist which introduce stable disulfide bonds into newly synthesized proteins. In this case, thiol oxidation can significantly cont ...
L2 - Aldehydes and Ketones
... carbonyl carbon is substituted with a hydroxyl forming a carboxyl group, creating a carboxylic acid. ...
... carbonyl carbon is substituted with a hydroxyl forming a carboxyl group, creating a carboxylic acid. ...
Analysis of structural robustness of metabolic
... and the directionality of reactions, which is available in many cases from the literature or on-line databases. A central concept in metabolic pathway analysis is that of elementary flux modes [18, 19]. An elementary mode is a minimal set of enzymes that can operate at steady state, such that all ir ...
... and the directionality of reactions, which is available in many cases from the literature or on-line databases. A central concept in metabolic pathway analysis is that of elementary flux modes [18, 19]. An elementary mode is a minimal set of enzymes that can operate at steady state, such that all ir ...
PURIFICATION OF TAP TAGGED YEAST PROTEINS Annika Väntänen
... efficient (only 16 ATP total yield from complete oxidation of glucose the yield is ...
... efficient (only 16 ATP total yield from complete oxidation of glucose the yield is ...
Protein structure
... During the translation of a gene into a protein, the protein is formed by the sequential joining of amino acids end-to-end to form a long chain-like molecule (polymer). A polymer of amino acids is often referred to as a polypeptide. The genome is capable of coding for 20 different amino acids whose ...
... During the translation of a gene into a protein, the protein is formed by the sequential joining of amino acids end-to-end to form a long chain-like molecule (polymer). A polymer of amino acids is often referred to as a polypeptide. The genome is capable of coding for 20 different amino acids whose ...
File S1 - G3: Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... Figure S4 Outline of sucrose to oil pathway in developing soybean seeds. This figure highlights the major enzymes and reactions in the pathway with some intermediates, enzymes, and transporters omitted for simplicity. Sucrose is transported into the cytosol via a sucrose transporter (not shown), an ...
... Figure S4 Outline of sucrose to oil pathway in developing soybean seeds. This figure highlights the major enzymes and reactions in the pathway with some intermediates, enzymes, and transporters omitted for simplicity. Sucrose is transported into the cytosol via a sucrose transporter (not shown), an ...
Slide 1
... • Carbohydrate attached to a lipid • Some are glycerol based, but most are sphingosine based • Glycosphingolipids • Cerebrosides • Gangliosides ...
... • Carbohydrate attached to a lipid • Some are glycerol based, but most are sphingosine based • Glycosphingolipids • Cerebrosides • Gangliosides ...
Uric acid estimation in plasma
... Salvage pathways collect hypoxanthine and guanine and recombine them with PRPP to form nucleotides in the HGPRT reaction Absence of HGPRT is cause of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome This increase may be due to PRPP feed-forward activation of de novo pathways the rate of purine synthesis is increased about 200X ...
... Salvage pathways collect hypoxanthine and guanine and recombine them with PRPP to form nucleotides in the HGPRT reaction Absence of HGPRT is cause of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome This increase may be due to PRPP feed-forward activation of de novo pathways the rate of purine synthesis is increased about 200X ...
LESSON 11. СOMMUNICATION BETWEEN CELLS. MECHANISM
... Function. The Gα subunit of all G proteins is a GTPase. It slowly hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP and thereby returns to its inactive, GDP-bound state. Gα then reassociates with Gβγ where it remains until it is reactivated by a hormone-receptor complex. G-protein-linked receptors. There are more tha ...
... Function. The Gα subunit of all G proteins is a GTPase. It slowly hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP and thereby returns to its inactive, GDP-bound state. Gα then reassociates with Gβγ where it remains until it is reactivated by a hormone-receptor complex. G-protein-linked receptors. There are more tha ...
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture
... substitutes for cereals in gluten-free diets.2 Furthermore, pseudocereals contain relatively high amounts of dietary ®bre, which improves lipid metabolism and takes part in the prevention of LDL-C oxidation.3,4 After processing, these plants can be used as ¯ours or ¯akes or in biscuits and breakfast ...
... substitutes for cereals in gluten-free diets.2 Furthermore, pseudocereals contain relatively high amounts of dietary ®bre, which improves lipid metabolism and takes part in the prevention of LDL-C oxidation.3,4 After processing, these plants can be used as ¯ours or ¯akes or in biscuits and breakfast ...
End-product control of enzymes of branched
... isoleucine-valine pathway, the combination of all three amino acids gave in individual experiments activities 0.12-0.19 of those with no supplementation, the ratio of the means being 0.16. Supplementation with threonine, or with leucine, isoleucine or valine singly or in pairwise combinations, gave ...
... isoleucine-valine pathway, the combination of all three amino acids gave in individual experiments activities 0.12-0.19 of those with no supplementation, the ratio of the means being 0.16. Supplementation with threonine, or with leucine, isoleucine or valine singly or in pairwise combinations, gave ...
GEN III MicroPlateTM
... Chocolate Agar with 6.5% CO2. Some very oxygen-sensitive Gram-positive bacteria also require the higher inoculation density of Protocol C2. See Table 1 below for a list. ...
... Chocolate Agar with 6.5% CO2. Some very oxygen-sensitive Gram-positive bacteria also require the higher inoculation density of Protocol C2. See Table 1 below for a list. ...
09_Lecture
... • A chemical equilibrium is established when forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate. • The equilibrium constant, K, defines the extent of a chemical reaction as a ratio of the concentration of the products to the concentration of the reactants. • If a chemical reaction at equilibrium i ...
... • A chemical equilibrium is established when forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate. • The equilibrium constant, K, defines the extent of a chemical reaction as a ratio of the concentration of the products to the concentration of the reactants. • If a chemical reaction at equilibrium i ...
Oxygen Radicals and Related Species
... of Reactive Species Long before the formation of molecules and ions was conceptualized by quantum mechanics, the discoverers of molecular oxygen in the late 18th century - Priestley, Scheele and Lavoisier - reported its beneficial and toxic effects on living organisms. These opposing effects result ...
... of Reactive Species Long before the formation of molecules and ions was conceptualized by quantum mechanics, the discoverers of molecular oxygen in the late 18th century - Priestley, Scheele and Lavoisier - reported its beneficial and toxic effects on living organisms. These opposing effects result ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.