
1 Organic Chemistry V : Enzyme Mechanisms and Natural Product
... In D2O, D is rapidly incorporated into the aldehyde (faster than the aldol reaction). In summary: • HO- is the catalyst • the rate depends on pH • often means a rate-determining reaction of a deprotonated species • usually only simple uni- or bi-molecular steps Specific acid and specific base cataly ...
... In D2O, D is rapidly incorporated into the aldehyde (faster than the aldol reaction). In summary: • HO- is the catalyst • the rate depends on pH • often means a rate-determining reaction of a deprotonated species • usually only simple uni- or bi-molecular steps Specific acid and specific base cataly ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 23: ACID BASE BALANCE I
... H+ in the tubular system is buffered before it is excreted. First it combines with the filtered HCO3- in the tubular system to produce water until all HCO3- is used up. Next the H+ combines with filtered phosphate in the tubules and the H2PO4- so produced is ...
... H+ in the tubular system is buffered before it is excreted. First it combines with the filtered HCO3- in the tubular system to produce water until all HCO3- is used up. Next the H+ combines with filtered phosphate in the tubules and the H2PO4- so produced is ...
Chemistry
... carbocations, carbanions, free radicals, carbenes and their stability and shape (with examples). b) Organic Stereochemistry-I Concepts of types of isomerism—Configuration and conformation isomerism. Fischer, Newman and Sawhorse projection formula with suitable examples ; geometrical isomerism, confi ...
... carbocations, carbanions, free radicals, carbenes and their stability and shape (with examples). b) Organic Stereochemistry-I Concepts of types of isomerism—Configuration and conformation isomerism. Fischer, Newman and Sawhorse projection formula with suitable examples ; geometrical isomerism, confi ...
Integration and Control - Academic Resources at Missouri Western
... Cytokinins • “Crown Gall” – a neoplasic growth due to infection by Agrobacterium tumifaciens. – A. tumifaciens carries the genes for production of cytokinin and auxins on a plasmid. Plasmid genes become a part of host cell genome. ...
... Cytokinins • “Crown Gall” – a neoplasic growth due to infection by Agrobacterium tumifaciens. – A. tumifaciens carries the genes for production of cytokinin and auxins on a plasmid. Plasmid genes become a part of host cell genome. ...
Slide 1
... - monomer = monosaccharide (simple sugar) CnH2nOn glucose, galactose, fructose are hexose sugars ribose, ribulose, deoxyribose are pentose sugars - monomers are linked together into polymers using dehydration synthesis - a removal of a water molecule (dehydration) and the synthesis of a bond. This r ...
... - monomer = monosaccharide (simple sugar) CnH2nOn glucose, galactose, fructose are hexose sugars ribose, ribulose, deoxyribose are pentose sugars - monomers are linked together into polymers using dehydration synthesis - a removal of a water molecule (dehydration) and the synthesis of a bond. This r ...
UDP-GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASES OF PLANT HORMONES
... Brassinosteroids, the plant steroid hormones, attach glucose residues through a hydroxyl group in position 23 (fig. 4) [38]. In tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana the modification is catalysed by the UDP-glycosyltransferase, UGT73C5 and its homologue, UGT73C6 [8, 32]. Apart from brassinolide (BL), the ...
... Brassinosteroids, the plant steroid hormones, attach glucose residues through a hydroxyl group in position 23 (fig. 4) [38]. In tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana the modification is catalysed by the UDP-glycosyltransferase, UGT73C5 and its homologue, UGT73C6 [8, 32]. Apart from brassinolide (BL), the ...
Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics
... pyrophosphate as its coenzyme while carbonic anhydrase uses zinc ion as its cofactor. ...
... pyrophosphate as its coenzyme while carbonic anhydrase uses zinc ion as its cofactor. ...
Mechanism of Translation
... 4. How are the termination codons different from other codons? A) They contain thymines. B) The termination codon always codes for methionine. C) They are not recognized by any tRNA molecules. D) Their conformations do not allow them to fit properly in the A site of the ribosome. ...
... 4. How are the termination codons different from other codons? A) They contain thymines. B) The termination codon always codes for methionine. C) They are not recognized by any tRNA molecules. D) Their conformations do not allow them to fit properly in the A site of the ribosome. ...
Benefits of Humus - Sea-90
... As stated in the previous slide, Humic acids have a definable molecular structure of which a fragment is illustrated below. The Humic acids of soil are a product of soil chemistry of which the precursor to humus formation is protein. The Humic acids are not organic matter in the true since as they h ...
... As stated in the previous slide, Humic acids have a definable molecular structure of which a fragment is illustrated below. The Humic acids of soil are a product of soil chemistry of which the precursor to humus formation is protein. The Humic acids are not organic matter in the true since as they h ...
5. CHAPTER XI PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... • Next is the regeneration of the beginning substrate, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. It is known as the photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle, or Calvin cycle. • A totally new molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate can be spun off with every three revolutions of the cycle. • The new glyceraldehyde 3-ph ...
... • Next is the regeneration of the beginning substrate, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. It is known as the photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle, or Calvin cycle. • A totally new molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate can be spun off with every three revolutions of the cycle. • The new glyceraldehyde 3-ph ...
Duchenne muscular dystrophy:
... described [21]. The patients’ characteristics are given in table II. It appears from figure 2 that only irreversible leucine oxidation was higher in the DMD group; however, neither the whole body leucine turnover rate nor the non-oxidative leucine disposal, an index of whole body protein synthesis, ...
... described [21]. The patients’ characteristics are given in table II. It appears from figure 2 that only irreversible leucine oxidation was higher in the DMD group; however, neither the whole body leucine turnover rate nor the non-oxidative leucine disposal, an index of whole body protein synthesis, ...
Dehydrogenase Complexes of Corn (Zea mays L.) and Soybean
... CoA, and NAD+ were 120.4, 3.8, and 16.0 .M. respectively (Table II). Haloxyfop inhibited corn etioplast PDC as an uncompetitive inhibitor with respect to pyruvate, and as a noncompetitive inhibitor with respect to CoA and NAD +. The Ki values of haloxyfop for pyruvate, CoA, and NAD+ were 10.5, 2.1 a ...
... CoA, and NAD+ were 120.4, 3.8, and 16.0 .M. respectively (Table II). Haloxyfop inhibited corn etioplast PDC as an uncompetitive inhibitor with respect to pyruvate, and as a noncompetitive inhibitor with respect to CoA and NAD +. The Ki values of haloxyfop for pyruvate, CoA, and NAD+ were 10.5, 2.1 a ...
Biological Science, 5e (Freeman) Chapter 3 Protein Structure and
... techniques in existence today is X-ray crystallography. The main difficulty with this technique is getting the protein to crystallize. Once crystallized, the protein is bombarded with X-rays to create a pattern that can be analyzed mathematically to determine the three-dimensional structure of the p ...
... techniques in existence today is X-ray crystallography. The main difficulty with this technique is getting the protein to crystallize. Once crystallized, the protein is bombarded with X-rays to create a pattern that can be analyzed mathematically to determine the three-dimensional structure of the p ...
1.1 Functional Groups of Biomolecules and their Reactions
... functional groups reactivity. For instance, alcohols, ethers, amines, thiols, sulfides, disulfides and phosphates (Table 1.1.1) all have a carbon forming a single bond with a more electronegative atom, causing the carbon to bear a partial positive charge (δ+). These modifications affect both the σ- ...
... functional groups reactivity. For instance, alcohols, ethers, amines, thiols, sulfides, disulfides and phosphates (Table 1.1.1) all have a carbon forming a single bond with a more electronegative atom, causing the carbon to bear a partial positive charge (δ+). These modifications affect both the σ- ...
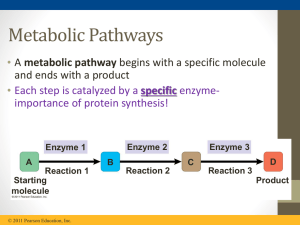
Document
... • A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product • Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzymeimportance of protein synthesis! ...
... • A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product • Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzymeimportance of protein synthesis! ...
CHEM 331 Problem Set #6
... assay for total blood glucose—that is, for solutions consisting of a mixture of β- and α-D-glucose. What are the circumstances required to make this possible? Aside from allowing the detection of smaller quantities of glucose, what advantage does glucose oxidase offer over Fehling’s reagent for the ...
... assay for total blood glucose—that is, for solutions consisting of a mixture of β- and α-D-glucose. What are the circumstances required to make this possible? Aside from allowing the detection of smaller quantities of glucose, what advantage does glucose oxidase offer over Fehling’s reagent for the ...
[Step 5] New Module Template 2009
... to exist on other planets. For example, Mars may have regions in its deep subsurface permafrost that could harbor endolith communities. The subsurface water ocean of Jupiter's moon Europa may harbor life, especially at hypothesized hydrothermal vents at the ocean ...
... to exist on other planets. For example, Mars may have regions in its deep subsurface permafrost that could harbor endolith communities. The subsurface water ocean of Jupiter's moon Europa may harbor life, especially at hypothesized hydrothermal vents at the ocean ...
Chapter 10 Enzymes - Angelo State University
... • The cell controls the rates of these reactions and the amount of any given product formed by regulating the action of the enzymes. ...
... • The cell controls the rates of these reactions and the amount of any given product formed by regulating the action of the enzymes. ...
COLOUR REACTIONS IN CHROMATOGRAPHY Fifteen location
... systems are used. The ninhydrin test requires a pH of approx. 5. Staining: Spray the strip and air-dry it in the dark at room temperature or at 60” for 30 min, or at 100’ for IO min. Drying slowly at room temperature is preferable for better separation of the spots. Some investigators avoid developm ...
... systems are used. The ninhydrin test requires a pH of approx. 5. Staining: Spray the strip and air-dry it in the dark at room temperature or at 60” for 30 min, or at 100’ for IO min. Drying slowly at room temperature is preferable for better separation of the spots. Some investigators avoid developm ...
Non-protein Nitrogen Compounds
... nitrogenous substances in the blood has traditionally been used to monitor renal function. Nitrogen containing compounds that are not proteins or polypeptides Useful clinical information is obtained from individual components of NPN fraction ...
... nitrogenous substances in the blood has traditionally been used to monitor renal function. Nitrogen containing compounds that are not proteins or polypeptides Useful clinical information is obtained from individual components of NPN fraction ...
Molecular Docking Studies of Isorhamnetin from Corchorus olitorius
... of insulin action [5, 13]. Patients suffering from type II diabetes are insulin-resistant. There are several mechanisms employed in the treatment of type II diabetes, these vary from changes in life-styles, exercises, insulin injections, and various anti-diabetic drugs. However, the management of th ...
... of insulin action [5, 13]. Patients suffering from type II diabetes are insulin-resistant. There are several mechanisms employed in the treatment of type II diabetes, these vary from changes in life-styles, exercises, insulin injections, and various anti-diabetic drugs. However, the management of th ...
DOC
... food conversion (maximise protein deposition in the animal) and to maximise growth performance under culture conditions. Understanding the physiological basis of observed growth in terms of anabolic and catabolic processes will then enable informed decisions to be made on the modification of diets a ...
... food conversion (maximise protein deposition in the animal) and to maximise growth performance under culture conditions. Understanding the physiological basis of observed growth in terms of anabolic and catabolic processes will then enable informed decisions to be made on the modification of diets a ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.

















![[Step 5] New Module Template 2009](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010026309_1-64025ceac588c710d9d2a78f0d1bf9df-300x300.png)




