Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... • Simple: Hydrolyzed to amino acids only • Conjugated: Bonded to a nonprotein group, such as sugar, nucleic acid, or lipid • Fibrous: Long, stringy filaments, insoluble in water; function as structure • Globular: Folded into spherical shape; function as enzymes, hormones, or transport proteins ...
... • Simple: Hydrolyzed to amino acids only • Conjugated: Bonded to a nonprotein group, such as sugar, nucleic acid, or lipid • Fibrous: Long, stringy filaments, insoluble in water; function as structure • Globular: Folded into spherical shape; function as enzymes, hormones, or transport proteins ...
Ch. 03 The Molecules of Life
... : The attraction forces between water molecules and the slight tendency to ionize are of crucial importance to the structure and function of biomolecules . Several emergent properties arise. ...
... : The attraction forces between water molecules and the slight tendency to ionize are of crucial importance to the structure and function of biomolecules . Several emergent properties arise. ...
the Acetyl-Coenzyme A
... genes of Aspergillus nidulans and Neurospora crassa has been cloned, sequenced and mapped to chromosome I. It contains an open reading frame of 2139 nucleotides, encoding a predicted gene product of 79.2 kDa. In contrast to its ascomycete homologs, there are no introns in the coding sequence. The fi ...
... genes of Aspergillus nidulans and Neurospora crassa has been cloned, sequenced and mapped to chromosome I. It contains an open reading frame of 2139 nucleotides, encoding a predicted gene product of 79.2 kDa. In contrast to its ascomycete homologs, there are no introns in the coding sequence. The fi ...
Characterization of new proteins found by analysis
... biologically characterized. Some of these are likely to be true proteins, i.e., ORFs actually transcribed and translated by the cell. For longer lengths (e.g. more than 500 amino acids) fortuitous ORFs are very unlikely and we can assume that the entire light-shaded bar at these lengths corresponds ...
... biologically characterized. Some of these are likely to be true proteins, i.e., ORFs actually transcribed and translated by the cell. For longer lengths (e.g. more than 500 amino acids) fortuitous ORFs are very unlikely and we can assume that the entire light-shaded bar at these lengths corresponds ...
10 Translocation in the Phloem Chapter
... between the two cells. The plasmodesmata are often complex and branched on the companion cell side. Companion cells play a role in the transport of photosynthetic products from producing cells in mature leaves to the sieve elements in the minor (small) veins of the leaf. They are also thought to tak ...
... between the two cells. The plasmodesmata are often complex and branched on the companion cell side. Companion cells play a role in the transport of photosynthetic products from producing cells in mature leaves to the sieve elements in the minor (small) veins of the leaf. They are also thought to tak ...
MS - Past Papers.org
... so that a (valid) comparison can be made / water is an (uncontrolled) variable; ...
... so that a (valid) comparison can be made / water is an (uncontrolled) variable; ...
Chapter 15
... must have part of its polypeptide chain hydrolyzed and removed before it becomes active. • An example is trypsin, a digestive enzyme. • It is synthesized and stored as trypsinogen, which has no enzyme activity. • It becomes active only after a six-amino acid fragment is hydrolyzed and removed from t ...
... must have part of its polypeptide chain hydrolyzed and removed before it becomes active. • An example is trypsin, a digestive enzyme. • It is synthesized and stored as trypsinogen, which has no enzyme activity. • It becomes active only after a six-amino acid fragment is hydrolyzed and removed from t ...
Chemical of Life
... Be able to name and briefly describe each of the 4 classes of biological macromolecules described in class. ...
... Be able to name and briefly describe each of the 4 classes of biological macromolecules described in class. ...
Slides
... Increases the rate of chemical reaction / biological process Remains unchanged Biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions Usually proteins ...
... Increases the rate of chemical reaction / biological process Remains unchanged Biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions Usually proteins ...
Biosynthesis of lipoxygenase, lipids and its fatty acid composition of
... V. Rudic, N. Popova, A. Crivova, S. Boortseva, I. Rastimeshina Institute of Microbiology, Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Moldova 1 Academiei Str., Chishinau, MD 2028, Republic of Moldova. ...
... V. Rudic, N. Popova, A. Crivova, S. Boortseva, I. Rastimeshina Institute of Microbiology, Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Moldova 1 Academiei Str., Chishinau, MD 2028, Republic of Moldova. ...
Post Exercise Carbohydrates May Be Counter
... muscular, first of all through the small amounts of carbs that are part of the MRP LoCarb, and more importantly through the gluconeogenic process in which the body forms only the carbs it needs by making glucose mainly from fats (the glycerol portion) and protein (various glucogenic amino acids). Th ...
... muscular, first of all through the small amounts of carbs that are part of the MRP LoCarb, and more importantly through the gluconeogenic process in which the body forms only the carbs it needs by making glucose mainly from fats (the glycerol portion) and protein (various glucogenic amino acids). Th ...
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... cinnamic and salicyclic acids (Babu & Wu, 2008 ; Osofrejova et al., 2010). The occurrence of phenols in land plants is universal. Important phenolic compounds have been identified in vascular plants, such as, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms (Canachan et al., 2000). Hypogallic and caffeic ...
... cinnamic and salicyclic acids (Babu & Wu, 2008 ; Osofrejova et al., 2010). The occurrence of phenols in land plants is universal. Important phenolic compounds have been identified in vascular plants, such as, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms (Canachan et al., 2000). Hypogallic and caffeic ...
Influence of the Side Chain in the Structure and Fragmentation of
... Amino acids usually present intramolecular hydrogen bonds which are crucial to understand their structure and reactivity. However, these hydrogen bonds can be largely modified upon ionization. Previous studies have shown that removing an electron from such a system modifies both the acidity and the ...
... Amino acids usually present intramolecular hydrogen bonds which are crucial to understand their structure and reactivity. However, these hydrogen bonds can be largely modified upon ionization. Previous studies have shown that removing an electron from such a system modifies both the acidity and the ...
Document
... • Energy exists in different forms but is neither created nor destroyed; it simply converts to another form. ...
... • Energy exists in different forms but is neither created nor destroyed; it simply converts to another form. ...
in Graminaceous Plants
... Nicotianamine aminotransferase (NAAT), the key enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of mugineic acid family phytosiderophores (MAs), catalyzes the amino transfer of nicotianamine (NA). MAs are found only in graminaceous plants, although NA has been detected in every plant so far investigated. Therefo ...
... Nicotianamine aminotransferase (NAAT), the key enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of mugineic acid family phytosiderophores (MAs), catalyzes the amino transfer of nicotianamine (NA). MAs are found only in graminaceous plants, although NA has been detected in every plant so far investigated. Therefo ...
A Comparative Genomic Method for Computational
... Availability of complete genomes of related bacteria allows comparative analysis of regulatory patterns (gene number, content, and order in groups of organisms) Conservation of candidate DnaA binding sites across species is additional evidence of regulatory functionality If a regulator is conserved ...
... Availability of complete genomes of related bacteria allows comparative analysis of regulatory patterns (gene number, content, and order in groups of organisms) Conservation of candidate DnaA binding sites across species is additional evidence of regulatory functionality If a regulator is conserved ...
levels_organiz_ch2
... • Activation energy is the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction • Enzymes are catalysts • Reduce energy of activation without being permanently changed or used up • Promote chemical reactions ...
... • Activation energy is the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction • Enzymes are catalysts • Reduce energy of activation without being permanently changed or used up • Promote chemical reactions ...
Isolation and Characterization of Plastidic Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
... plastids from oilseed rape embryos by the dependence of starch synthesis on exogenous ATP (Flugge, 1998). Pyruvate has been shown to be one of the most effective substrates for fatty acid synthesis by the plastids giving a rate five times better than acetate in castor bean endosperm and mustard coty ...
... plastids from oilseed rape embryos by the dependence of starch synthesis on exogenous ATP (Flugge, 1998). Pyruvate has been shown to be one of the most effective substrates for fatty acid synthesis by the plastids giving a rate five times better than acetate in castor bean endosperm and mustard coty ...
S2 Table: Contribution of different substrates to respiration of
... muscle of A. aegypti males. Values were expressed as mean ± SD of nmol oxygen consumed/min/mg protein with the following substrates: 10 mM pyruvate + 10 mM proline (Pyr+Pro), 20 mM sn glycerol-3 phosphate (G3P) or 10 µM palmitoylcarnitine + 5 mM malate (PC+Mal). Addition of OXPHOS modulators were in ...
... muscle of A. aegypti males. Values were expressed as mean ± SD of nmol oxygen consumed/min/mg protein with the following substrates: 10 mM pyruvate + 10 mM proline (Pyr+Pro), 20 mM sn glycerol-3 phosphate (G3P) or 10 µM palmitoylcarnitine + 5 mM malate (PC+Mal). Addition of OXPHOS modulators were in ...
Redox Reactions - Hillsborough County Public Schools
... H is always +1 (except when attached to more electronegative metals, Li, Na, Ca, and Al 7. Group 1A, 2A, and 3A always have an oxidation number equal to the group number (equal to the charge it would have if it were a ion with noble gas ...
... H is always +1 (except when attached to more electronegative metals, Li, Na, Ca, and Al 7. Group 1A, 2A, and 3A always have an oxidation number equal to the group number (equal to the charge it would have if it were a ion with noble gas ...
Enter Topic Title in each section above
... Q. Explain the role of ADP in relation to the small amount of energy released during the first stage of Q. For what is ATP an abbreviation? respiration. A. First stage uses energy, combines with phosphate, to form ATP. ATP stores energy in high energy bond Q. What is the first stage process of respi ...
... Q. Explain the role of ADP in relation to the small amount of energy released during the first stage of Q. For what is ATP an abbreviation? respiration. A. First stage uses energy, combines with phosphate, to form ATP. ATP stores energy in high energy bond Q. What is the first stage process of respi ...
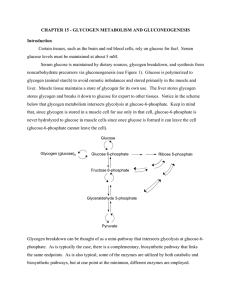
CHAPTER 15 - GLYCOGEN METABOLISM AND
... Certain tissues, such as the brain and red blood cells, rely on glucose for fuel. Serum glucose levels must be maintained at about 5 mM. Serum glucose is maintained by dietary sources, glycogen breakdown, and synthesis from noncarbohydrate precursors via gluconeogenesis (see Figure 1). Glucose is po ...
... Certain tissues, such as the brain and red blood cells, rely on glucose for fuel. Serum glucose levels must be maintained at about 5 mM. Serum glucose is maintained by dietary sources, glycogen breakdown, and synthesis from noncarbohydrate precursors via gluconeogenesis (see Figure 1). Glucose is po ...
CONTENTS
... Aleeva S.V., Koksharov S.A. FEATURES OF BIOCHEMICAL MACERATION OF DOMESTIC AND IMPORT LINEN RAW: CONTRASTIVE ANALYSIS OF CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF PECTIN The chemical state analysis of carboxyl groups in structural links of polyuronide compounds for four kinds of a linen fibre of domestic (Kaluga, Volog ...
... Aleeva S.V., Koksharov S.A. FEATURES OF BIOCHEMICAL MACERATION OF DOMESTIC AND IMPORT LINEN RAW: CONTRASTIVE ANALYSIS OF CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF PECTIN The chemical state analysis of carboxyl groups in structural links of polyuronide compounds for four kinds of a linen fibre of domestic (Kaluga, Volog ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.