Chemistry - Birkenhead School
... Visualise and represent 2D and 3D forms including two dimensional representations of 3D objects. Content Opportunities for skills development Students should be able to: draw dot and cross diagrams for the molecules H2, Cl2, O2, N2, HCl, H2O, NH3 and CH4 represent the covalent bonds in small mol ...
... Visualise and represent 2D and 3D forms including two dimensional representations of 3D objects. Content Opportunities for skills development Students should be able to: draw dot and cross diagrams for the molecules H2, Cl2, O2, N2, HCl, H2O, NH3 and CH4 represent the covalent bonds in small mol ...
In vivo analysis of straight-chain and branched
... can be formed from the condensation of two acetate molecules [22]. This process, which may be responsible for providing the majority of butyryl-CoA for palmitoyl-CoA biosynthesis, has not been investigated in streptomycetes. In mammalian mammary glands [23] and Euglena gracilis [a], butyryl-CoA used ...
... can be formed from the condensation of two acetate molecules [22]. This process, which may be responsible for providing the majority of butyryl-CoA for palmitoyl-CoA biosynthesis, has not been investigated in streptomycetes. In mammalian mammary glands [23] and Euglena gracilis [a], butyryl-CoA used ...
Immunohistochemical localization of fatty acid transporters and
... sites and have been termed “free” or “ectopic” glands, as represented by the meibomian glands and preputial glands. Fatty acids can be synthesized de novo by an enzyme fatty acid synthase, which is strongly expressed in sebaceous glands as well as the epidermis (21). Some of them—essential fatty aci ...
... sites and have been termed “free” or “ectopic” glands, as represented by the meibomian glands and preputial glands. Fatty acids can be synthesized de novo by an enzyme fatty acid synthase, which is strongly expressed in sebaceous glands as well as the epidermis (21). Some of them—essential fatty aci ...
Lab 5 Sugar Fermentation in Yeast
... alcoholic beverages. Yeast is able to metabolize some foods, but not others. In order for an organism to make use of a potential source of food, it must be capable of transporting the food into its cells. It must also have the proper enzymes capable of breaking the food’s chemical bonds in a useful ...
... alcoholic beverages. Yeast is able to metabolize some foods, but not others. In order for an organism to make use of a potential source of food, it must be capable of transporting the food into its cells. It must also have the proper enzymes capable of breaking the food’s chemical bonds in a useful ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... Glucose‐1‐P formed by phosphorolytic cleavage of glycogen is converted into glucose‐6‐P by Phosphoglucomutase Glucose 6‐phosphate derived from glycogen can be: Used as a fuel for anaerobic or aerobic metabolism as in, for instance, muscle; Converted into free glucose in the liver and subsequ ...
... Glucose‐1‐P formed by phosphorolytic cleavage of glycogen is converted into glucose‐6‐P by Phosphoglucomutase Glucose 6‐phosphate derived from glycogen can be: Used as a fuel for anaerobic or aerobic metabolism as in, for instance, muscle; Converted into free glucose in the liver and subsequ ...
The Body`s Building Blocks
... whole. They are broken down into individual amino acids and dipeptides (two amino acids hooked together), which are then absorbed through the wall of the small intestine. After passing into the bloodstream, the small components travel to body sites where they are needed, and are reassembled into spe ...
... whole. They are broken down into individual amino acids and dipeptides (two amino acids hooked together), which are then absorbed through the wall of the small intestine. After passing into the bloodstream, the small components travel to body sites where they are needed, and are reassembled into spe ...
- Wiley Online Library
... achieved through the spatial separation of dark and light reactions, either intracellularly, as found in single-cell C4 species, or intercellularly. In single-cell C4, intracellular compartmentalization of enzymatic activities enables a twostep carbon fixation process where the initial carboxylation ...
... achieved through the spatial separation of dark and light reactions, either intracellularly, as found in single-cell C4 species, or intercellularly. In single-cell C4, intracellular compartmentalization of enzymatic activities enables a twostep carbon fixation process where the initial carboxylation ...
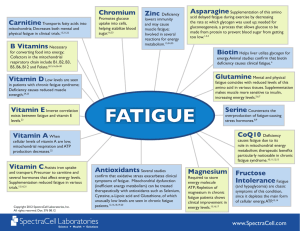
V I T A M Í N Y
... production. It is linked to cancer immunity and helps fight the formation of homocysteine. Helps children with learning difficulties, may prevent dandruff, eczema, and psoriasis. Helps balance hormonal changes in women. ...
... production. It is linked to cancer immunity and helps fight the formation of homocysteine. Helps children with learning difficulties, may prevent dandruff, eczema, and psoriasis. Helps balance hormonal changes in women. ...
CM22555559
... cases1 to 4.Bagging is used also in the sensitivity analysis procedure. A ROC curve depicts the performance of a classifier without regard to class distribution or error costs. They plot the number of positives included in the samples on the vertical axis, expressed as a percentage of the total numb ...
... cases1 to 4.Bagging is used also in the sensitivity analysis procedure. A ROC curve depicts the performance of a classifier without regard to class distribution or error costs. They plot the number of positives included in the samples on the vertical axis, expressed as a percentage of the total numb ...
Meteoritic Amino Acids: Diversity in Compositions Reflects Parent
... chondrites vary greatly with class and petrographic type. Structural distributions are shown as relative abundances of isomers of C5 amino acids, normalized to the total number of possible isomers (i.e., random selection of amine position during formation should produce 25% each of α, β, γ, and δ is ...
... chondrites vary greatly with class and petrographic type. Structural distributions are shown as relative abundances of isomers of C5 amino acids, normalized to the total number of possible isomers (i.e., random selection of amine position during formation should produce 25% each of α, β, γ, and δ is ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition Glycolysis Lectures
... •Be aware that other sugars can enter the glycolysis pathway ...
... •Be aware that other sugars can enter the glycolysis pathway ...
Document
... By contrast to what we would expect on the basis of our comparison of nectary gland anatomy and sugar/amino acid ratios of nectar, BAKER and BAKER (1973 a, b, 1975, 1976) argue that there is a trend for evolution towards higher amino acid contents. These authors investigated various classes of polli ...
... By contrast to what we would expect on the basis of our comparison of nectary gland anatomy and sugar/amino acid ratios of nectar, BAKER and BAKER (1973 a, b, 1975, 1976) argue that there is a trend for evolution towards higher amino acid contents. These authors investigated various classes of polli ...
A Search for Peptide Ligase: Cosolvent
... kinetic approach, however, requires the use of an ester as an acyl donor and is limited to those enzymes forming an acyl-enzyme intermediate. The hydrolyses of esters and amides catalyzed by such proteases are similar in mechanism but different in ratedetermining steps.1° Formation of acyl-intermedi ...
... kinetic approach, however, requires the use of an ester as an acyl donor and is limited to those enzymes forming an acyl-enzyme intermediate. The hydrolyses of esters and amides catalyzed by such proteases are similar in mechanism but different in ratedetermining steps.1° Formation of acyl-intermedi ...
red algae
... •Pectin is also used in throat lozenges as a demulcent. In cosmetic products, pectin acts as stabilizer. Pectin is also used in wound healing preparations and specialty medical adhesives, such as colostomy devices •Pectin is not digested, and is considered a beneficial dietary fiber. In human digest ...
... •Pectin is also used in throat lozenges as a demulcent. In cosmetic products, pectin acts as stabilizer. Pectin is also used in wound healing preparations and specialty medical adhesives, such as colostomy devices •Pectin is not digested, and is considered a beneficial dietary fiber. In human digest ...
BE100a - Interchim
... and effetcs (oxidative damages). It is hence the first part of catabolism, contrasting to anabolism processes that use the chemical energy to build molecules such as tissues and organs. Aerobic cellular respiration, a process requiring the use of oxygen, is the most efficient form of ATP production. ...
... and effetcs (oxidative damages). It is hence the first part of catabolism, contrasting to anabolism processes that use the chemical energy to build molecules such as tissues and organs. Aerobic cellular respiration, a process requiring the use of oxygen, is the most efficient form of ATP production. ...
File
... matter as much. Proteins do not exist as a string of amino acids, but must fold into a 3 dimensional (3D) shape to function. These folded proteins exist in a water environment. Proteins fold based on the chemical characteristics of their amino acids. The 3D shape is very important for each protein t ...
... matter as much. Proteins do not exist as a string of amino acids, but must fold into a 3 dimensional (3D) shape to function. These folded proteins exist in a water environment. Proteins fold based on the chemical characteristics of their amino acids. The 3D shape is very important for each protein t ...
How will Hemoglobin Affect the Winner of this Year`s Super Bowl
... matter as much. Proteins do not exist as a string of amino acids, but must fold into a 3 dimensional (3D) shape to function. These folded proteins exist in a water environment. Proteins fold based on the chemical characteristics of their amino acids. The 3D shape is very important for each protein t ...
... matter as much. Proteins do not exist as a string of amino acids, but must fold into a 3 dimensional (3D) shape to function. These folded proteins exist in a water environment. Proteins fold based on the chemical characteristics of their amino acids. The 3D shape is very important for each protein t ...
... Amino acid 2. Only the protonated form of histidine can participate acid in protein in electrostatic interactions, therefore any effects Energy HA A A HA on the deprotonated form can be ignored. 3. The negative charge on the aspartic acid residue will stabilize the + charge on the histidine side cha ...
Vitamins
... It affects especially the brain, because TPP is required for CHO metabolism, and the brain depends on glucose metabolism for energy. ...
... It affects especially the brain, because TPP is required for CHO metabolism, and the brain depends on glucose metabolism for energy. ...
Alignments
... Pairwise alignment result of human beta globin and myoglobin: the score is a sum of match, mismatch, gap creation, and gap extension scores ...
... Pairwise alignment result of human beta globin and myoglobin: the score is a sum of match, mismatch, gap creation, and gap extension scores ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.