Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... During fasting or starvation, when carbohydrate intake is too low, oxaloacetate levels fall so that flux through citrate synthase is impaired, causing acetyl-CoA levels to rise. ...
... During fasting or starvation, when carbohydrate intake is too low, oxaloacetate levels fall so that flux through citrate synthase is impaired, causing acetyl-CoA levels to rise. ...
Metabolism in Nematode Feeding Sites
... was enhanced in INV mutants, which in turn better supported the development of nematodes. The authors therefore concluded that the alteration of INVs and SUSs expression led to local and systemic changes in sugar processing and allocation, in the sourceesink relationship, and in the availability of ...
... was enhanced in INV mutants, which in turn better supported the development of nematodes. The authors therefore concluded that the alteration of INVs and SUSs expression led to local and systemic changes in sugar processing and allocation, in the sourceesink relationship, and in the availability of ...
Growing Membranes, Sustaining Cells
... cells. (A) The synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis) in liver cells depends on three metabolic compartments: the cytoplasm, mitochondrial matrix, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen. Three key kinases in glycolysis—hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase—catalyze nonreversible reactio ...
... cells. (A) The synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis) in liver cells depends on three metabolic compartments: the cytoplasm, mitochondrial matrix, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen. Three key kinases in glycolysis—hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase—catalyze nonreversible reactio ...
As a PDF file
... 1.2. Glycolysis (Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) In glycolysis (Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway), under normal conditions where sugars are not limiting and oxygen is confined, one glucose molecule is theoretically fermented to two lactic acid molecules resulting in a net gain of two molecules of ATP ...
... 1.2. Glycolysis (Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) In glycolysis (Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway), under normal conditions where sugars are not limiting and oxygen is confined, one glucose molecule is theoretically fermented to two lactic acid molecules resulting in a net gain of two molecules of ATP ...
odour away
... The mechanism of odour neutralization by Odour Away is manifold due to the manifold types of odourous compounds produced by decaying organic matter such as hydrogen sulphide, ammonia, amines and methyl-mercaptans. Each group of microbes in Odour Away has unique properties, which make them effective ...
... The mechanism of odour neutralization by Odour Away is manifold due to the manifold types of odourous compounds produced by decaying organic matter such as hydrogen sulphide, ammonia, amines and methyl-mercaptans. Each group of microbes in Odour Away has unique properties, which make them effective ...
Advanced Higher Chemistry Resource Guide
... This resource guide has been produced in response to requests from staff who attended the NQ Sciences events at Hampden Stadium in December 2013. Those attending felt it would be useful to have a document which helped them navigate to the most relevant resources quickly. The following pages show the ...
... This resource guide has been produced in response to requests from staff who attended the NQ Sciences events at Hampden Stadium in December 2013. Those attending felt it would be useful to have a document which helped them navigate to the most relevant resources quickly. The following pages show the ...
Inhibitors are structural analogs of true substrate
... enzyme of tricarboxylic acid cycle participates in reaction of substrate phosphorylation? In a patient are manifested symptoms of intoxication with arsenic compounds. What metabolic process is damaged taking into account that arsen containing substances inactivate lipoic acid? ...
... enzyme of tricarboxylic acid cycle participates in reaction of substrate phosphorylation? In a patient are manifested symptoms of intoxication with arsenic compounds. What metabolic process is damaged taking into account that arsen containing substances inactivate lipoic acid? ...
Influence of milk source and ripening time on free amino
... 1991; Fresno et al., 1993; Barcina et al., 1995). Primary proteolysis in cheese may be defined as the set of those chemical changes in p- and a,-caseins (and large polypeptides derived thereof) that are detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Rank et al., 1985); products of secondary proteol ...
... 1991; Fresno et al., 1993; Barcina et al., 1995). Primary proteolysis in cheese may be defined as the set of those chemical changes in p- and a,-caseins (and large polypeptides derived thereof) that are detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Rank et al., 1985); products of secondary proteol ...
26P PROCEEDINGS OF THE BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY
... yields that may be obtained of partial fragments, say 50-100 residues long, isolated from them. For many large RNA species it may be possible to isolate such ...
... yields that may be obtained of partial fragments, say 50-100 residues long, isolated from them. For many large RNA species it may be possible to isolate such ...
enzymes
... α α‐Amylase y ase • α‐Amylase is an enzyme that hydrolyses alpha‐bonds of large alpha‐linked polysacharides such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose yielding glucose and maltose. • It It is the major form of amylase found in humans and other is the major form of amylase found i ...
... α α‐Amylase y ase • α‐Amylase is an enzyme that hydrolyses alpha‐bonds of large alpha‐linked polysacharides such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose yielding glucose and maltose. • It It is the major form of amylase found in humans and other is the major form of amylase found i ...
Hepatic Steatosis - Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
... show liver steatosis.14,15 Conversely, mice lacking HSL have low plasma FFA levels and low hepatic TG content.16 Finally, muscle-specific modulation of lipoprotein lipase may result in altered distribution of tissue TGs. In mice with musclespecific LPL overexpression, muscle TG content is increased, ...
... show liver steatosis.14,15 Conversely, mice lacking HSL have low plasma FFA levels and low hepatic TG content.16 Finally, muscle-specific modulation of lipoprotein lipase may result in altered distribution of tissue TGs. In mice with musclespecific LPL overexpression, muscle TG content is increased, ...
The CS2 fimbrial antigen from escherichia coli, purification
... liberated by blending. Initial purification was obtained by isoelectric- and magnesium chloride precipitation and the protein was thereby isolated to approx. 80% purity in the form of intact fimbriae. Testing with ELISA showed that this preparation contained a small amount of material which gave a p ...
... liberated by blending. Initial purification was obtained by isoelectric- and magnesium chloride precipitation and the protein was thereby isolated to approx. 80% purity in the form of intact fimbriae. Testing with ELISA showed that this preparation contained a small amount of material which gave a p ...
Molecular Cloning and Expression of a 2-Arylpropionyl
... (compare Fig. 6A) (29). Thus, a common feature of 2-arylpropionyl-CoA-epimerase and carnitine dehydratase is the affinity for CoA-linked thioester substrates. The formation of the thioester leads to an acidic a carbon atom. This is an important prerequisite for the interaction with a basic moiety in ...
... (compare Fig. 6A) (29). Thus, a common feature of 2-arylpropionyl-CoA-epimerase and carnitine dehydratase is the affinity for CoA-linked thioester substrates. The formation of the thioester leads to an acidic a carbon atom. This is an important prerequisite for the interaction with a basic moiety in ...
Plant Microbial and mineral contributions to amino acid and protein
... amphoteric functional groups of proteinaceous compounds are predicted to interact with SOM and minerals so as to be less mobile and more protected from disassociation and decomposition. There remains, however, lack of field-based evidence supportive of protein accrual associated with soil minerals. T ...
... amphoteric functional groups of proteinaceous compounds are predicted to interact with SOM and minerals so as to be less mobile and more protected from disassociation and decomposition. There remains, however, lack of field-based evidence supportive of protein accrual associated with soil minerals. T ...
Schuenemann_Cytochrome P450
... the ferric low-spin to the ferric high-spin state (S=5/2). The transfer of the first electron originating from NAD(P)H via redox proteins (flavin and iron-sulfur proteins) reduces the iron to the ferrous high-spin state (S=2). Subsequent binding of molecular oxygen to the iron forms a diamagnetic Fe ...
... the ferric low-spin to the ferric high-spin state (S=5/2). The transfer of the first electron originating from NAD(P)H via redox proteins (flavin and iron-sulfur proteins) reduces the iron to the ferrous high-spin state (S=2). Subsequent binding of molecular oxygen to the iron forms a diamagnetic Fe ...
Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides
... indicated by locants (see 3AA-2.2). The configuration, if known, should be indicated (see 3AA-3, 3AA-4). New trivial names should not be coined for newly discovered a-amino acids unless there are compelling reasons. When they are needed (e.g. because the substance is important and its semisystematic ...
... indicated by locants (see 3AA-2.2). The configuration, if known, should be indicated (see 3AA-3, 3AA-4). New trivial names should not be coined for newly discovered a-amino acids unless there are compelling reasons. When they are needed (e.g. because the substance is important and its semisystematic ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
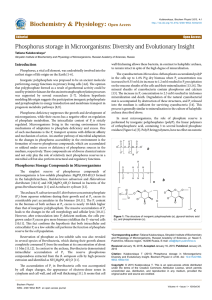
... pressure and simultaneously are an energy reserve, because the energy of their phosphodiester bond is the same as in ATP molecule. The role of polyP as a phosphate reserve has been proved for many microorganisms belonging to different taxa, from archaea to fungi [15-17]. The amount of these polymers ...
... pressure and simultaneously are an energy reserve, because the energy of their phosphodiester bond is the same as in ATP molecule. The role of polyP as a phosphate reserve has been proved for many microorganisms belonging to different taxa, from archaea to fungi [15-17]. The amount of these polymers ...
Nucleic acid enzymes
... synthetases could have also been RNA catalysts. A 45nucleotide-long tRNA aminoacylation ribozyme was selected evolving a previously identified sequence [25]. This catalyst showed improved catalytic activity and is able to aminoacylate several tRNA in trans (not as a selfmodifier) with phenylalanine ...
... synthetases could have also been RNA catalysts. A 45nucleotide-long tRNA aminoacylation ribozyme was selected evolving a previously identified sequence [25]. This catalyst showed improved catalytic activity and is able to aminoacylate several tRNA in trans (not as a selfmodifier) with phenylalanine ...
3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
... most important structural polysaccharides –It is found in the cell walls of plants –It is indigestible for most animals due to the orientation of the bonds between glucose ...
... most important structural polysaccharides –It is found in the cell walls of plants –It is indigestible for most animals due to the orientation of the bonds between glucose ...
Enterobacteriaceae.
... Motility Agars Sulfide-indole-motility (SIM) is a semisolid motility agar that contains peptonized iron for detection of H2S and tryptophan for indole production. Pure motility agar lacks an H2S indicator and tryptophan for indole production, and contains tetrazolium salts that are reduced to red f ...
... Motility Agars Sulfide-indole-motility (SIM) is a semisolid motility agar that contains peptonized iron for detection of H2S and tryptophan for indole production. Pure motility agar lacks an H2S indicator and tryptophan for indole production, and contains tetrazolium salts that are reduced to red f ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.