Document
... catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell. Metabolic pathways are determined by enzymes. Enzymes are encoded by genes. ...
... catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell. Metabolic pathways are determined by enzymes. Enzymes are encoded by genes. ...
DO ANTIBODIES RECOGNIZE AMINO ACID SIDE CHAINS OF
... contain unique V sequences homologous to the original antigen but in reverse orientation . Synthetic peptide inhibition experiments confirmed the ability of a reversed sequence to resemble the nominal antigenic epitope . In contrast to earlier studies in which internal image determinants were prese ...
... contain unique V sequences homologous to the original antigen but in reverse orientation . Synthetic peptide inhibition experiments confirmed the ability of a reversed sequence to resemble the nominal antigenic epitope . In contrast to earlier studies in which internal image determinants were prese ...
Enzymes - Weber State University
... Irreversible Inhibitors are toxic. In the laboratory they can be used to map the active site. These inhibitors often form covalent linkages to amino acids at the active site. DIPF (diisopropylphosphofluoridate) forms a covalent linkage to serine. If serine plays an important catalytic role for the e ...
... Irreversible Inhibitors are toxic. In the laboratory they can be used to map the active site. These inhibitors often form covalent linkages to amino acids at the active site. DIPF (diisopropylphosphofluoridate) forms a covalent linkage to serine. If serine plays an important catalytic role for the e ...
The Utilization of Propionate by Micrococcus
... Organisms used. The strain of Micrococcus denitrzjicans, obtained from Dr June Lascelles, had been originally supplied by Dr W. Verhoeven. Growth of the organism. Cultures of Micrococcus denitrificans were maintained and grown as described by Kornberg & Morris (1965) except that sodium propionate wa ...
... Organisms used. The strain of Micrococcus denitrzjicans, obtained from Dr June Lascelles, had been originally supplied by Dr W. Verhoeven. Growth of the organism. Cultures of Micrococcus denitrificans were maintained and grown as described by Kornberg & Morris (1965) except that sodium propionate wa ...
... This exam consists of 6 pages and 11 questions with 1 bonus question. Total points are 100. Allot 1 min/2 points. On questions with choices, all of your answers will be graded and the best scoring answer will be used. Please use the space provided, or the back of the preceding page. 1. (6 pts) Pleas ...
Chapter 3—Thermodynamics of Biological Systems MULTIPLE
... 3. Which statement pertaining to the three basic systems is true? a. The internal energy of an isolated system is mostly conserved. b. Open systems can exchange matter with other open systems. c. Open systems can exchange matter with a closed system. d. The internal energy of an open system is alway ...
... 3. Which statement pertaining to the three basic systems is true? a. The internal energy of an isolated system is mostly conserved. b. Open systems can exchange matter with other open systems. c. Open systems can exchange matter with a closed system. d. The internal energy of an open system is alway ...
Local protein synthesis in neuronal axons: why and
... to axons, such as guidance cues, growth factors, and nerve injury, promote translation of selective mRNAs, a process required for the axon’s ability to respond to these cues. One of the critical questions in the field of axonal protein synthesis is how mRNA-specific local translation is regulated by ...
... to axons, such as guidance cues, growth factors, and nerve injury, promote translation of selective mRNAs, a process required for the axon’s ability to respond to these cues. One of the critical questions in the field of axonal protein synthesis is how mRNA-specific local translation is regulated by ...
Organic and Bio-Molecular Chemistry
... The origin of modern Organic Chemistry can be dated at the beginning of the 19th century, when scientists such as Gay-Lussac (1810) and Berzelius (1814) developed methods of analysis of the compounds derived from living organisms, allowing a systematic study which put into evidence the common charac ...
... The origin of modern Organic Chemistry can be dated at the beginning of the 19th century, when scientists such as Gay-Lussac (1810) and Berzelius (1814) developed methods of analysis of the compounds derived from living organisms, allowing a systematic study which put into evidence the common charac ...
Two examples of biomarker lipid applica³ons to studies of carbon
... In the lab, we use alkaline cupric oxida/on at high temperature to depolymerize and oxidize ether linkages. Once this has been done, aqueous solu/ons are made acid, and LOP extracted into organic solvents. The LOP are dried and made into vola/le trimethylsilyl ethers for gas chromatography‐mass s ...
... In the lab, we use alkaline cupric oxida/on at high temperature to depolymerize and oxidize ether linkages. Once this has been done, aqueous solu/ons are made acid, and LOP extracted into organic solvents. The LOP are dried and made into vola/le trimethylsilyl ethers for gas chromatography‐mass s ...
CHM 303 - Unaab.edu.ng
... Fatty Acids in Food: Saturated Versus Unsaturated Fats consumed in the modern human diet vary widely in their fatty acid compositions. The table below provides a brief summary. The incidence of cardiovascular disease is correlated with diets high in saturated fatty acids. By contrast, a diet that is ...
... Fatty Acids in Food: Saturated Versus Unsaturated Fats consumed in the modern human diet vary widely in their fatty acid compositions. The table below provides a brief summary. The incidence of cardiovascular disease is correlated with diets high in saturated fatty acids. By contrast, a diet that is ...
NAD (H) Linked Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions using Coupled
... by glutaraldehyde. Silanization in Method 1 was carried out in dry acetone, whereas Method 2 used aqueous solutions. Hence, the lower loading in Method 2 can be attributed to the breakage of the Al-OSi bond, resulting in lesser glutaraldehyde molecules available at the surface for coupling. Therefor ...
... by glutaraldehyde. Silanization in Method 1 was carried out in dry acetone, whereas Method 2 used aqueous solutions. Hence, the lower loading in Method 2 can be attributed to the breakage of the Al-OSi bond, resulting in lesser glutaraldehyde molecules available at the surface for coupling. Therefor ...
Regulation of enzyme activity
... It means modification of enzyme activity of many enzymes through formation of covalent bonds e.g. 1. Methylation (addition of methyl group). 2. Hydroxylation (addition of hydroxyl group). 3. Adenylation (addition of adenylic acid). 4. Phosphorylation (addition of phosphate group) Phosphorylation is ...
... It means modification of enzyme activity of many enzymes through formation of covalent bonds e.g. 1. Methylation (addition of methyl group). 2. Hydroxylation (addition of hydroxyl group). 3. Adenylation (addition of adenylic acid). 4. Phosphorylation (addition of phosphate group) Phosphorylation is ...
Amino Acid Analysis Amino acid analysis refers to the methodology
... Hydrolysis of protein and peptide samples is necessary for amino acid analysis of these molecules. The glassware used for hydrolysis must be very clean to avoid erroneous results. Glove powders and fingerprints on hydrolysis tubes may cause contamination. To clean glass hydrolysis tubes, boil tubes ...
... Hydrolysis of protein and peptide samples is necessary for amino acid analysis of these molecules. The glassware used for hydrolysis must be very clean to avoid erroneous results. Glove powders and fingerprints on hydrolysis tubes may cause contamination. To clean glass hydrolysis tubes, boil tubes ...
BC Science 10 Workbook Answers
... 6. Overexploitation can result in extinction of a species and a loss of genetic diversity. In turn, the populations are less resistant to disease and less able to adapt to changes in their environment. 7. Traditional ecological knowledge takes the form of ...
... 6. Overexploitation can result in extinction of a species and a loss of genetic diversity. In turn, the populations are less resistant to disease and less able to adapt to changes in their environment. 7. Traditional ecological knowledge takes the form of ...
ism ismismismismismrapidrevisionquestionsismismismismismism
... (i) Combination between nitrogen and hydrogen to form ammonia in the presence of iron catalyst in Haber’s process. Fe N2 + 3H2 2NH3 (ii) Zeolites catalyst ZSM-5 is used to convert alcohol to gasoline by dehydration. (iii) The enzyme zymase converts glucose into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Zyma ...
... (i) Combination between nitrogen and hydrogen to form ammonia in the presence of iron catalyst in Haber’s process. Fe N2 + 3H2 2NH3 (ii) Zeolites catalyst ZSM-5 is used to convert alcohol to gasoline by dehydration. (iii) The enzyme zymase converts glucose into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Zyma ...
Cellular Respiration
... Chemical Energy and Food • Food provides living things with the chemical building blocks they need to grow and reproduce. • Food molecules contain energy that is released when its chemical bonds are broken. • Energy stored in food is expressed in units of calories. • Cells use all sorts of molecules ...
... Chemical Energy and Food • Food provides living things with the chemical building blocks they need to grow and reproduce. • Food molecules contain energy that is released when its chemical bonds are broken. • Energy stored in food is expressed in units of calories. • Cells use all sorts of molecules ...
Supplementary Figure 1
... evolution; therefore the branch lengths correspond to amino acid substitutions per time unit. Evidently, UbS27a domains are less conserved than ribosomal S27a domains or homologs to SUMO1, despite the presence of a hypervariable loop at the N-terminus of SUMO1. Particularly indicative of a high rate ...
... evolution; therefore the branch lengths correspond to amino acid substitutions per time unit. Evidently, UbS27a domains are less conserved than ribosomal S27a domains or homologs to SUMO1, despite the presence of a hypervariable loop at the N-terminus of SUMO1. Particularly indicative of a high rate ...
Nitrogen Balance and Protein Requirements: Definition and
... they must be introduced with the diet in a proportion that will fit with the organism’s metabolic needs. On the other hand, in the absence of dietary NEAA, despite the theoretical capability of the body to synthesise them, nitrogen will be needed for their de novo synthesis. This nitrogen in turn mu ...
... they must be introduced with the diet in a proportion that will fit with the organism’s metabolic needs. On the other hand, in the absence of dietary NEAA, despite the theoretical capability of the body to synthesise them, nitrogen will be needed for their de novo synthesis. This nitrogen in turn mu ...
Carbohydrate and Amino Acid Metabolism in the
... * Corresponding author; e-mail [email protected]; fax 33– ...
... * Corresponding author; e-mail [email protected]; fax 33– ...
C1. The start codon begins at the fifth nucleotide. The amino acid
... C16. Bases that have been chemically modified can occur at various locations throughout the tRNA molecule. The significance of all of these modifications is not entirely known. However, within the anticodon region, base modification alters base pairing to allow the anticodon to recognize two or mor ...
... C16. Bases that have been chemically modified can occur at various locations throughout the tRNA molecule. The significance of all of these modifications is not entirely known. However, within the anticodon region, base modification alters base pairing to allow the anticodon to recognize two or mor ...
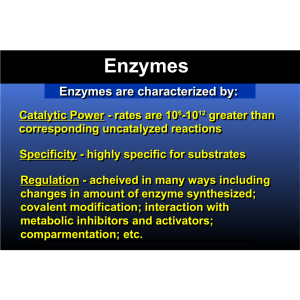
Enzymes Enzymes are characterized by
... equation that relates the rate of catalysis (v) to the concentration of enzyme and substrate and the rates of the individual steps in the kinetic pathway: Starting point is that the rate at which ...
... equation that relates the rate of catalysis (v) to the concentration of enzyme and substrate and the rates of the individual steps in the kinetic pathway: Starting point is that the rate at which ...
Document
... C16. Bases that have been chemically modified can occur at various locations throughout the tRNA molecule. The significance of all of these modifications is not entirely known. However, within the anticodon region, base modification alters base pairing to allow the anticodon to recognize two or mor ...
... C16. Bases that have been chemically modified can occur at various locations throughout the tRNA molecule. The significance of all of these modifications is not entirely known. However, within the anticodon region, base modification alters base pairing to allow the anticodon to recognize two or mor ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.