Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
... Nonsense mutations = change of codon for an aa to STOP Usually lethal – truncated protein Can be rescued by mutation in a different part of the genome ...
... Nonsense mutations = change of codon for an aa to STOP Usually lethal – truncated protein Can be rescued by mutation in a different part of the genome ...
Cell Respiration WebQuest(09)
... Go to: Biology in Motion. Read & complete the activity. (http://www.biologyinmotion.com/atp/index.html) 1. What is ATP? ...
... Go to: Biology in Motion. Read & complete the activity. (http://www.biologyinmotion.com/atp/index.html) 1. What is ATP? ...
TD12 Characterization of DnaJ substrate specificity Reference
... DnaK= E.coli Hsp 70 type chaperone DnaJ= E.coli Hsp 40 type cochaperone *Note- DnaK and DnaJ are both PROTEINS. Question: What is the role of DnaJ? Observations: -DnaJ itself can bind unfolded proteins -This binding can prevent protein aggregation->in this sense, DnaJ is a chaperone on its own. -But ...
... DnaK= E.coli Hsp 70 type chaperone DnaJ= E.coli Hsp 40 type cochaperone *Note- DnaK and DnaJ are both PROTEINS. Question: What is the role of DnaJ? Observations: -DnaJ itself can bind unfolded proteins -This binding can prevent protein aggregation->in this sense, DnaJ is a chaperone on its own. -But ...
Chemistry
... Differences between atoms give elements their different chemical properties. Atoms of one or more substances (reactants) undergo some ‘rearrangements’ during a chemical change (reaction). These rearrangements form new and different substances (products). After the chemical reaction, all the atoms of ...
... Differences between atoms give elements their different chemical properties. Atoms of one or more substances (reactants) undergo some ‘rearrangements’ during a chemical change (reaction). These rearrangements form new and different substances (products). After the chemical reaction, all the atoms of ...
Aberrant Lipid Metabolism Promotes Prostate Cancer: Role in Cell
... (Figure 1). Fatty acids (from diet or from triglyceride (TG) breakdown) can be used for fuel (via β-oxidation) and promote growth, or used to generate lipid signaling molecules that shape the fate of the cell, like eicosanoids [42,43] and phospholipids [44]. Etomoxir is a safe irreversible inhibitor ...
... (Figure 1). Fatty acids (from diet or from triglyceride (TG) breakdown) can be used for fuel (via β-oxidation) and promote growth, or used to generate lipid signaling molecules that shape the fate of the cell, like eicosanoids [42,43] and phospholipids [44]. Etomoxir is a safe irreversible inhibitor ...
RNA–Amino Acid Binding - University of Colorado-MCDB
... Comparison and moderate extrapolation from these structures suggest that it will be possible for RNA sites to exist that bind most of the 20 major amino acids, though the abundances of RNA structures containing sites will likely vary, as will their affinity and discrimination. The first order of bus ...
... Comparison and moderate extrapolation from these structures suggest that it will be possible for RNA sites to exist that bind most of the 20 major amino acids, though the abundances of RNA structures containing sites will likely vary, as will their affinity and discrimination. The first order of bus ...
Poon, Andy: Predicting Phosphorylation: A critique of the NetPhos program and potential alternatives
... The purpose of using quantitative pattern matching was to possibly identify known motifs common to phosphorylated proteins. Perhaps documented motifs existed, initially attributed to other protein features, which may be indicative of phosphorylation as well. (For instance, perhaps these databases r ...
... The purpose of using quantitative pattern matching was to possibly identify known motifs common to phosphorylated proteins. Perhaps documented motifs existed, initially attributed to other protein features, which may be indicative of phosphorylation as well. (For instance, perhaps these databases r ...
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Science Learning Center
... oxidation-reduction reaction. Here, the reaction mixture (water, amylase, undigested starch, and maltose) is mixed with an alkaline solution of 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) and boiled for 5-10 minutes. Due to the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O), maltose participates in an oxidation-reduction ...
... oxidation-reduction reaction. Here, the reaction mixture (water, amylase, undigested starch, and maltose) is mixed with an alkaline solution of 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) and boiled for 5-10 minutes. Due to the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O), maltose participates in an oxidation-reduction ...
Glucose-Fatty Acid Interaction in Skeletal Muscle and Adipose
... Fatty acids are an important source of energy for many tissues, including skeletal muscle, which is the main site of the manifestation of insulin resistance. On the other hand, as surfactants they are toxic substances and even when bound to protein carrier their elevated concentration in the serum i ...
... Fatty acids are an important source of energy for many tissues, including skeletal muscle, which is the main site of the manifestation of insulin resistance. On the other hand, as surfactants they are toxic substances and even when bound to protein carrier their elevated concentration in the serum i ...
Full-Text PDF
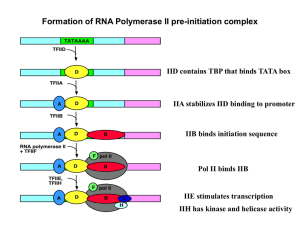
... (mRNA) that will allow for differential gene expression patterns to emerge during the process of transcription. The mRNAs are subsequently processed by an array of splicing and editing mechanisms before exiting the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm, the mRNAs will interact with large ri ...
... (mRNA) that will allow for differential gene expression patterns to emerge during the process of transcription. The mRNAs are subsequently processed by an array of splicing and editing mechanisms before exiting the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm, the mRNAs will interact with large ri ...
Trypsinogen from bovine pancreas Product Number T1143 Storage
... bridges. The proenzyme is activated only after it reaches the lumen of the small intestine. Enterokinase activates pancreatic trypsinogen to trypsin by the hydrolysis of a hexapeptide from the NH2 terminus. ...
... bridges. The proenzyme is activated only after it reaches the lumen of the small intestine. Enterokinase activates pancreatic trypsinogen to trypsin by the hydrolysis of a hexapeptide from the NH2 terminus. ...
IEMs Emergency Management
... – Exaggerated startle reaction. – Hypertonia ( decrease in sleep). – violent flexor spasms of limbs and neck muscles. elicited by tapping the tip of the nose. – SIDS has been reported. – Intellect is usually normal. ...
... – Exaggerated startle reaction. – Hypertonia ( decrease in sleep). – violent flexor spasms of limbs and neck muscles. elicited by tapping the tip of the nose. – SIDS has been reported. – Intellect is usually normal. ...
Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism: Plasticity and Evolution
... Cc) and light in fully hydrated leaves is defined as Apot. To achieve the same Apot at small RWC as at large RWC, Cc must saturate Rubisco and so Ca must be sufficient to overcome the limitation of gs. If Apot at small RWC does not attain the value of Apot at large RWC, despite CO2 saturation, then ...
... Cc) and light in fully hydrated leaves is defined as Apot. To achieve the same Apot at small RWC as at large RWC, Cc must saturate Rubisco and so Ca must be sufficient to overcome the limitation of gs. If Apot at small RWC does not attain the value of Apot at large RWC, despite CO2 saturation, then ...
Mechanisms underlying skeletal muscle insulin resistance induced
... Saturated fatty acids activate inflammatory signaling pathways directly through interaction with members of Toll-like receptor (TLR) family and indirectly through the secretion of cytokines including TNF-a, IL-1b and IL-6 [59-61]. TLRs are an evolutionarily ancient pattern-recognition class of recep ...
... Saturated fatty acids activate inflammatory signaling pathways directly through interaction with members of Toll-like receptor (TLR) family and indirectly through the secretion of cytokines including TNF-a, IL-1b and IL-6 [59-61]. TLRs are an evolutionarily ancient pattern-recognition class of recep ...
Evidence for the presence of photorespiration in desiccation
... Despite the pivotal importance of phosphoglycollate ‘recycling’, photorespiration does not appear to be solely an energy-consuming process that plants use to cope with the oxygenase activity of Rubisco. Many authors have suggested different roles for the photorespiratory cycle other than carbon reco ...
... Despite the pivotal importance of phosphoglycollate ‘recycling’, photorespiration does not appear to be solely an energy-consuming process that plants use to cope with the oxygenase activity of Rubisco. Many authors have suggested different roles for the photorespiratory cycle other than carbon reco ...
STUDY GUIDE
... Condensation polymers are polymers formed when monomers join during condensation reactions. The properties of addition polymers can be varied by selecting monomers with certain substituent atoms or groups. Polyesters are formed by condensation reactions between carboxylic acids and alcohols that res ...
... Condensation polymers are polymers formed when monomers join during condensation reactions. The properties of addition polymers can be varied by selecting monomers with certain substituent atoms or groups. Polyesters are formed by condensation reactions between carboxylic acids and alcohols that res ...
Nutritional Control of Growth and Development in Yeast
... simply by activating this pathway. Similarly, blocking signaling through the pathway concurrent with glucose addition eliminates most, albeit not all, of the responses. Thus, the PKA pathway is both necessary and sufficient for a majority of the transcriptional responses of the cell to glucose (Zama ...
... simply by activating this pathway. Similarly, blocking signaling through the pathway concurrent with glucose addition eliminates most, albeit not all, of the responses. Thus, the PKA pathway is both necessary and sufficient for a majority of the transcriptional responses of the cell to glucose (Zama ...
Urinalysis
... Reagent tablet – Coppe r sulfate, citric acid, sodium hydroxide and sodium carb onate. Add tablet to 5 drops of urine in a glass tube and look for a color cha nge in a spe cified time. Compare color change (blue to green to orange) to a chart for quantitation. ...
... Reagent tablet – Coppe r sulfate, citric acid, sodium hydroxide and sodium carb onate. Add tablet to 5 drops of urine in a glass tube and look for a color cha nge in a spe cified time. Compare color change (blue to green to orange) to a chart for quantitation. ...
Conserved Tryptophan Residues within Putative Transmembrane
... different transmembrane helices prediction servers was used to locate the position of TM6 (Table 1). According to the predictions, 24 amino acids from position 257 to 280 of OATP1B1 were selected for alanine-scanning analysis (Fig. 2). These ...
... different transmembrane helices prediction servers was used to locate the position of TM6 (Table 1). According to the predictions, 24 amino acids from position 257 to 280 of OATP1B1 were selected for alanine-scanning analysis (Fig. 2). These ...
Heart Failure and Loss of Metabolic Control
... (0970518N), and the Fondation Leducq (11CVD04). Zhao V. Wang was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the AHA (10POST4320009). The authors report no conflicts of interest. Reprints: Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Texas Southweste ...
... (0970518N), and the Fondation Leducq (11CVD04). Zhao V. Wang was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the AHA (10POST4320009). The authors report no conflicts of interest. Reprints: Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Texas Southweste ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.