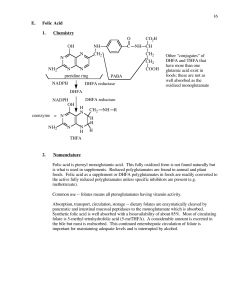
16 E. Folic Acid 1. Chemistry coenzyme DHFA DHFA reductase
... Nomenclature Folic acid is pteroyl monoglutamic acid. This fully oxidized form is not found naturally but is what is used in supplements. Reduced polyglutamates are found in animal and plant foods. Folic acid as a supplement or DHFA polyglutamates in foods are readily converted to the active fully r ...
... Nomenclature Folic acid is pteroyl monoglutamic acid. This fully oxidized form is not found naturally but is what is used in supplements. Reduced polyglutamates are found in animal and plant foods. Folic acid as a supplement or DHFA polyglutamates in foods are readily converted to the active fully r ...
Food fight: sexual conflict over free amino acids in the nuptial gifts of
... acids (Warwick, 1999; Gershman et al., 2012) including alanine, serine, histidine, proline, valine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine and tryptophan, and threonine, which have phagostimulatory effects in insects (Leckstein & Llewellyn, 1974; Srivastava & Auclair, 1974; Cook, 1977). However, females ...
... acids (Warwick, 1999; Gershman et al., 2012) including alanine, serine, histidine, proline, valine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine and tryptophan, and threonine, which have phagostimulatory effects in insects (Leckstein & Llewellyn, 1974; Srivastava & Auclair, 1974; Cook, 1977). However, females ...
Study of Different Variants of Mo Enzyme crARC and the Interaction
... proteins have been shwon to be involved in NO synthesis by different ways. In this regard, in vitro studies have shown that human ARCO is also able to catalyze the reduction of the NO precursor N-omega-hydroxy-L-arginine (NOHA) to arginine [20]. In this sense, a variety of several enzymes have been ...
... proteins have been shwon to be involved in NO synthesis by different ways. In this regard, in vitro studies have shown that human ARCO is also able to catalyze the reduction of the NO precursor N-omega-hydroxy-L-arginine (NOHA) to arginine [20]. In this sense, a variety of several enzymes have been ...
Amino Acids [PDF:247KB]
... food name, etc. of food listed to be consistent with the Food Composition Tables 2015, and new assignment of index numbers to foods. Additionally, from the viewpoint of ensuring convenience for the users with the increased number of foods listed, the component values calculated from the ratio of raw ...
... food name, etc. of food listed to be consistent with the Food Composition Tables 2015, and new assignment of index numbers to foods. Additionally, from the viewpoint of ensuring convenience for the users with the increased number of foods listed, the component values calculated from the ratio of raw ...
(mmg) operon of Bacillus
... various industries. Hence this organism is extensively studied. The genome of this bacterium has around 4000 protein coding sequences, which include 87% of the genome sequence. Because of its ability to use different carbohydrates, the glycolytic pathway along with the TCA cycle is utilized in this ...
... various industries. Hence this organism is extensively studied. The genome of this bacterium has around 4000 protein coding sequences, which include 87% of the genome sequence. Because of its ability to use different carbohydrates, the glycolytic pathway along with the TCA cycle is utilized in this ...
Engineering of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase reaction and
... starch (amylopectin in this case). Many starch-degrading enzymes are hydrolytic, cleaving the linkages in the starch molecule followed by the reaction of the cleavage product with water, resulting in a new reducing end. These can be roughly divided into amylases, hydrolysing K(1^4) linkages, and deb ...
... starch (amylopectin in this case). Many starch-degrading enzymes are hydrolytic, cleaving the linkages in the starch molecule followed by the reaction of the cleavage product with water, resulting in a new reducing end. These can be roughly divided into amylases, hydrolysing K(1^4) linkages, and deb ...
Isotope Fractionation: Why Aren`t We What We Eat?
... Understanding and interpreting these isotopic signals, unfortunately, is not always easy. The aim of this paper is to provide background information about isotope biogeochemistry and nitrogen metabolism that will aid in the interpretation of these isotopic signals. ...
... Understanding and interpreting these isotopic signals, unfortunately, is not always easy. The aim of this paper is to provide background information about isotope biogeochemistry and nitrogen metabolism that will aid in the interpretation of these isotopic signals. ...
"big IB objectives"-use the blank paper technique
... 2.4.1 – Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes 2.4.2 – explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophyllic properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes 2.4.5 – explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion 2.4.6 ...
... 2.4.1 – Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes 2.4.2 – explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophyllic properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes 2.4.5 – explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion 2.4.6 ...
Predicting functional linkages from gene fusions with
... benchmark. The database categorises 1283 E. coli proteins into 24 main pathways, including metabolic pathways (such as carbohydrate and energy metabolism), and general cellular systems (such as transcription, translation, and sorting and degradation). Within each main category, proteins are further ...
... benchmark. The database categorises 1283 E. coli proteins into 24 main pathways, including metabolic pathways (such as carbohydrate and energy metabolism), and general cellular systems (such as transcription, translation, and sorting and degradation). Within each main category, proteins are further ...
Growth independent rhamnolipid production from glucose using the
... Background: Rhamnolipids are potent biosurfactants with high potential for industrial applications. However, rhamnolipids are currently produced with the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa during growth on hydrophobic substrates such as plant oils. The heterologous production of rhamnolip ...
... Background: Rhamnolipids are potent biosurfactants with high potential for industrial applications. However, rhamnolipids are currently produced with the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa during growth on hydrophobic substrates such as plant oils. The heterologous production of rhamnolip ...
1 Excess of free fatty acids as a cause of metabolic
... A number of studies in animals and humans, however, is incompatible with this concept and observed lipid-induced IR in skeletal muscle without an impairment of mitochondrial function (Brands et al. 2011; Hoeks et al. 2011; Fisher-Wellman et al. 2013) or with impairment which developed long time aft ...
... A number of studies in animals and humans, however, is incompatible with this concept and observed lipid-induced IR in skeletal muscle without an impairment of mitochondrial function (Brands et al. 2011; Hoeks et al. 2011; Fisher-Wellman et al. 2013) or with impairment which developed long time aft ...
Hepatic Failure: Role for biochemists and nutrition experts
... incr eas ed in HF (7) and mus t be ins tituted as a par t of the Nutr itional S uppor t along with neomycin which helps to lower the ammonia bur den by r educing the activity of the s ynthetas e. (8) B r anched chain amino acids mus t be pr ovided as a par t of the s upplementation and the pr otein ...
... incr eas ed in HF (7) and mus t be ins tituted as a par t of the Nutr itional S uppor t along with neomycin which helps to lower the ammonia bur den by r educing the activity of the s ynthetas e. (8) B r anched chain amino acids mus t be pr ovided as a par t of the s upplementation and the pr otein ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... The utilization of amino acids for growth and their effects on nitrogen fixation differ greatly among the several strains of each species of Azospirllum spp. that were examined. A. brasiiense grew poorly or not at all on glutamate, aspartate, serine, or histidine as the sole nitrogen and carbon sour ...
... The utilization of amino acids for growth and their effects on nitrogen fixation differ greatly among the several strains of each species of Azospirllum spp. that were examined. A. brasiiense grew poorly or not at all on glutamate, aspartate, serine, or histidine as the sole nitrogen and carbon sour ...
Salcedo-SoraAndMcAul
... Infectious diseases are still a major burden to human health and economic development. For example, in 2013 mortality due to tuberculosis 2013 was estimated at 1.4 million people.1 Moreover, Malaria causes an astonishing 200 to 500 million of clinical episodes a year2–4 with nearly 600 thousand deat ...
... Infectious diseases are still a major burden to human health and economic development. For example, in 2013 mortality due to tuberculosis 2013 was estimated at 1.4 million people.1 Moreover, Malaria causes an astonishing 200 to 500 million of clinical episodes a year2–4 with nearly 600 thousand deat ...
UNIT-II - E
... Apart from carbon and nitrogen sources, the fermentation medium normally contains inorganic salts, providing magnesium, manganese, phosphate and potassium, and limiting levels of biotin. Corynebacteria are nutritionally fastidious and may also require other vitamins, amino acids, purines and pyr ...
... Apart from carbon and nitrogen sources, the fermentation medium normally contains inorganic salts, providing magnesium, manganese, phosphate and potassium, and limiting levels of biotin. Corynebacteria are nutritionally fastidious and may also require other vitamins, amino acids, purines and pyr ...
A Précis on Selenium
... intakes of selenium may need to be increased from dietary supplements. Plants, grasses and cereal grains take up selenium from the soil as inorganic salts (selenites and selenates) and convert these first to selenium salts and then to organic compounds, mainly as selenomethionine. Animals then obtai ...
... intakes of selenium may need to be increased from dietary supplements. Plants, grasses and cereal grains take up selenium from the soil as inorganic salts (selenites and selenates) and convert these first to selenium salts and then to organic compounds, mainly as selenomethionine. Animals then obtai ...
Conceptual Questions C1. Answer: The start codon begins at the
... Initiation: The mRNA, initiator tRNA, and initiation factors associate with the small ribosomal subunit; then the large subunit associates. Elongation: The ribosome moves one codon at a time down the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing polypeptide chain. Three sites on the ribosome, ...
... Initiation: The mRNA, initiator tRNA, and initiation factors associate with the small ribosomal subunit; then the large subunit associates. Elongation: The ribosome moves one codon at a time down the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing polypeptide chain. Three sites on the ribosome, ...
Chapter 20 Prokaryotes
... Transformation occurs when bacterium picks up free pieces of DNA from other prokaryotes. Transduction occurs when bacteriophages carry portions of bacterial DNA from one cell to another. When faced with unfavorable conditions, some bacteria form endospores. ...
... Transformation occurs when bacterium picks up free pieces of DNA from other prokaryotes. Transduction occurs when bacteriophages carry portions of bacterial DNA from one cell to another. When faced with unfavorable conditions, some bacteria form endospores. ...
Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: current state, challenges
... aeration rate, shear stress, dissolved oxygen, and bioreactor type) significantly influence the microbial HA production. The pH and temperature for HA production by S. zooepidemicus were usually at 7.0 and 37°C, respectively [26,27]. The microbial HA production by S. zooepidemicus is a typically vis ...
... aeration rate, shear stress, dissolved oxygen, and bioreactor type) significantly influence the microbial HA production. The pH and temperature for HA production by S. zooepidemicus were usually at 7.0 and 37°C, respectively [26,27]. The microbial HA production by S. zooepidemicus is a typically vis ...
Leptin Exhibits Pluripotent Effects on Appetite and Metabolism
... melanocyte-stimulating hormone). The ventral tegmental area (VTA) contains dopamine neurons that are important in modulating motivated behavior, addiction and reward. VTA dopamine neurons express leptin receptors, thus respond to leptin with activation of an intracellular JAK-STAT pathway and a redu ...
... melanocyte-stimulating hormone). The ventral tegmental area (VTA) contains dopamine neurons that are important in modulating motivated behavior, addiction and reward. VTA dopamine neurons express leptin receptors, thus respond to leptin with activation of an intracellular JAK-STAT pathway and a redu ...
Table xx - Hindawi
... Axon guidance: The pathway shows three subpathways leading to input for the “Regulation of actin cytoskeleton” pathway. Chicken line differences resulted in a higher expression of all three subpathways in line B compared to line A. Following Salmonella infection both lines show up regulation of the ...
... Axon guidance: The pathway shows three subpathways leading to input for the “Regulation of actin cytoskeleton” pathway. Chicken line differences resulted in a higher expression of all three subpathways in line B compared to line A. Following Salmonella infection both lines show up regulation of the ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.


![Amino Acids [PDF:247KB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002278939_1-1b03d0bc0e7fdaaa14234846bba6ef6c-300x300.png)




















