From the pudding cake to the Super Symmetry
... negative energy represent positrons, antiparticle of electrons; In 1933 Blackett and Occhialini observed with the Cavendish cloud chamber the positron and explicitly associate it to the particle predicted by Dirac. the prediction and discovery of antiparticles was a new revolution in the particl ...
... negative energy represent positrons, antiparticle of electrons; In 1933 Blackett and Occhialini observed with the Cavendish cloud chamber the positron and explicitly associate it to the particle predicted by Dirac. the prediction and discovery of antiparticles was a new revolution in the particl ...
Redalyc.Atomic radiative corrections without QED: role of the zero
... Received 25 January 2013; accepted 17 May 2013 We derive the atomic radiative corrections predicted by QED using an alternative approach that offers the advantage of physical clarity and transparency. The element that gives rise to these corrections is the fluctuating zero-point radiation field (ZPF ...
... Received 25 January 2013; accepted 17 May 2013 We derive the atomic radiative corrections predicted by QED using an alternative approach that offers the advantage of physical clarity and transparency. The element that gives rise to these corrections is the fluctuating zero-point radiation field (ZPF ...
lecture 19 (zipped power point) (update: 13Jan 04)
... matter wave associated with a given particle (or an physical entity) as The wave function, Y(x,t) ...
... matter wave associated with a given particle (or an physical entity) as The wave function, Y(x,t) ...
Electrostatics - Princeton ISD
... Use Testable question and cooperative groups, Lab 86 p 277 from conceptual physic series have students charge electroscopes and to determine the charge on various different materials. Review the triboelectric series and verify selected items on list for their charge attraction ...
... Use Testable question and cooperative groups, Lab 86 p 277 from conceptual physic series have students charge electroscopes and to determine the charge on various different materials. Review the triboelectric series and verify selected items on list for their charge attraction ...
Press Release Equivalence principle also valid for atoms
... leaning tower in Pisa. He found that all objects reached the ground at the same time. This illustrates the more general result that in a gravitational field the motion of all bodies is the same independent of their mass and composition. Einstein took up this finding to formulate the “equivalence pri ...
... leaning tower in Pisa. He found that all objects reached the ground at the same time. This illustrates the more general result that in a gravitational field the motion of all bodies is the same independent of their mass and composition. Einstein took up this finding to formulate the “equivalence pri ...
South Pasadena · Chemistry
... 4. There are five 4d orbitals. List the quantum numbers for each orbital. n l ml ...
... 4. There are five 4d orbitals. List the quantum numbers for each orbital. n l ml ...
Chapter 1
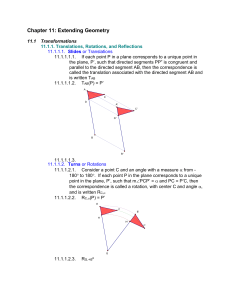
... 11.1.2.1.1. Reflectional symmetry 11.1.2.1.2. line of symmetry 11.1.2.1.3. n rotational symmetry 11.1.2.1.4. center of rotational symmetry 11.1.3. Transformations that Change Size 11.1.3.1. size transformations 11.1.3.1.1. If point O corresponds to itself, and each other point P in the plane corres ...
... 11.1.2.1.1. Reflectional symmetry 11.1.2.1.2. line of symmetry 11.1.2.1.3. n rotational symmetry 11.1.2.1.4. center of rotational symmetry 11.1.3. Transformations that Change Size 11.1.3.1. size transformations 11.1.3.1.1. If point O corresponds to itself, and each other point P in the plane corres ...
2/a
... • In classical mechanics the state of a system with a number of particles at any time is defined by designating the particle and momentum coordinates of all particles. • In quantum mechanics the state of a system is defined by a state function Ψ that contains all the information we can obtain about ...
... • In classical mechanics the state of a system with a number of particles at any time is defined by designating the particle and momentum coordinates of all particles. • In quantum mechanics the state of a system is defined by a state function Ψ that contains all the information we can obtain about ...
Review 21-22
... Quiz Thursday • Ch.21-22 • one 3x5 inch card notes f/b (do not bring larger) • constants provided – units are not provided ...
... Quiz Thursday • Ch.21-22 • one 3x5 inch card notes f/b (do not bring larger) • constants provided – units are not provided ...
Quantum Scattering with the Driven Schrödinger Approach and Complex Scaling Nils Elander
... The success in solving the driven Schrödinger equation by ECS depends on whether the driving term vanishes for complex values of the radial coordinates. The driven Schrödinger equation formulation (2, 5) perfectly meets this requirement since the potential on the right hand side is of finite range. ...
... The success in solving the driven Schrödinger equation by ECS depends on whether the driving term vanishes for complex values of the radial coordinates. The driven Schrödinger equation formulation (2, 5) perfectly meets this requirement since the potential on the right hand side is of finite range. ...
Abstracts - Departamento de Matemáticas
... The main example will be the sine-Gordon model, which will be used to illustrate features that are key to the study of many other models. For example, the classical and quantum spectrum, conservation laws, scattering (including a brief look at the Yang-Baxter equation) and bound states. If time allo ...
... The main example will be the sine-Gordon model, which will be used to illustrate features that are key to the study of many other models. For example, the classical and quantum spectrum, conservation laws, scattering (including a brief look at the Yang-Baxter equation) and bound states. If time allo ...
Stationary states and time
... A wave function possessing both space and time variables could be written ...
... A wave function possessing both space and time variables could be written ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.