PH302 Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
... Statistical mechanics is branch of physics that deals with understand collective response from the single particle behavior. This course explains how the statistical approach is effective in predicting the thermodynamics of system from the constituent particles. Methods of statistical mechanics are ...
... Statistical mechanics is branch of physics that deals with understand collective response from the single particle behavior. This course explains how the statistical approach is effective in predicting the thermodynamics of system from the constituent particles. Methods of statistical mechanics are ...
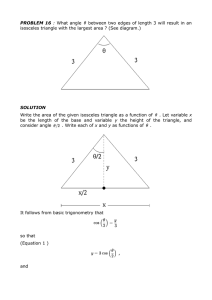
PROBLEM 16 : What angle between two edges of
... We wish to MAXIMIZE the AREA of the isosceles triangle A = (1/2) (length of base) (height) = (1/2) xy . Before we differentiate, use Equations 1 and 2 to rewrite the right-hand side as a function of only. Then A = (1/2) xy ...
... We wish to MAXIMIZE the AREA of the isosceles triangle A = (1/2) (length of base) (height) = (1/2) xy . Before we differentiate, use Equations 1 and 2 to rewrite the right-hand side as a function of only. Then A = (1/2) xy ...
Document
... Consistent neither with classical physics (which would predict a continuous distribution of μ) nor with our quantum mechanics so far (which always predicts an odd number of groups and just one for an s state). ...
... Consistent neither with classical physics (which would predict a continuous distribution of μ) nor with our quantum mechanics so far (which always predicts an odd number of groups and just one for an s state). ...
Concept of Law in Physics On the Concept of Law in Physics
... properties. The full quantum state C of gravity and matter depends on the three-dimensional metric only, but is invariant under three-dimensional coordinate transformations. It does not contain any external time parameter t. The reason for this ‘timeless’ nature is obvious. In general relativity, a ...
... properties. The full quantum state C of gravity and matter depends on the three-dimensional metric only, but is invariant under three-dimensional coordinate transformations. It does not contain any external time parameter t. The reason for this ‘timeless’ nature is obvious. In general relativity, a ...
physics colloquium
... FeSe is currently one of the most hotly debated iron-based systems due in part to its very high Tc when monolayers are placed on STO substrates, and in part due to the fact that the material exhibits a structural distortion near TS ~ 90K without any concomitant magnetic order. In addition, undoped b ...
... FeSe is currently one of the most hotly debated iron-based systems due in part to its very high Tc when monolayers are placed on STO substrates, and in part due to the fact that the material exhibits a structural distortion near TS ~ 90K without any concomitant magnetic order. In addition, undoped b ...
Review for Exam 1
... Mechanics. Specifically, blackbody radiator, photoelectric effect, and the electron-slit experiment are important in the development of quantum mechanics. What are these, and how did they help define the theory of small particles/waves? What is the work function? How is the wavelength of light or it ...
... Mechanics. Specifically, blackbody radiator, photoelectric effect, and the electron-slit experiment are important in the development of quantum mechanics. What are these, and how did they help define the theory of small particles/waves? What is the work function? How is the wavelength of light or it ...
3-5 Continuity and End Behavior
... a. The graph of same-day shipping function is discontinuous at each integral value of w in its domain because the function does not approach the same value from the left and the right. For example, as w approaches 70 from the left, C(w) approaches 229.25, but as w approaches 70 from the right, C(w) ...
... a. The graph of same-day shipping function is discontinuous at each integral value of w in its domain because the function does not approach the same value from the left and the right. For example, as w approaches 70 from the left, C(w) approaches 229.25, but as w approaches 70 from the right, C(w) ...
Initial Stages of Bose-Einstein Condensation
... can be performed in such detail that a more elaborate theory is required to fully understand the outcome of these future experiments. Indeed, the first steps toward this goal have already been made recently [6]. As a result of these exciting developments, we aim in this paper to present such a more ...
... can be performed in such detail that a more elaborate theory is required to fully understand the outcome of these future experiments. Indeed, the first steps toward this goal have already been made recently [6]. As a result of these exciting developments, we aim in this paper to present such a more ...
Chapter 9
... Momentum in a closed system A system that does not gain or lose mass is said to be a closed system. Also, all forces affecting the system are internal forces. The net external force on a closed system is zero and the system is called an isolated system. ...
... Momentum in a closed system A system that does not gain or lose mass is said to be a closed system. Also, all forces affecting the system are internal forces. The net external force on a closed system is zero and the system is called an isolated system. ...
document
... “... As usually conceived, however, this arbitrariness is subject to the following limitation: once one chooses [the color and phase of the wavefunction] at one space-time point, one is then not free to make any choices at other space-time points. It seems that this is not consistent with the locali ...
... “... As usually conceived, however, this arbitrariness is subject to the following limitation: once one chooses [the color and phase of the wavefunction] at one space-time point, one is then not free to make any choices at other space-time points. It seems that this is not consistent with the locali ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.