Cancer Research Project
... 5. What are the symptoms and physiological problems of this cancer? 6. What signaling pathway is this gene involved in? 7. What current treatments are available or under investigation regarding this type of oncogene (or the cancer it causes). 4. Along with the answers to these questions, you should ...
... 5. What are the symptoms and physiological problems of this cancer? 6. What signaling pathway is this gene involved in? 7. What current treatments are available or under investigation regarding this type of oncogene (or the cancer it causes). 4. Along with the answers to these questions, you should ...
Nutrigenomics
... Dietary chemicals indirectly regulate some of TFs. SREBPs are activated by protease cleavage, an event regulated by low levels of foxy sterols and changes in insulin/glucose and PUFAS PUFA intake can modulate the gene expression of several enzymes involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. Dieta ...
... Dietary chemicals indirectly regulate some of TFs. SREBPs are activated by protease cleavage, an event regulated by low levels of foxy sterols and changes in insulin/glucose and PUFAS PUFA intake can modulate the gene expression of several enzymes involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. Dieta ...
DIY DNA.Study Plan-Obj
... 1. Identify the main function of nucleic acids in the cell. 2. Indicate, in a general way, the nature of viruses (structure, sizes relative to other cells, shapes, and how they function). 3. Indicate what is needed in cells so they can repeatedly carry out a complex series of chemical reactions in a ...
... 1. Identify the main function of nucleic acids in the cell. 2. Indicate, in a general way, the nature of viruses (structure, sizes relative to other cells, shapes, and how they function). 3. Indicate what is needed in cells so they can repeatedly carry out a complex series of chemical reactions in a ...
Cells can contain one type or a mixture of organelle genomes
... Degredation of organelles in male gametes of some organisms In some plants paternal organelle genomes are distributed to cells that are destined to not become part of the embryo during early development In some organisms, the zygote destroys paternal organelle after fertilization Other organisms, pa ...
... Degredation of organelles in male gametes of some organisms In some plants paternal organelle genomes are distributed to cells that are destined to not become part of the embryo during early development In some organisms, the zygote destroys paternal organelle after fertilization Other organisms, pa ...
Genetics is
... 4.) Meiosis is used only for ____________ reproduction. This process produces ____________________ cells! Important in making what? __________________ 5.) Describe DNA’s “home” based on the PP picture that is displayed. 6.) DNA contains the ___________ material for the ________ organism! It is passe ...
... 4.) Meiosis is used only for ____________ reproduction. This process produces ____________________ cells! Important in making what? __________________ 5.) Describe DNA’s “home” based on the PP picture that is displayed. 6.) DNA contains the ___________ material for the ________ organism! It is passe ...
Integration of heterogeneous informations sources for
... •SWISS-PROT syntax and controlled vocabulary •Regular expressions as constraints ...
... •SWISS-PROT syntax and controlled vocabulary •Regular expressions as constraints ...
Techniques in Mouse
... of a gene in certain tissue late in development but the gene is also necessary early in development. A traditional knockout would result in a mutant that does not develop to stage needed. • Cre is a recombinase that excises DNA located in between LoxP sites • You generate two transgenic lines one th ...
... of a gene in certain tissue late in development but the gene is also necessary early in development. A traditional knockout would result in a mutant that does not develop to stage needed. • Cre is a recombinase that excises DNA located in between LoxP sites • You generate two transgenic lines one th ...
Molecular Genetics S Brown 30th May 2014
... The FISH technique utilizes DNA probes that are specific to regions of individual chromosomes. The probe attaches to the spread of chromosomes from a cell, then a fluorescein stain is applied. This "paints" the chromosome so that it is visible with the aid of a fluorescent microscope. In the exampl ...
... The FISH technique utilizes DNA probes that are specific to regions of individual chromosomes. The probe attaches to the spread of chromosomes from a cell, then a fluorescein stain is applied. This "paints" the chromosome so that it is visible with the aid of a fluorescent microscope. In the exampl ...
gene regulation
... base of tRNA may form H-bonds with more than 1 kind of nucleotide • Ie AAU and AAC Asn ...
... base of tRNA may form H-bonds with more than 1 kind of nucleotide • Ie AAU and AAC Asn ...
File
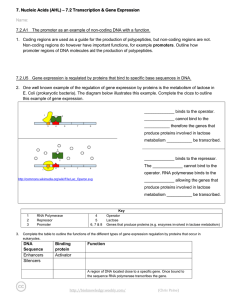
... 7.2.U4 Splicing of mRNA increases the number of different proteins an organism can produce. 16. The splicing process above can happen in different ways to the same gene. a. Describe how this happens. ...
... 7.2.U4 Splicing of mRNA increases the number of different proteins an organism can produce. 16. The splicing process above can happen in different ways to the same gene. a. Describe how this happens. ...
Biosafety and recombinant DNA technology
... • Animals carrying foreign genetic material (transgenic animals) should be handled in containment levels appropriate to the characteristics of the products of the foreign genes. • Animals with targeted deletions of specific genes (“knock-out” animals) do not generally present particular biological h ...
... • Animals carrying foreign genetic material (transgenic animals) should be handled in containment levels appropriate to the characteristics of the products of the foreign genes. • Animals with targeted deletions of specific genes (“knock-out” animals) do not generally present particular biological h ...
The Anatomy of the Human Genome
... those involving model organisms. Comparative genomics is a valuable way to gain understanding of the structure and function of the human genome and its genes. Expressed sequence tags (ESTs), that is, complementary DNA created from messenger RNA by reverse transcription, were developed in 199144 as a ...
... those involving model organisms. Comparative genomics is a valuable way to gain understanding of the structure and function of the human genome and its genes. Expressed sequence tags (ESTs), that is, complementary DNA created from messenger RNA by reverse transcription, were developed in 199144 as a ...
Social media policy
... The number of bases that are read at one time (that is the number of letters that will appear in each read). This differs between technologies, so optimum fragment length varies. Recessive allele A gene variant in one copy of a pair of genes that will not affect the individual. Reference genome An e ...
... The number of bases that are read at one time (that is the number of letters that will appear in each read). This differs between technologies, so optimum fragment length varies. Recessive allele A gene variant in one copy of a pair of genes that will not affect the individual. Reference genome An e ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translation. The ribosomes use information from mRNA to produce proteins 11. Why is crossing ...
... 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translation. The ribosomes use information from mRNA to produce proteins 11. Why is crossing ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... Item 3: Summarize the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes ■ Chromosome – structure in the nucleus consisting of one long thread of DNA that is tightly coiled around special proteins called histones ■ DNA – molecule composed of nucleotides, providing the blueprint for the making of pro ...
... Item 3: Summarize the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes ■ Chromosome – structure in the nucleus consisting of one long thread of DNA that is tightly coiled around special proteins called histones ■ DNA – molecule composed of nucleotides, providing the blueprint for the making of pro ...
Chapter 26: Biotechnology
... sequence the DNA bases of each chromosome and to map the genes on each chromosome; the first goal is completed. Gene therapy is now being used to replace defective genes with healthy genes and to help cure various human ills. ...
... sequence the DNA bases of each chromosome and to map the genes on each chromosome; the first goal is completed. Gene therapy is now being used to replace defective genes with healthy genes and to help cure various human ills. ...
Figure 1
... between the sensory region and the non-sensory region. Mprs18c is strongly expressed in the sensory region. Sagital sections. Scale bar: 100 µm (valid for A, B, C,D). E & F: Two examples of transcripts expressed in the retina:Mid1 (Midline 1) and Fubp1 (Far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1) ...
... between the sensory region and the non-sensory region. Mprs18c is strongly expressed in the sensory region. Sagital sections. Scale bar: 100 µm (valid for A, B, C,D). E & F: Two examples of transcripts expressed in the retina:Mid1 (Midline 1) and Fubp1 (Far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1) ...
Chapter 26: Biotechnology
... sequence the DNA bases of each chromosome and to map the genes on each chromosome; the first goal is completed. Gene therapy is now being used to replace defective genes with healthy genes and to help cure various human ills. ...
... sequence the DNA bases of each chromosome and to map the genes on each chromosome; the first goal is completed. Gene therapy is now being used to replace defective genes with healthy genes and to help cure various human ills. ...
DNA technology
... • Circular DNA from bacteria = plasmids • Target DNA recombined in plasmid • Bacteria rapidly reproduces many clones ...
... • Circular DNA from bacteria = plasmids • Target DNA recombined in plasmid • Bacteria rapidly reproduces many clones ...
semester i lsm3252 evolution and comparative
... Dawkins, R. 1989. The Selfish Gene. Reprinted from 1976 edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Futuyma, D. 1998. Evolutionary Biology, 3rd edition. Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates Inc. Maynard Smith, J., and Szathmáry, E. 1999. The origins of life: From the birth of life to the origin of langua ...
... Dawkins, R. 1989. The Selfish Gene. Reprinted from 1976 edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Futuyma, D. 1998. Evolutionary Biology, 3rd edition. Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates Inc. Maynard Smith, J., and Szathmáry, E. 1999. The origins of life: From the birth of life to the origin of langua ...
Experience 2 Follow-up 1. Answer the following
... 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. ...
... 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. ...
Forum: Environmental Commission 2016 Issue: Eliminating Disease
... The use of genetic engineering to eliminate diseases of the immune system has existed as early as the 1970s, when scientists proposed it for treatment of hereditary diseases as a result of mutated genes. The basis for this treatment would be to remove the gene causing the disease, and replacing it w ...
... The use of genetic engineering to eliminate diseases of the immune system has existed as early as the 1970s, when scientists proposed it for treatment of hereditary diseases as a result of mutated genes. The basis for this treatment would be to remove the gene causing the disease, and replacing it w ...
Evolution after Darwin - Max-Planck
... young remain at their mothers’ breast for an average of five years, and even as long as seven to eight years in the case of the Orangutan. This change in the course of the evolution of human children is based on reliable access to “supplementary” nutrition. “This results in childhood in humans inclu ...
... young remain at their mothers’ breast for an average of five years, and even as long as seven to eight years in the case of the Orangutan. This change in the course of the evolution of human children is based on reliable access to “supplementary” nutrition. “This results in childhood in humans inclu ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.