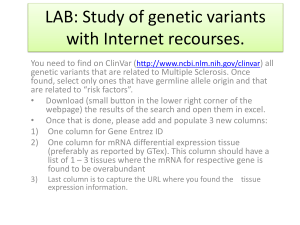
Genetics Open Ended Questions
... Genetic engineering generally involves choosing and isolating the gene to be inserted. Isolation usually involves using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to create multiple copies of the gene. Once isolated, the gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid. The gene to be inserted into the genetically mo ...
... Genetic engineering generally involves choosing and isolating the gene to be inserted. Isolation usually involves using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to create multiple copies of the gene. Once isolated, the gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid. The gene to be inserted into the genetically mo ...
From Genome Sequencing to Biology in the Lab of Milk and
... common gene in an ancestral species. • Paralogs = genes that have diverged due to gene duplication. • Orthologs are more likely than paralogs to have conserved function. • Orthologs cannot be identified using BLAST or FASTA sequence comparison alone. • Reliable ortholog identification requires phylo ...
... common gene in an ancestral species. • Paralogs = genes that have diverged due to gene duplication. • Orthologs are more likely than paralogs to have conserved function. • Orthologs cannot be identified using BLAST or FASTA sequence comparison alone. • Reliable ortholog identification requires phylo ...
APOC1 gene rs4420638 SNP
... (medicine) The arrest of a secretion or bodily discharge In genetics, epistasis pertains to the interaction of the genes at two or more loci, and as a result the effect of the gene depends on the presence of one or more modifier genes. There is that one gene or allele masking the phenotypic expressi ...
... (medicine) The arrest of a secretion or bodily discharge In genetics, epistasis pertains to the interaction of the genes at two or more loci, and as a result the effect of the gene depends on the presence of one or more modifier genes. There is that one gene or allele masking the phenotypic expressi ...
Bacteria Evolving - American Museum of Natural History
... mutations. Mutations are any change in the sequence of DNA nucleotides within an organism’s genome. The main cause of mutations are exposure to foreign chemicals or radiation, errors during DNA replication, and from insertion or deletion of DNA segments. If a mutation is beneficial, it gives the org ...
... mutations. Mutations are any change in the sequence of DNA nucleotides within an organism’s genome. The main cause of mutations are exposure to foreign chemicals or radiation, errors during DNA replication, and from insertion or deletion of DNA segments. If a mutation is beneficial, it gives the org ...
Sex-Linked Genes
... by taking an egg from one sheep and replacing its nucleus the nucleus from another sheep. The egg then grows into a copy of the sheep with that nucleus. ...
... by taking an egg from one sheep and replacing its nucleus the nucleus from another sheep. The egg then grows into a copy of the sheep with that nucleus. ...
Chapter 10
... • Purpose – We don’t know the function of the gene until it doesn’t work. Intentional Use of Mutagens Alkylating Agents (chemical) – remove a DNA base and another can be added Acridines (dye) – base is removed but not replaced causing a frameshift mutation Scientist cannot really choose where the mu ...
... • Purpose – We don’t know the function of the gene until it doesn’t work. Intentional Use of Mutagens Alkylating Agents (chemical) – remove a DNA base and another can be added Acridines (dye) – base is removed but not replaced causing a frameshift mutation Scientist cannot really choose where the mu ...
Gene Section ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... GADD45 in the cell cycle regulation: involved in mediating cell cycle arrest in response to radiationinduced DNA damage; required in the regulation of G1/S and S phase checkpoints; other probable functions similar to that of homologs in other species, ...
... GADD45 in the cell cycle regulation: involved in mediating cell cycle arrest in response to radiationinduced DNA damage; required in the regulation of G1/S and S phase checkpoints; other probable functions similar to that of homologs in other species, ...
PPT2
... • The aim of stem cell research is to supply cells for the repair of damaged or diseased organs • One benefit of DNA technology is identification of human genes in which mutation plays a role in genetic diseases • Advances in DNA technology and genetic research are important to the development of n ...
... • The aim of stem cell research is to supply cells for the repair of damaged or diseased organs • One benefit of DNA technology is identification of human genes in which mutation plays a role in genetic diseases • Advances in DNA technology and genetic research are important to the development of n ...
The process by which a species becomes better suited to
... D. The best adapted individuals survive and reproduce, contributing the most genes to the next generation E. Individuals that mutate in response to their environment will survive ...
... D. The best adapted individuals survive and reproduce, contributing the most genes to the next generation E. Individuals that mutate in response to their environment will survive ...
Basic Bioinformatics
... But: extracting that information is difficult. How to convert a string of ACGT’s into knowledge of how the organism works is hard. Most of the work is on the computer, with key confirming experiments done in the “wet lab”. The sequence below contains a gene critical for life: the gene that initiates ...
... But: extracting that information is difficult. How to convert a string of ACGT’s into knowledge of how the organism works is hard. Most of the work is on the computer, with key confirming experiments done in the “wet lab”. The sequence below contains a gene critical for life: the gene that initiates ...
Basic Bioinformatics - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... But: extracting that information is difficult. How to convert a string of ACGT’s into knowledge of how the organism works is hard. Most of the work is on the computer, with key confirming experiments done in the “wet lab”. The sequence below contains a gene critical for life: the gene that initiates ...
... But: extracting that information is difficult. How to convert a string of ACGT’s into knowledge of how the organism works is hard. Most of the work is on the computer, with key confirming experiments done in the “wet lab”. The sequence below contains a gene critical for life: the gene that initiates ...
Basic Bioinformatics
... But: extracting that information is difficult. How to convert a string of ACGT’s into knowledge of how the organism works is hard. Most of the work is on the computer, with key confirming experiments done in the “wet lab”. The sequence below contains a gene critical for life: the gene that initiates ...
... But: extracting that information is difficult. How to convert a string of ACGT’s into knowledge of how the organism works is hard. Most of the work is on the computer, with key confirming experiments done in the “wet lab”. The sequence below contains a gene critical for life: the gene that initiates ...
Chapter 10: Retroelements in the Mouse
... True or False? The germline content of ecotropic, xenotropic and polytropic MuLV has been shown to undergo gain or loss due to reinsertions or deletions in germ cells; loss of germline proviruses seems to occur more frequently than gain. Which of these statements regarding proviral reinsertion is fa ...
... True or False? The germline content of ecotropic, xenotropic and polytropic MuLV has been shown to undergo gain or loss due to reinsertions or deletions in germ cells; loss of germline proviruses seems to occur more frequently than gain. Which of these statements regarding proviral reinsertion is fa ...
Databases - Orly Alter`s
... g) Compare the raster and spot image displays. Can you detect similar expression patterns in both displays? ...
... g) Compare the raster and spot image displays. Can you detect similar expression patterns in both displays? ...
MS Word Version
... was of such great advantage that adults able to digest milk left more surviving offspring, and the genetic change swept through the population. This instance of gene-culture interaction turns out to be far from unique. In the last few years, biologists have been able to scan the whole human genome f ...
... was of such great advantage that adults able to digest milk left more surviving offspring, and the genetic change swept through the population. This instance of gene-culture interaction turns out to be far from unique. In the last few years, biologists have been able to scan the whole human genome f ...
Human Culture, an Evolutionary Force
... was of such great advantage that adults able to digest milk left more surviving offspring, and the genetic change swept through the population. This instance of gene-culture interaction turns out to be far from unique. In the last few years, biologists have been able to scan the whole human genome f ...
... was of such great advantage that adults able to digest milk left more surviving offspring, and the genetic change swept through the population. This instance of gene-culture interaction turns out to be far from unique. In the last few years, biologists have been able to scan the whole human genome f ...
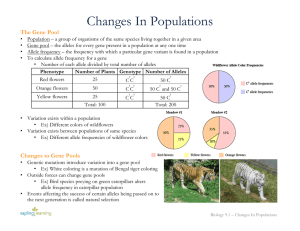
Changes In Populations
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... expressed, interrupt most eukaryotic genes • Exons = portions of a gene that are expressed ...
... expressed, interrupt most eukaryotic genes • Exons = portions of a gene that are expressed ...
A detailed gene map of pig chromosome 4, where the first
... corresponding human gene homology is presented for 101 genes/markers from the RH and linkage maps, 34 that maps to HSA8 and 67 to HSA1. The markers cover the entire length of SSC4 but an emphasis has been made to put markers within the region harbouring the FAT1 QTL, 23 markers has been added to thi ...
... corresponding human gene homology is presented for 101 genes/markers from the RH and linkage maps, 34 that maps to HSA8 and 67 to HSA1. The markers cover the entire length of SSC4 but an emphasis has been made to put markers within the region harbouring the FAT1 QTL, 23 markers has been added to thi ...
Methods
... genome and lyse the cells, taking with them pieces of the bacterial genome that contained the sequence that had been manipulated. These phage were then used to infect other bacterial strains and recombination between the genes of the recipient cell and the genes from the lysed or donor cells was all ...
... genome and lyse the cells, taking with them pieces of the bacterial genome that contained the sequence that had been manipulated. These phage were then used to infect other bacterial strains and recombination between the genes of the recipient cell and the genes from the lysed or donor cells was all ...
070329Syl
... give short summaries of assigned papers and answer direct questions on them and other course content. For each class two students will be asked to read all of the assigned papers and possibly an additional one. Each is then available to present the entire paper. Others are asked to read the assigned ...
... give short summaries of assigned papers and answer direct questions on them and other course content. For each class two students will be asked to read all of the assigned papers and possibly an additional one. Each is then available to present the entire paper. Others are asked to read the assigned ...
Genes and Cell Division
... genes to form a new organism • Meiosis – The process during which genetic information is copied during sexual reproduction • What is the difference between meiosis and mitosis? – In Meiosis only half of the genes are passed on, the other half come from the second parent. In mitosis all the genes are ...
... genes to form a new organism • Meiosis – The process during which genetic information is copied during sexual reproduction • What is the difference between meiosis and mitosis? – In Meiosis only half of the genes are passed on, the other half come from the second parent. In mitosis all the genes are ...
Intro to Biotechnology
... • The production of human embryos for use in research • Goal of this process is not to create cloned human beings, but rather to harvest stem cells that can be used to study human development and to treat disease. • Stem cells are important to biomedical researchers because they can be used to gener ...
... • The production of human embryos for use in research • Goal of this process is not to create cloned human beings, but rather to harvest stem cells that can be used to study human development and to treat disease. • Stem cells are important to biomedical researchers because they can be used to gener ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.