From DNA to Proteins
... It is caused by point mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for a transmembrane protein that acts as an ion pump. The CFTR gene is found on chromosome 7. It codes for 1480 amino acids. There are over 1000 known mutations, which can affect the function of the CFTR gene in different ways. In around ...
... It is caused by point mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for a transmembrane protein that acts as an ion pump. The CFTR gene is found on chromosome 7. It codes for 1480 amino acids. There are over 1000 known mutations, which can affect the function of the CFTR gene in different ways. In around ...
Microarray_module_lecture_(both_courses)
... Here: 9.21% are in the red shaded area. p= 0.09 Accept null hypothesis: Treatment and control are NOT different, M = 0 ...
... Here: 9.21% are in the red shaded area. p= 0.09 Accept null hypothesis: Treatment and control are NOT different, M = 0 ...
Gendia-Brochure-STID
... 1. In case of normal STID results in both partners : no specific follow up is necessary unless ultrasound examination of the fetus reveals anomalies and further fetal studies might be indicated. 2. In case one of the couple is carrier: 2A. If one of the partners is a carrier of a mutation in a rare ...
... 1. In case of normal STID results in both partners : no specific follow up is necessary unless ultrasound examination of the fetus reveals anomalies and further fetal studies might be indicated. 2. In case one of the couple is carrier: 2A. If one of the partners is a carrier of a mutation in a rare ...
Eat to Regulate Your Genes?
... gene is a segment of DNA that can be “transcribed” into messenger RNA, which then is (or may be) “translated” into protein. The entire process is broadly known as “gene expression.” However, one of the hottest fields of research in molecular biology over the past decade or two has to do with DNA reg ...
... gene is a segment of DNA that can be “transcribed” into messenger RNA, which then is (or may be) “translated” into protein. The entire process is broadly known as “gene expression.” However, one of the hottest fields of research in molecular biology over the past decade or two has to do with DNA reg ...
Screenings Test for Inherited Disease (STID)
... 1. In case of normal STID results in both partners : no specific follow up is necessary unless ultrasound examination of the fetus reveals anomalies and further fetal studies might be indicated. 2. In case one of the couple is carrier: 2A. If one of the partners is a carrier of a mutation in a rare ...
... 1. In case of normal STID results in both partners : no specific follow up is necessary unless ultrasound examination of the fetus reveals anomalies and further fetal studies might be indicated. 2. In case one of the couple is carrier: 2A. If one of the partners is a carrier of a mutation in a rare ...
Report IV. 2015. june
... The heat shock transcription factor HSF1 directly regulates the activity of four UPR (unfolded protein response) genes in the nematode Caenorhabditos elegans. Heat shock provokes endoplasmic reticulum stress in mammalian cells; however, silencing of Hsf1 did not decrease the level of stress markers, ...
... The heat shock transcription factor HSF1 directly regulates the activity of four UPR (unfolded protein response) genes in the nematode Caenorhabditos elegans. Heat shock provokes endoplasmic reticulum stress in mammalian cells; however, silencing of Hsf1 did not decrease the level of stress markers, ...
2-Familial adenomatous polyposis coli
... Most common polymorphisms are neutral, but some cause subtle changes in gene expression or in protein structure and function .It is thought that these polymorphisms lead to variations in phenotype within the general population, including variations in susceptibility to common diseases. An example is ...
... Most common polymorphisms are neutral, but some cause subtle changes in gene expression or in protein structure and function .It is thought that these polymorphisms lead to variations in phenotype within the general population, including variations in susceptibility to common diseases. An example is ...
Gene Expression
... mRNA sequence and translates it into the ________ _______ sequence of the protein. The ribosome starts at the sequence _______, and then reads 3 nucleotides at a time. Each 3-nucleotide codon specifies a particular amino __________. The “stop” ________ (UAA, UAG, and UGA) tell the ribosome that the ...
... mRNA sequence and translates it into the ________ _______ sequence of the protein. The ribosome starts at the sequence _______, and then reads 3 nucleotides at a time. Each 3-nucleotide codon specifies a particular amino __________. The “stop” ________ (UAA, UAG, and UGA) tell the ribosome that the ...
ASA POSTER-2008
... identified, mapped and then remobilized for localized gene targeting. A robust platform was developed to use transposon targeting approaches in barley to complement existing, extensive genomic resources. In our NSF Plant Genome Research Project we (i) generated 200 single-copy Ds TNPs, (ii) determin ...
... identified, mapped and then remobilized for localized gene targeting. A robust platform was developed to use transposon targeting approaches in barley to complement existing, extensive genomic resources. In our NSF Plant Genome Research Project we (i) generated 200 single-copy Ds TNPs, (ii) determin ...
Diapositive 1
... description, accession number…), external links (MGI, Homologene …) and internal data (Transcriptomic data, EST, MACSIMS, MAGOS). In the future, each gene will be characterized by a retinal propensity score. The website will be designed for natural language requests through the use of our in-house d ...
... description, accession number…), external links (MGI, Homologene …) and internal data (Transcriptomic data, EST, MACSIMS, MAGOS). In the future, each gene will be characterized by a retinal propensity score. The website will be designed for natural language requests through the use of our in-house d ...
Name
... (5) Define and distinguish between heterochromatin and euchromatin. heterochromatin is the condensed, gene poor DNA found mainly near centromeres and telomeres euchromatin is the less condensed, gene rich DNA where most genes are transcribed (5) Define and distinguish between centromere and telomere ...
... (5) Define and distinguish between heterochromatin and euchromatin. heterochromatin is the condensed, gene poor DNA found mainly near centromeres and telomeres euchromatin is the less condensed, gene rich DNA where most genes are transcribed (5) Define and distinguish between centromere and telomere ...
Lecture Notes with Key Images
... the nature of the double helix (on the left) and the chemical components making up each strand (on the right). ...
... the nature of the double helix (on the left) and the chemical components making up each strand (on the right). ...
Name_______________________ Period
... If two genes are linked on the same chromosome, we call this combination the parental combination. These genes will be transmitted as a unit and will not sort independently. However, during meiosis, crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes, and the linked genes can become “unlinked.” In g ...
... If two genes are linked on the same chromosome, we call this combination the parental combination. These genes will be transmitted as a unit and will not sort independently. However, during meiosis, crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes, and the linked genes can become “unlinked.” In g ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. State the purpose of each. Why must the genetic code be written in triplets of nucleotides? From where do ribosomes orginate? Describe the relationship between a DNA triplet, a codon, and an anticodon. What is the evolutionary si ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. State the purpose of each. Why must the genetic code be written in triplets of nucleotides? From where do ribosomes orginate? Describe the relationship between a DNA triplet, a codon, and an anticodon. What is the evolutionary si ...
Gene duplication and divergence
... There are thousands of gene families within the human genome. Like the globin gene family, each of these families is made up of related but slightly different members that arose from an ancestral form. One example is the histone gene family that gives rise to the various different histone proteins t ...
... There are thousands of gene families within the human genome. Like the globin gene family, each of these families is made up of related but slightly different members that arose from an ancestral form. One example is the histone gene family that gives rise to the various different histone proteins t ...
EOC Practice Quiz (5) - Duplin County Schools
... c. a polyploidy. d. recombinant DNA. 16. A gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry a plasmid containing foreign DNA from those that do not is called a (an) a. resistance gene. b. antibiotic. c. genetic marker. d. clone. Objective 3.3.3 17. The human genome was sequenced a. by ...
... c. a polyploidy. d. recombinant DNA. 16. A gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry a plasmid containing foreign DNA from those that do not is called a (an) a. resistance gene. b. antibiotic. c. genetic marker. d. clone. Objective 3.3.3 17. The human genome was sequenced a. by ...
Transgenic Organisms - OG
... • May be the first known naturally-occurring transgenic species • It is able to use the chloroplasts from the algae on which it feeds to create energy by photosynthesis. No other animals have the genes necessary to utilize chloroplasts this way. • The gene sequence identical to that of an algal phot ...
... • May be the first known naturally-occurring transgenic species • It is able to use the chloroplasts from the algae on which it feeds to create energy by photosynthesis. No other animals have the genes necessary to utilize chloroplasts this way. • The gene sequence identical to that of an algal phot ...
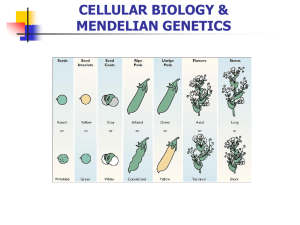
Lecture: Mendelian Genetics
... Monogenic = Trait coded for by a single gene (ex. Taster trait for “PTC”) Polygenic = Trait coded for by more than one gene (ex. Skin color) ...
... Monogenic = Trait coded for by a single gene (ex. Taster trait for “PTC”) Polygenic = Trait coded for by more than one gene (ex. Skin color) ...
locomotion in a consanguineous kindred the gene
... exons and encoding 1941 amino acids (Fig. 2A). Proline at this site was present in all species analyzed (Fig. 2C), including the most distantly related sequenced ortholog, the Tetraodon nigroviridis WDR81 protein, which is 47.8% identical and 57.2% similar and has a distance score of 0.76 compared w ...
... exons and encoding 1941 amino acids (Fig. 2A). Proline at this site was present in all species analyzed (Fig. 2C), including the most distantly related sequenced ortholog, the Tetraodon nigroviridis WDR81 protein, which is 47.8% identical and 57.2% similar and has a distance score of 0.76 compared w ...
Gene Set Analysis with Phenotypic Screening Data Results and Validation Purpose
... positive gene sets • The analysis was run on a viral infection cell proliferation assay then the significant sets were clustered (below). The themes are consistent with validated targets and pathways in viral infection. ...
... positive gene sets • The analysis was run on a viral infection cell proliferation assay then the significant sets were clustered (below). The themes are consistent with validated targets and pathways in viral infection. ...
Transcription – Part II
... 5. Explain termination of transcription in eukaryotes. 6. Explain the 5’ capping mechanism. Be sure to include all relevant components. 7. Explain the polyadenylation mechanism. Be sure to include all relevant components. Transcriptional Regulation - Eukaryotes 8. Regulation of gene expression in eu ...
... 5. Explain termination of transcription in eukaryotes. 6. Explain the 5’ capping mechanism. Be sure to include all relevant components. 7. Explain the polyadenylation mechanism. Be sure to include all relevant components. Transcriptional Regulation - Eukaryotes 8. Regulation of gene expression in eu ...
Traditional and Modern Breeding Methods
... • Oil, starch and amino acids • Nutrient quality Achieving all these goals will require not only traditional breeder skills, but will be accelerated by the use of novel molecular techniques and biotechnology ...
... • Oil, starch and amino acids • Nutrient quality Achieving all these goals will require not only traditional breeder skills, but will be accelerated by the use of novel molecular techniques and biotechnology ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.