1 - Videolectures
... A shows the contribution to a sibling relative risk of type 2 diabetes for each of seven SNPs, as estimated from data reported by Manolio et al.1 with the use of formulas from Risch and Merikangas2 and plotted against the rank order of the SNPs in terms of the magnitude of their contributions. B sh ...
... A shows the contribution to a sibling relative risk of type 2 diabetes for each of seven SNPs, as estimated from data reported by Manolio et al.1 with the use of formulas from Risch and Merikangas2 and plotted against the rank order of the SNPs in terms of the magnitude of their contributions. B sh ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND GENETIC ENGINEERING
... used in genetic engineering? Plasmids are circular DNA molecules found in bacteria that are often used for genetic engineering. The plasmid is cut with the same restriction enzyme used to cut out the gene of interest. Once the plasmid has the new gene, it is called recombinant DNA. ...
... used in genetic engineering? Plasmids are circular DNA molecules found in bacteria that are often used for genetic engineering. The plasmid is cut with the same restriction enzyme used to cut out the gene of interest. Once the plasmid has the new gene, it is called recombinant DNA. ...
File - Schuette Science
... There are two major mistakes that can happen: 1. Chromosomal Mutations 2. Gene Mutations ...
... There are two major mistakes that can happen: 1. Chromosomal Mutations 2. Gene Mutations ...
UBC`s Bioinformatics Centre: Dreams, plans and action
... – Ensembl is fully automated, and this does not allow userdriven input. ...
... – Ensembl is fully automated, and this does not allow userdriven input. ...
PDF
... the chromosomes and move progressively along the DNA strand, synthesizing long and complex molecules of RNA as they go. The process intensifies as more polymerase becomes available, and the consequence is an unfolding of the chromosomal DNA to form thousands of loops or transcription units, and ulti ...
... the chromosomes and move progressively along the DNA strand, synthesizing long and complex molecules of RNA as they go. The process intensifies as more polymerase becomes available, and the consequence is an unfolding of the chromosomal DNA to form thousands of loops or transcription units, and ulti ...
BIO208
... 11. A bacterial cell has a lactose operon but the promoter is defective (mutated). All else is normal. The bacteria is transformed with a plasmid that contains a wildtype (non-mutated) promoter, amp resistance gene, and origin of replication. Can the cell utilize lactose when grown in the presence o ...
... 11. A bacterial cell has a lactose operon but the promoter is defective (mutated). All else is normal. The bacteria is transformed with a plasmid that contains a wildtype (non-mutated) promoter, amp resistance gene, and origin of replication. Can the cell utilize lactose when grown in the presence o ...
Regulation
... II. Regulation of transcription (induction and repression): A. Some enzymes are always made at the same levels. 1. This is called: __________________ expression 2. The enzyme is always present regardless of nutrients available to the organism. 3. The control of mRNA levels is governed by: ...
... II. Regulation of transcription (induction and repression): A. Some enzymes are always made at the same levels. 1. This is called: __________________ expression 2. The enzyme is always present regardless of nutrients available to the organism. 3. The control of mRNA levels is governed by: ...
High Mutation Rates Have Driven Extensive Structural
... >23 changes in length >4.4 X 10-4 per father-toson transmission Specimens who displayed frequent changes also showed limited copy number variation. ...
... >23 changes in length >4.4 X 10-4 per father-toson transmission Specimens who displayed frequent changes also showed limited copy number variation. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
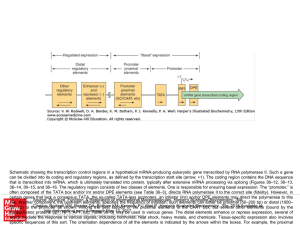
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
Heredity and the Environment
... each chromosome has 23 single stranded chromosomes; when sperm and egg unite, there is a unique pairing of chromosomes, thus genetic diversity is accomplished ...
... each chromosome has 23 single stranded chromosomes; when sperm and egg unite, there is a unique pairing of chromosomes, thus genetic diversity is accomplished ...
Epigenetics
... • Their single X can be either maternal or paternal in origin • The ones with a maternal X are much more likely to have the social problems • All boys have a maternally-derived X • So, there could be imprinted gene(s) on the X, which are involved in social function • When maternally inherited this c ...
... • Their single X can be either maternal or paternal in origin • The ones with a maternal X are much more likely to have the social problems • All boys have a maternally-derived X • So, there could be imprinted gene(s) on the X, which are involved in social function • When maternally inherited this c ...
File ap notes chapter 15
... genes are located on different chromosomes When recombinant frequency is less than 50% genes are located on the same chromosome; recombinants result from crossing over; amount of recombinants is related to the distance between the two gene’s loci ...
... genes are located on different chromosomes When recombinant frequency is less than 50% genes are located on the same chromosome; recombinants result from crossing over; amount of recombinants is related to the distance between the two gene’s loci ...
Full text - UBC Psychology - University of British Columbia
... doing research on people has different implications from doing research on fruit flies, because people are affected by the theories that they encounter. Learning of scientific theories changes the ways people look at the world and at themselves. Now, if all theories were communicated in such a way t ...
... doing research on people has different implications from doing research on fruit flies, because people are affected by the theories that they encounter. Learning of scientific theories changes the ways people look at the world and at themselves. Now, if all theories were communicated in such a way t ...
When humans first ventured out of Africa some 60000 years ago
... region (HVR 1 and 2), where the rate of mutation has been shown to be up to a hundred times greater than that of the nuclear genome. Because of its much shorter length (several hundred nucleotides versus millions of nucleotides for the Y), the HVR can be quickly scanned to reveal many informative mu ...
... region (HVR 1 and 2), where the rate of mutation has been shown to be up to a hundred times greater than that of the nuclear genome. Because of its much shorter length (several hundred nucleotides versus millions of nucleotides for the Y), the HVR can be quickly scanned to reveal many informative mu ...
Sex-omics - Florida State University College of Medicine
... We identified 12 core DEGs that have sex-specific differential gene expression in the hippocampus of males and females. A) Venn diagram of the sex-specific DEGs that overlap between the different strains. The genes that overlap in all strains make up a sub-set of the core DEGs (PWD is not shown due ...
... We identified 12 core DEGs that have sex-specific differential gene expression in the hippocampus of males and females. A) Venn diagram of the sex-specific DEGs that overlap between the different strains. The genes that overlap in all strains make up a sub-set of the core DEGs (PWD is not shown due ...
Glossary for Ancient DNA and Human Evolution
... Transcription Factor Proteins: Alter gene expression by binding directly or indirectly to DNA. Genotype: The two alleles at one or more diploid loci. Mutation: Change of a DNA sequence. Indels: Insertions or deletions of DNA sequence. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Single nucleotide differe ...
... Transcription Factor Proteins: Alter gene expression by binding directly or indirectly to DNA. Genotype: The two alleles at one or more diploid loci. Mutation: Change of a DNA sequence. Indels: Insertions or deletions of DNA sequence. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Single nucleotide differe ...
Pippa Thomson - University of Edinburgh
... –Adult and embryonic stage- Microarray –Confirmation/Investigation of changes –Series of embryonic; postnatal and adult stages –Drug treated adult mice ...
... –Adult and embryonic stage- Microarray –Confirmation/Investigation of changes –Series of embryonic; postnatal and adult stages –Drug treated adult mice ...
Genetics Mendel
... Principle of Segregation - The two factors for a characteristic separate during the formation of eggs and sperm. Principle of Independent Assortment - The factors for different characteristics are distributed to reproductive cells independently. ...
... Principle of Segregation - The two factors for a characteristic separate during the formation of eggs and sperm. Principle of Independent Assortment - The factors for different characteristics are distributed to reproductive cells independently. ...
A primer on the structure and function of genes
... and double strand forms. Regions of RNA molecules, although found in the form a single polynucleotide chains, often pair up with other regions of the same chain, forming secondary structures. Also, base pairing between G and U is possible, whereas pairing between G and T in DNA does not occur. ...
... and double strand forms. Regions of RNA molecules, although found in the form a single polynucleotide chains, often pair up with other regions of the same chain, forming secondary structures. Also, base pairing between G and U is possible, whereas pairing between G and T in DNA does not occur. ...
PPT Chapter 03 Nature Nurture Quiz
... • B) there would be a trivial reduction in human diversity. • C) the human race would evolve to a very unusual form. • D) future humans would be unable to deal with colder climates. ...
... • B) there would be a trivial reduction in human diversity. • C) the human race would evolve to a very unusual form. • D) future humans would be unable to deal with colder climates. ...
Name: Date: Period: Part I. The Lac Operon. Follow this link: http:
... Part II. Hox genes. Visit this website: http://www.dnaftb.org/37/index.html. Now read through the concept tab. Once completed click on the animation tab and begin answering the questions below. Recall that the purpose of this worksheet is not to get quick, right answers but to comprehend what you a ...
... Part II. Hox genes. Visit this website: http://www.dnaftb.org/37/index.html. Now read through the concept tab. Once completed click on the animation tab and begin answering the questions below. Recall that the purpose of this worksheet is not to get quick, right answers but to comprehend what you a ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.