Gene Ontology Analysis with Cytoscape
... Gene Ontology (GO) is now an essential resource in bioinformatics. It defines a controlled vocabulary of terms in biological process, molecular function, and cellular location, and relates the terms in a somewhat-organized fashion. Expert curators assign genes to GO categories, and the majority of g ...
... Gene Ontology (GO) is now an essential resource in bioinformatics. It defines a controlled vocabulary of terms in biological process, molecular function, and cellular location, and relates the terms in a somewhat-organized fashion. Expert curators assign genes to GO categories, and the majority of g ...
reproduction
... have entered our genomes throughout the course of evolution, mainly by viral transfection (Jaenisch 1997, Yoder et al. 1997). Forty-five percent of the human genome consists of viral retrotranposons and endogenous retroviruses (Lander et al. 2001), repeat sequences that are capable of moving around ...
... have entered our genomes throughout the course of evolution, mainly by viral transfection (Jaenisch 1997, Yoder et al. 1997). Forty-five percent of the human genome consists of viral retrotranposons and endogenous retroviruses (Lander et al. 2001), repeat sequences that are capable of moving around ...
(Japan), organized by Nori Satoh
... possible relationships of altered roles of RA in urochordate development to genomic events, such as rupture of the Hox-cluster, in the context of a new understanding of chordate phylogeny. (Cañestro and Postlethwait, 2007 Dev Biol) ...
... possible relationships of altered roles of RA in urochordate development to genomic events, such as rupture of the Hox-cluster, in the context of a new understanding of chordate phylogeny. (Cañestro and Postlethwait, 2007 Dev Biol) ...
Mining medical data using multiple corpora
... The first idea was to access automatically GenBank entries corresponding to genes from Transcriptomics server thanks to AccNum. GenBank is part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration, which comprises the DNA DataBank of Japan (DDBJ), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory ...
... The first idea was to access automatically GenBank entries corresponding to genes from Transcriptomics server thanks to AccNum. GenBank is part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration, which comprises the DNA DataBank of Japan (DDBJ), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory ...
Multiple disease genes cause hypertrophic - Heart
... scope of such genetic testing. Genetic diagnosis based on identification of MHC mutations is itself complex because of the large variety of mutations causing disease. Some of the mutations have been identified in several families (for example Arg4O3Gln, Val606Met, and Arg7 1 9Trp (table), but many o ...
... scope of such genetic testing. Genetic diagnosis based on identification of MHC mutations is itself complex because of the large variety of mutations causing disease. Some of the mutations have been identified in several families (for example Arg4O3Gln, Val606Met, and Arg7 1 9Trp (table), but many o ...
SERK and APOSTART. Candidate Genes for
... the sexual process. Since natural apomixis does not, on the basis of available information, seem to result from the failure of a single reproductive pathway gene, but rather from an epistatic, possibly silencing, action exerted on the normal sexual reproductive pathway by a set of genes inherited as ...
... the sexual process. Since natural apomixis does not, on the basis of available information, seem to result from the failure of a single reproductive pathway gene, but rather from an epistatic, possibly silencing, action exerted on the normal sexual reproductive pathway by a set of genes inherited as ...
Genomics 1
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Isolate genomic DNA and break into fragments. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Isolate genomic DNA and break into fragments. ...
on Mendel`s principles of heredity
... humans: sickle cell anemia • Sickle cell anemia is a single gene, recessive disease that causes red blood cells to “sickle” (“C” shaped) as shown here. • The disease can be painful if one allele is inherited and even more serious if two alleles are inherited (one from each parent). ...
... humans: sickle cell anemia • Sickle cell anemia is a single gene, recessive disease that causes red blood cells to “sickle” (“C” shaped) as shown here. • The disease can be painful if one allele is inherited and even more serious if two alleles are inherited (one from each parent). ...
5 CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Types of Ribonucleic
... structure in the pri-miRNA will be cleaved by RNase-III-type enzyme Dicer and nuclear microprocessor complex (Drosha and its cofactor) to form a stem-loop structure miRNA precursor (pre-miRNA; Yang and Mattes, 2008). For human, the microprocessor complex is consisted of Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome ...
... structure in the pri-miRNA will be cleaved by RNase-III-type enzyme Dicer and nuclear microprocessor complex (Drosha and its cofactor) to form a stem-loop structure miRNA precursor (pre-miRNA; Yang and Mattes, 2008). For human, the microprocessor complex is consisted of Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome ...
Inheritance of Retinal Degenerations
... and cannot pass the gene (and the disease) on to his or her future children. Most often, families with an autosomal dominant retinal degeneration can trace the disease back through several generations. Rarely, in some of these families, the disease seems to have skipped one or more generations. In s ...
... and cannot pass the gene (and the disease) on to his or her future children. Most often, families with an autosomal dominant retinal degeneration can trace the disease back through several generations. Rarely, in some of these families, the disease seems to have skipped one or more generations. In s ...
PersPecTIves - Ralf Sommer
... ventral patterning genes have shown striking differences between T. castaneum and D. melanogaster in the function of individual genes and of genetic networks (BOX 2). In particular, gene duplications and subfunctionalization are crucial for extra-embryonic membrane formation and dorso–ventral patter ...
... ventral patterning genes have shown striking differences between T. castaneum and D. melanogaster in the function of individual genes and of genetic networks (BOX 2). In particular, gene duplications and subfunctionalization are crucial for extra-embryonic membrane formation and dorso–ventral patter ...
INHERITANCE OF RETINAL DEGENERATIONS
... and cannot pass the gene (and the disease) on to his or her future children. Most often, families with an autosomal dominant retinal degeneration can trace the disease back through several generations. Rarely, in some of these families, the disease seems to have skipped one or more generations. In s ...
... and cannot pass the gene (and the disease) on to his or her future children. Most often, families with an autosomal dominant retinal degeneration can trace the disease back through several generations. Rarely, in some of these families, the disease seems to have skipped one or more generations. In s ...
“There is no doubt that man, as an animal, inherits characteristics
... not only recessive but is also linked in some way to sex. The subsequent appearance of two other spontaneous mutations (rudimentary wings and yellow body color) also linked to sex further suggested to Morgan that these three genes might be carried on the same chromosome and that this chromosome is t ...
... not only recessive but is also linked in some way to sex. The subsequent appearance of two other spontaneous mutations (rudimentary wings and yellow body color) also linked to sex further suggested to Morgan that these three genes might be carried on the same chromosome and that this chromosome is t ...
Mendel and Heredity - Glasgow Independent Schools
... •Mendelian theory explains simple patterns of inheritance. In these patterns, two of several versions of a gene combine and result in one of several possible traits. In modern terms, the law of segregation holds that when an organism produces gametes, each pair of alleles is separated and each gamet ...
... •Mendelian theory explains simple patterns of inheritance. In these patterns, two of several versions of a gene combine and result in one of several possible traits. In modern terms, the law of segregation holds that when an organism produces gametes, each pair of alleles is separated and each gamet ...
5 The Genetics of Bacteria and Their Viruses
... You are given two strains of E. coli. The Hfr strain is arg+ ala+ glu+ pro+ leu+ Ts; the F– strain is arg– ala– glu– pro– leu– Tr. All the markers are nutritional except T, which determines sensitivity or resistance to phage T1. The order of entry is as given, with arg+ entering the recipient first ...
... You are given two strains of E. coli. The Hfr strain is arg+ ala+ glu+ pro+ leu+ Ts; the F– strain is arg– ala– glu– pro– leu– Tr. All the markers are nutritional except T, which determines sensitivity or resistance to phage T1. The order of entry is as given, with arg+ entering the recipient first ...
current micro 40/5 - Bashan Foundation
... in A. nidulans. These genes are spread over the genome in S. PCC 6803 [26] and have not yet been characterized for A. variabilis. Although the hydrogenase genes from several cyanobacteria have been described up to now, transcript analyses of the hup and hox genes have been performed solely for Nosto ...
... in A. nidulans. These genes are spread over the genome in S. PCC 6803 [26] and have not yet been characterized for A. variabilis. Although the hydrogenase genes from several cyanobacteria have been described up to now, transcript analyses of the hup and hox genes have been performed solely for Nosto ...
chapter 13 meiosis and sexual life cycles
... from both parents are present in the nucleus of the fertilized egg, or zygote. Almost all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is subdivided into chromosomes in the nucleus. Tiny amounts of DNA are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Every living species has a characteristic number of chromos ...
... from both parents are present in the nucleus of the fertilized egg, or zygote. Almost all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is subdivided into chromosomes in the nucleus. Tiny amounts of DNA are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Every living species has a characteristic number of chromos ...
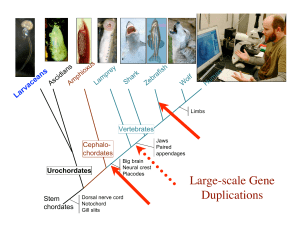
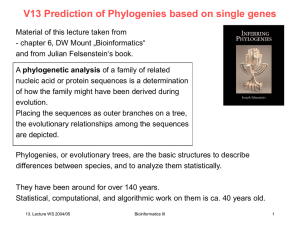
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... supported only a few alternative trees, (2) most genes could have strongly supported one phylogeny and a few genes strongly supported only a small number of alternatives, (3) there could have been some combinations of these scenarios so that each branch among alternative phylogenies had either weak ...
... supported only a few alternative trees, (2) most genes could have strongly supported one phylogeny and a few genes strongly supported only a small number of alternatives, (3) there could have been some combinations of these scenarios so that each branch among alternative phylogenies had either weak ...
Distinct Roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer
... dsRNA processing depletion of dicer results in reduced effectiveness of injected siRNA Dicer binds to components of RISC (R2D2) & binds tightly to siRNA Role of Dicer in siRISC is not well characterized… The authors took a genetic approach to study Dicer function in Drosophila ...
... dsRNA processing depletion of dicer results in reduced effectiveness of injected siRNA Dicer binds to components of RISC (R2D2) & binds tightly to siRNA Role of Dicer in siRISC is not well characterized… The authors took a genetic approach to study Dicer function in Drosophila ...
CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES
... from both parents are present in the nucleus of the fertilized egg, or zygote. Almost all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is subdivided into chromosomes in the nucleus. Tiny amounts of DNA are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Every living species has a characteristic number of chromos ...
... from both parents are present in the nucleus of the fertilized egg, or zygote. Almost all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is subdivided into chromosomes in the nucleus. Tiny amounts of DNA are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Every living species has a characteristic number of chromos ...
Genetic Information: A Metaphor In Search of a Theory*
... notion of information. A signal cannot both correlate with a source and not correlate with it, nor can a signal correlate with a source that does not exist. The most promising attempts to give a naturalistic account of intentional information are the so-called ‘teleosemantic’ theories to be discusse ...
... notion of information. A signal cannot both correlate with a source and not correlate with it, nor can a signal correlate with a source that does not exist. The most promising attempts to give a naturalistic account of intentional information are the so-called ‘teleosemantic’ theories to be discusse ...
Genetic Repair for Optimization under Constraints Inspired by
... studies and was the first plant genome to be sequenced. The Arabidopsis plant has one of the smallest genomes with about 157 million base pairs and five chromosomes. The Arabidopsis genome encodes 27,000 genes and 35,000 proteins. Lolle et al [3] investigated A. thaliana plants with an organ fusion ...
... studies and was the first plant genome to be sequenced. The Arabidopsis plant has one of the smallest genomes with about 157 million base pairs and five chromosomes. The Arabidopsis genome encodes 27,000 genes and 35,000 proteins. Lolle et al [3] investigated A. thaliana plants with an organ fusion ...
A family of human Y chromosomes has dispersed throughout
... Fig. 1. Inversion – deletion models of the origins of b2/b3 deletions. (A) The ampliconic complex embedding AZFc, shown to scale [3]. The central bar depicts the organization of the constituent amplicons, which are color-coded; sequences with the same color are >99.9% identical. The genomic extents ...
... Fig. 1. Inversion – deletion models of the origins of b2/b3 deletions. (A) The ampliconic complex embedding AZFc, shown to scale [3]. The central bar depicts the organization of the constituent amplicons, which are color-coded; sequences with the same color are >99.9% identical. The genomic extents ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.