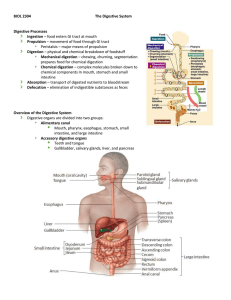
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... SPECIAL STRUCTURES IN THE MOUTH BREAK DOWN FOOD PHYSICALLY BY CHEWING AND GRINDING THE FOOD, A PROCESS CALLED MASTICATION ...
... SPECIAL STRUCTURES IN THE MOUTH BREAK DOWN FOOD PHYSICALLY BY CHEWING AND GRINDING THE FOOD, A PROCESS CALLED MASTICATION ...
The Digestive System
... diarrhea (usually with blood), vomiting or weight loss • The immune system attacking the gastrointestinal tract and producing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract • No cure, but stem cell research is promising • medication to control symptoms, maintain remission and prevent relapses ...
... diarrhea (usually with blood), vomiting or weight loss • The immune system attacking the gastrointestinal tract and producing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract • No cure, but stem cell research is promising • medication to control symptoms, maintain remission and prevent relapses ...
Study Guide
... c) stomach d) small intestine e) pharynx 3. The movement of food through the small intestine by waves of contraction and relaxation of the tract wall is a) ingestion b) mass movements c) mixing d) peristalsis 4. Select the statement that is correct. Saliva a) is produced by glands in the pharynx b) ...
... c) stomach d) small intestine e) pharynx 3. The movement of food through the small intestine by waves of contraction and relaxation of the tract wall is a) ingestion b) mass movements c) mixing d) peristalsis 4. Select the statement that is correct. Saliva a) is produced by glands in the pharynx b) ...
Digestive
... Site of most enzymatic digestion and absorption Secretions and buffers provided by pancreas, liver, gall bladder Three subdivisions: Duodenum Jejunum Ileum Ileocecal sphincter - transition between small and large intestine ...
... Site of most enzymatic digestion and absorption Secretions and buffers provided by pancreas, liver, gall bladder Three subdivisions: Duodenum Jejunum Ileum Ileocecal sphincter - transition between small and large intestine ...
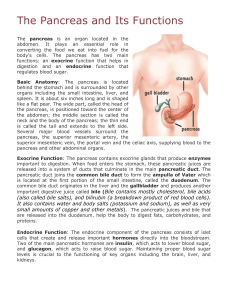
The Pancreas and Its Functions
... Two of the main pancreatic hormones are insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar, and glucagon, which acts to raise blood sugar. Maintaining proper blood sugar levels is crucial to the functioning of key organs including the brain, liver, and kidneys. ...
... Two of the main pancreatic hormones are insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar, and glucagon, which acts to raise blood sugar. Maintaining proper blood sugar levels is crucial to the functioning of key organs including the brain, liver, and kidneys. ...
DigestiveSystem1stEbony
... Identify if there is mechanical &/or chemical digestion occuring Picture of the organ Identify any secretions produced Function of secretions Use only 1 slide. Make sure it is neat & easy to read. ...
... Identify if there is mechanical &/or chemical digestion occuring Picture of the organ Identify any secretions produced Function of secretions Use only 1 slide. Make sure it is neat & easy to read. ...
Digestive system simulation - UNT's College of Education
... If I give myself a cookie…where will it go? ...
... If I give myself a cookie…where will it go? ...
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... -occurs when the liver can’t replace damaged tissue fast enough -healthy liver tissue is destroyed and replaced with CT -liver becomes enlarged (CT & cell division = hyperplasia) -due to alcohol, viruses, heavy metals, drugs, etc… ...
... -occurs when the liver can’t replace damaged tissue fast enough -healthy liver tissue is destroyed and replaced with CT -liver becomes enlarged (CT & cell division = hyperplasia) -due to alcohol, viruses, heavy metals, drugs, etc… ...
THE HUMAN INTESTINAL MICROFLORA AND PROBIOTICS
... bacteria primarily colonize the small intestine, while the Bifidobacteria are anaerobic (without oxygen) bacteria that colonize in the large intestine. In a healthy intestinal environment, these “beneficial bacteria” attach themselves to the surface of the intestinal tract where they multiply and be ...
... bacteria primarily colonize the small intestine, while the Bifidobacteria are anaerobic (without oxygen) bacteria that colonize in the large intestine. In a healthy intestinal environment, these “beneficial bacteria” attach themselves to the surface of the intestinal tract where they multiply and be ...
Why Study Nutrition?
... Comprise approximately 60% of annual cow costs in cow-calf operations 50-75% in other species ...
... Comprise approximately 60% of annual cow costs in cow-calf operations 50-75% in other species ...
names
... 13. Spleen--Return to the folds of the mesentery, this dark red spherical object serves as a holding area for blood. ...
... 13. Spleen--Return to the folds of the mesentery, this dark red spherical object serves as a holding area for blood. ...
Diseases in theDigestive System
... Intestinal Hormones • N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine: Hormones released by the small intestine into the bloodstream when it processes fat. NAPEs travels to • the hypothalamus in the brain and suppress appetite. This mechanism could be relevant for treating obesity • Cholecystokinin: is a peptide ho ...
... Intestinal Hormones • N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine: Hormones released by the small intestine into the bloodstream when it processes fat. NAPEs travels to • the hypothalamus in the brain and suppress appetite. This mechanism could be relevant for treating obesity • Cholecystokinin: is a peptide ho ...
Carbohydrate Digestion
... slowing the gastric emptying and producing a feeling of fullness. The majority of carbohydrate digestion is accomplished in the small intestine. As chyme enters the duodenum, the pancreas is stimulated to secrete amylase which mixes with the chyme and hydrolyzes any remaining starch into maltose. Th ...
... slowing the gastric emptying and producing a feeling of fullness. The majority of carbohydrate digestion is accomplished in the small intestine. As chyme enters the duodenum, the pancreas is stimulated to secrete amylase which mixes with the chyme and hydrolyzes any remaining starch into maltose. Th ...
Digestivesystem
... Fulminant hepatitis - rare where sever symptoms come with altered behavior and personality. If this person is not treated promptly kidney failure, liver failure or death can result. ...
... Fulminant hepatitis - rare where sever symptoms come with altered behavior and personality. If this person is not treated promptly kidney failure, liver failure or death can result. ...
Lining of the Digestive System
... Normal tissue replaced by fibrous connective tissue 75% caused by excessive alcohol consumption CHOLECYSTITIS Inflammation of gallbladder CHOLELITHIASIS Gallstones Can block the bile duct causing pain and digestive disorders Small ones may pass on their own, large ones surgically removed ...
... Normal tissue replaced by fibrous connective tissue 75% caused by excessive alcohol consumption CHOLECYSTITIS Inflammation of gallbladder CHOLELITHIASIS Gallstones Can block the bile duct causing pain and digestive disorders Small ones may pass on their own, large ones surgically removed ...
Large Intestinal Diarrhea
... be determined: fecal CPE was detected in nondiarrheic dogs, however it was more prevalent among in diarrheic dogs. The following antibiotics are reported efficacious against C. perfringens: in acute cases metronidazole (10 mg/kg BID for 7 days), amoxicillin (10-20 mg/kg BID to TID for 7 days), in chr ...
... be determined: fecal CPE was detected in nondiarrheic dogs, however it was more prevalent among in diarrheic dogs. The following antibiotics are reported efficacious against C. perfringens: in acute cases metronidazole (10 mg/kg BID for 7 days), amoxicillin (10-20 mg/kg BID to TID for 7 days), in chr ...
The Digestive System
... • Extends from pyloric sphincter to the large intestine • Receives secretions from the pancreas and liver • Completes digestion of nutrients in chyme and absorbs nutrients of digestion • Mixing movements and peristalsis – chyme moves through in 3-10 hours • Transports digestive residue to the large ...
... • Extends from pyloric sphincter to the large intestine • Receives secretions from the pancreas and liver • Completes digestion of nutrients in chyme and absorbs nutrients of digestion • Mixing movements and peristalsis – chyme moves through in 3-10 hours • Transports digestive residue to the large ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Seven
... ensures intestinal contents are able to traverse forward but have no way of flowing backwards. Once the digestive juices have broken down the food, they are no longer ...
... ensures intestinal contents are able to traverse forward but have no way of flowing backwards. Once the digestive juices have broken down the food, they are no longer ...
The Digestive System Chapter 16
... - connects stomach to large intestine; 15-20’ long; 1” diameter; held ...
... - connects stomach to large intestine; 15-20’ long; 1” diameter; held ...
Comparative Digestive Systems
... not require digestion because most of their nutrients are already small enough to be absorbed into the cell • However, some, like the paramecium are able to bring in solid particles as food vacuoles. These use lysosomes (packed with hydrolytic enzymes) to breakdown the contents of the food vacuoles. ...
... not require digestion because most of their nutrients are already small enough to be absorbed into the cell • However, some, like the paramecium are able to bring in solid particles as food vacuoles. These use lysosomes (packed with hydrolytic enzymes) to breakdown the contents of the food vacuoles. ...
أعلى النموذج salivary amylase salivary glands, mouth hydrolyzes
... secreted in response to chyme to stimulate pancreatic enzyme and bile release duodenum secreted when chyme is very fatty to inhibit stomach peristalis so chyme is released more slowly to duodenum pancrease, small intestine hydrolyzes specific peptide bonds, converts chymotrypsinogen to active chymot ...
... secreted in response to chyme to stimulate pancreatic enzyme and bile release duodenum secreted when chyme is very fatty to inhibit stomach peristalis so chyme is released more slowly to duodenum pancrease, small intestine hydrolyzes specific peptide bonds, converts chymotrypsinogen to active chymot ...
chapter 6-the digestive system
... A. The Liver-organ located in the right, upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. It weighs about three pounds. The liver is the largest glandular structure in the body. 1. The Hepatic Portal Blood System-blood vessels that bring nutrient rich blood from the small intestine to the liver. The liver re ...
... A. The Liver-organ located in the right, upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. It weighs about three pounds. The liver is the largest glandular structure in the body. 1. The Hepatic Portal Blood System-blood vessels that bring nutrient rich blood from the small intestine to the liver. The liver re ...
Weak peristaltic contractions move food slowly toward the jejunum
... and hence ingestion of dietary lipids. Fat malabsorption is known as Steatorrhea. If bile salt uptake is impaired (either via obstruction, liver dysfunction or Ileal dysfyunction [decreased bile salt uptake]) then these vitamins are prone to malabsorption. Vitamin D deficiency can cause bone disorde ...
... and hence ingestion of dietary lipids. Fat malabsorption is known as Steatorrhea. If bile salt uptake is impaired (either via obstruction, liver dysfunction or Ileal dysfyunction [decreased bile salt uptake]) then these vitamins are prone to malabsorption. Vitamin D deficiency can cause bone disorde ...
Digestion study guide
... 3) Describe the similarities and differences between the intestinal transport of glucose, galactose, and fructose. 4) Describe with graphs the two methods used to diagnose lactose intolerance (blood glucose and H2 in breath). 5) Use a diagram to outline the assimilation of a large protein. Identify ...
... 3) Describe the similarities and differences between the intestinal transport of glucose, galactose, and fructose. 4) Describe with graphs the two methods used to diagnose lactose intolerance (blood glucose and H2 in breath). 5) Use a diagram to outline the assimilation of a large protein. Identify ...
Intestine transplantation

Intestine transplantation, intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. The rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regiments, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.