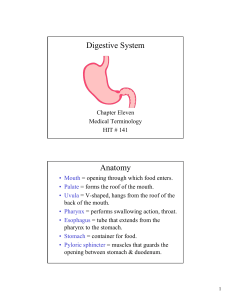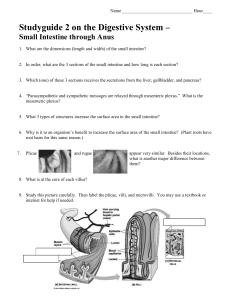
Studyguide 2 on the Digestive System
... 9. Study this picture carefully. Then label the plicae, villi, and microvilli. You may use a textbook or internet for help if needed. ...
... 9. Study this picture carefully. Then label the plicae, villi, and microvilli. You may use a textbook or internet for help if needed. ...
Animal Systems- Nutrient Absorption
... working together to break down food into simple, useable substances. The energy of foods is contained in the molecules of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins, but the molecules are too big to pass through your cells’ membranes. The digestive system uses two processes to break down food: mechanical d ...
... working together to break down food into simple, useable substances. The energy of foods is contained in the molecules of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins, but the molecules are too big to pass through your cells’ membranes. The digestive system uses two processes to break down food: mechanical d ...
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3: Student Resource Sheet
... What is the oral cavity and what does it contain? What is the function of the salivary glands? What is the function of the tongue? What is a bolus? Where are the soft and hard palate located and what are their functions? What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the oral cavity? ...
... What is the oral cavity and what does it contain? What is the function of the salivary glands? What is the function of the tongue? What is a bolus? Where are the soft and hard palate located and what are their functions? What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the oral cavity? ...
Human Digestion and Absorption
... Stomach cells and what they produce: Mucus cells - produces mucus Parietal cells - produce hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor Chief cells - pepsinogen (inactive form of protein digestive enzyme) Enteroendocrine cells - produces: gastrin - cause gastric glands to increase activity s ...
... Stomach cells and what they produce: Mucus cells - produces mucus Parietal cells - produce hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor Chief cells - pepsinogen (inactive form of protein digestive enzyme) Enteroendocrine cells - produces: gastrin - cause gastric glands to increase activity s ...
Notes
... -receives chyme from stomach & secretions from pancreas & liver 2) Jejunum: starts at 1st bend, 2.5m (8ft) -most of chemical digestion & nutrient absorption occurs ...
... -receives chyme from stomach & secretions from pancreas & liver 2) Jejunum: starts at 1st bend, 2.5m (8ft) -most of chemical digestion & nutrient absorption occurs ...
The digestive system can be divided into two main parts: the
... The liver, gallbladder and pancreas all play an important role in the digestion of food. The liver produces bile, which is then stored in the gallbladder. Bile is then released into the small intestine as needed, where it dissolves fat so that it can be absorbed into the body. The pancreas secretes ...
... The liver, gallbladder and pancreas all play an important role in the digestion of food. The liver produces bile, which is then stored in the gallbladder. Bile is then released into the small intestine as needed, where it dissolves fat so that it can be absorbed into the body. The pancreas secretes ...
Frog Dissection
... – you must get at least 20 of the 25 questions correct before you can dissect ...
... – you must get at least 20 of the 25 questions correct before you can dissect ...
Digestion Clip by Brainpop
... • Mechanical or Physical: breaking food down by cutting, chewing and grinding. • Chemical: breaking food into small molecules through chemical reactions with enzymes. ...
... • Mechanical or Physical: breaking food down by cutting, chewing and grinding. • Chemical: breaking food into small molecules through chemical reactions with enzymes. ...
Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
... When this happens, the intestine can no longer hold its content so bacteria and waste products pass through the intestinal wall and enter the baby’s bloodstream or abdominal cavity. This makes a baby very sick, possibly causing a lifethreatening infection. ...
... When this happens, the intestine can no longer hold its content so bacteria and waste products pass through the intestinal wall and enter the baby’s bloodstream or abdominal cavity. This makes a baby very sick, possibly causing a lifethreatening infection. ...
Feline Inflammatory Bowel Disease
... diarrhea. The term actually refers to a group of diseases that are characterized by the invasion of inflammatory cells into the cat’s intestinal wall. ...
... diarrhea. The term actually refers to a group of diseases that are characterized by the invasion of inflammatory cells into the cat’s intestinal wall. ...
Disorders of the GIT – ILEUS Caused by the obstruction of the
... − symptoms may be present even if the acid is not present in the esophagus − heartburn can be seen as chest pain, which requires the exclusion of cardiac ...
... − symptoms may be present even if the acid is not present in the esophagus − heartburn can be seen as chest pain, which requires the exclusion of cardiac ...
Digestive System: True-False Review
... Glucose and amino acids are absorbed into the lacteal of a villus. Glycerol and fatty acids (ie. triglycerides) are absorbed into the capillaries of a villus. Blood enters a villus through a venule; blood leaves by an arteriole. Sucrase converts sucrose into glucose + galactose. Enzymes may be destr ...
... Glucose and amino acids are absorbed into the lacteal of a villus. Glycerol and fatty acids (ie. triglycerides) are absorbed into the capillaries of a villus. Blood enters a villus through a venule; blood leaves by an arteriole. Sucrase converts sucrose into glucose + galactose. Enzymes may be destr ...
Digestive System Anatomy
... Abdominoplasty = surgical repair of the abdomen. Anoplasty = surgical repair of the anus. Appendectomy = excision of the appendix. Celiotomy = incision into the abdominal cavity. Cholecystectomy = excision of the gallbladder. Colectomy = excision of the colon. Colostomy = artificial opening into the ...
... Abdominoplasty = surgical repair of the abdomen. Anoplasty = surgical repair of the anus. Appendectomy = excision of the appendix. Celiotomy = incision into the abdominal cavity. Cholecystectomy = excision of the gallbladder. Colectomy = excision of the colon. Colostomy = artificial opening into the ...
Digestive System Review with answers
... Mechanically breaks down food into smaller pieces; Chemically breaks down starch using enzymes Esophagus A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Food moves down by peristalsis. Stomach Most mechanical digestion takes place here; muscular J-shaped pouch in the abdomen; chemical digest ...
... Mechanically breaks down food into smaller pieces; Chemically breaks down starch using enzymes Esophagus A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Food moves down by peristalsis. Stomach Most mechanical digestion takes place here; muscular J-shaped pouch in the abdomen; chemical digest ...
Liver
... • Teeth – cut, tear and crush – Salivation – chemical digestion begins • Moistens food – salt, water, mucous • Amylase – starch breakdown to sugars • Lysozyme – breaks down cells (especially pathogens) ...
... • Teeth – cut, tear and crush – Salivation – chemical digestion begins • Moistens food – salt, water, mucous • Amylase – starch breakdown to sugars • Lysozyme – breaks down cells (especially pathogens) ...
Digestive System Study Guide
... Epiglottis - A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering. Rectum - A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated. ...
... Epiglottis - A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering. Rectum - A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated. ...
Learning Objectives 15 Digestive System
... Describe the general functions of the digestive system, and name its two major divisions Explain the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion, and name the end products of digestion Describe the structure and functions of the teeth and tongue Describe the functions of saliva Describe the ...
... Describe the general functions of the digestive system, and name its two major divisions Explain the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion, and name the end products of digestion Describe the structure and functions of the teeth and tongue Describe the functions of saliva Describe the ...
unit 4
... Slowly releases chyme into the duodenum Where the majority of digestion occurs – final digestion of all macromolecules into monomers. Receives enzymes from pancreas and wall of duodenum. Stores bile until it is needed to emulsify fats ...
... Slowly releases chyme into the duodenum Where the majority of digestion occurs – final digestion of all macromolecules into monomers. Receives enzymes from pancreas and wall of duodenum. Stores bile until it is needed to emulsify fats ...
Digestion ppt
... factor is sensed and is lowered A response the body has to an occurrence that disturbs the homeostasis of the body. As the body reacts to that occurrence and moves closer to homeostasis, the receptors are shut down, thus causing fewer effectors to produce a product that’s needed to bring the body b ...
... factor is sensed and is lowered A response the body has to an occurrence that disturbs the homeostasis of the body. As the body reacts to that occurrence and moves closer to homeostasis, the receptors are shut down, thus causing fewer effectors to produce a product that’s needed to bring the body b ...
The Digestive System - Anoka-Hennepin School District 11
... factor is sensed and is lowered A response the body has to an occurrence that disturbs the homeostasis of the body. As the body reacts to that occurrence and moves closer to homeostasis, the receptors are shut down, thus causing fewer effectors to produce a product that’s needed to bring the body b ...
... factor is sensed and is lowered A response the body has to an occurrence that disturbs the homeostasis of the body. As the body reacts to that occurrence and moves closer to homeostasis, the receptors are shut down, thus causing fewer effectors to produce a product that’s needed to bring the body b ...
The Digestive System Chapter 16
... Disorders of the Intestines Intestinal obstruction: complete stoppage or serious impairment to the passage of intestinal contents. Diarrhea: dia (through) rrhea (flow); abnormal frequency of loose or watery stools that can lead to dehydration Constipation: decrease in frequency of the passage o ...
... Disorders of the Intestines Intestinal obstruction: complete stoppage or serious impairment to the passage of intestinal contents. Diarrhea: dia (through) rrhea (flow); abnormal frequency of loose or watery stools that can lead to dehydration Constipation: decrease in frequency of the passage o ...
The Human Body in Health and Illness
... acids, which are absorbed into villi • Common proteases -Pepsin, stomach -Trypsin, pancreas -Chymotrypsin, pancreas -Enterokinase, duodenum ...
... acids, which are absorbed into villi • Common proteases -Pepsin, stomach -Trypsin, pancreas -Chymotrypsin, pancreas -Enterokinase, duodenum ...
Name - Mr. Lesiuk
... 1. What is another name for the mouth? 2. What type of digestion are the teeth responsible for? 3. What list two functions of the salivary glands? 4. Name all three types of salivary glands. 5. How does your tongue participate in the digestion? 6. Prior to swallowing, the food is pushed to this part ...
... 1. What is another name for the mouth? 2. What type of digestion are the teeth responsible for? 3. What list two functions of the salivary glands? 4. Name all three types of salivary glands. 5. How does your tongue participate in the digestion? 6. Prior to swallowing, the food is pushed to this part ...
Intestine transplantation

Intestine transplantation, intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. The rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regiments, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.