6 Basic Mammalian Anatomy I
... 13. The stomach connects to what part of the small intestine? duodenum 14. Identify the gland that is located by lifting the stomach. pancreas 15. Name a lymphoid organ in the abdominal cavity. spleen 16. The lungs belong to what system of the body? respiratory 17. The pancreas belongs to what syste ...
... 13. The stomach connects to what part of the small intestine? duodenum 14. Identify the gland that is located by lifting the stomach. pancreas 15. Name a lymphoid organ in the abdominal cavity. spleen 16. The lungs belong to what system of the body? respiratory 17. The pancreas belongs to what syste ...
frog dissection formal laboratory paper
... dissection and general observations of the dissection. Include: a. Description of what you observed when you examined the mouth. Include a minimum of three observations you made. b. Description of what you observed when you completed the dissection of the abdomen. Include a minimum of three observat ...
... dissection and general observations of the dissection. Include: a. Description of what you observed when you examined the mouth. Include a minimum of three observations you made. b. Description of what you observed when you completed the dissection of the abdomen. Include a minimum of three observat ...
Digestive System
... But aren’t the stomach cells made of protein? –Pepsin is produced and secreted in an inactive form called pepsinogen • which is converted into the active form by the low pH. • This protects the cell from self-digestion ...
... But aren’t the stomach cells made of protein? –Pepsin is produced and secreted in an inactive form called pepsinogen • which is converted into the active form by the low pH. • This protects the cell from self-digestion ...
Gastrointestinal System PowerPoint
... Approximately 5 – 6 feet long Separated from small intestine by ileocecal valve Forms framework around small intestine Absorbs water Eliminates waste Contains bacteria that produce vitamin K and B12 ...
... Approximately 5 – 6 feet long Separated from small intestine by ileocecal valve Forms framework around small intestine Absorbs water Eliminates waste Contains bacteria that produce vitamin K and B12 ...
Digestive System and The Eye Assessment Guide
... examples of the following words: Vertebrae, marrow, cartilage, joint (immovable and movable), tendon, ligament, voluntary and involuntary muscles, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. ...
... examples of the following words: Vertebrae, marrow, cartilage, joint (immovable and movable), tendon, ligament, voluntary and involuntary muscles, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. ...
Effect of Intensity of Feeding on the Intestinal Microflora of Pigs
... growing pigs differed in composition and energetic and nutritional value, with constant protein to energy ratio (Table I). In intensive feeding this ratio was 13.12 : 1 and in extensive feeding 13.04 : 1. The fibre content per 1 kg mixture was: in group I 3.43%, in group E 12.03%. Following fatt ...
... growing pigs differed in composition and energetic and nutritional value, with constant protein to energy ratio (Table I). In intensive feeding this ratio was 13.12 : 1 and in extensive feeding 13.04 : 1. The fibre content per 1 kg mixture was: in group I 3.43%, in group E 12.03%. Following fatt ...
Small Intestine - DENTISTRY 2012
... • The effect of the immune response may be total flattening of mucosal villi (and hence loss of surface area), affecting the proximal more than the distal small intestine. • Lymphocytes and other inflammatory cells accumulate in the lamina propria. • The age of presentation with symptomatic diarrhe ...
... • The effect of the immune response may be total flattening of mucosal villi (and hence loss of surface area), affecting the proximal more than the distal small intestine. • Lymphocytes and other inflammatory cells accumulate in the lamina propria. • The age of presentation with symptomatic diarrhe ...
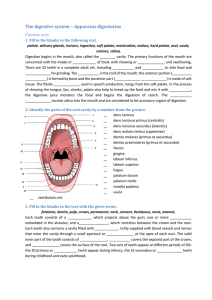
The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius
... dehydratatio, gastrorrhagia, perforatio, dyspnoea,melaena, anorexia, ulcus ventriculi, syncope, _______________ is a catchall term for infection or irritation of the digestive tract, particularly the stomach and intestine. Major symptoms include (feeling sick)__________ and (throwing up from the sto ...
... dehydratatio, gastrorrhagia, perforatio, dyspnoea,melaena, anorexia, ulcus ventriculi, syncope, _______________ is a catchall term for infection or irritation of the digestive tract, particularly the stomach and intestine. Major symptoms include (feeling sick)__________ and (throwing up from the sto ...
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3: Student Resource Sheet
... Vater which is located at the first portion of the small intestine, called the duodenum. The common bile duct originates in the liver and the gallbladder and produces another important digestive juice called bile. The pancreatic juices and bile that are released into the duodenum, help the body to d ...
... Vater which is located at the first portion of the small intestine, called the duodenum. The common bile duct originates in the liver and the gallbladder and produces another important digestive juice called bile. The pancreatic juices and bile that are released into the duodenum, help the body to d ...
Small Bowel Manometry - American Neurogastroenterology and
... Antroduodenal or small bowel manometry study provides information regarding the muscle activity of the stomach and small bowel during fasting, after a meal, and during sleep. These tests may help determine what area of the GI tract is not working properly - the stomach, the small intestine or both. ...
... Antroduodenal or small bowel manometry study provides information regarding the muscle activity of the stomach and small bowel during fasting, after a meal, and during sleep. These tests may help determine what area of the GI tract is not working properly - the stomach, the small intestine or both. ...
large intestine
... Mass movement [strong peristaltic waves] • Gastro-colic Reflex – when food enters the stomach, mass movements are triggered in the colon. • It is mediated from stomach to the colon by gastrin and extrinsic autonomic nerves. • It pushes the colonic contents into rectum triggering the defecation refl ...
... Mass movement [strong peristaltic waves] • Gastro-colic Reflex – when food enters the stomach, mass movements are triggered in the colon. • It is mediated from stomach to the colon by gastrin and extrinsic autonomic nerves. • It pushes the colonic contents into rectum triggering the defecation refl ...
lab 7 digestive system 1 - Dr. Justo Lopez Website
... It is the major digestive and absorptive organ of the body. It extends from the pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve (19.7 ft ) Functions: 1- To complete digestion 2- To absorb 99% of the digested nutrients Duodenum (10 inches) It receives the pancreas and liver secretions that mix with the chym ...
... It is the major digestive and absorptive organ of the body. It extends from the pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve (19.7 ft ) Functions: 1- To complete digestion 2- To absorb 99% of the digested nutrients Duodenum (10 inches) It receives the pancreas and liver secretions that mix with the chym ...
Digestive System
... 3 systems will be addressed in detail in the lesson to follow: Ruminants—have four stomach compartments Monogastric—have one stomach Modified Monogastric—have one stomach but the ability to digest roughages ...
... 3 systems will be addressed in detail in the lesson to follow: Ruminants—have four stomach compartments Monogastric—have one stomach Modified Monogastric—have one stomach but the ability to digest roughages ...
document
... pancreatic juices. •These are also shot into the duodenum to help with the digestive process. ...
... pancreatic juices. •These are also shot into the duodenum to help with the digestive process. ...
The Digestive System
... ____ Using projected images as an aide, locate the following abdominal organs. With the liver still elevated, identify the stomach on the left side of the abdominal cavity. Locate the point near the midline where he esophagus enters the stomach. This is the lower esophageal sphincter. ____ At the o ...
... ____ Using projected images as an aide, locate the following abdominal organs. With the liver still elevated, identify the stomach on the left side of the abdominal cavity. Locate the point near the midline where he esophagus enters the stomach. This is the lower esophageal sphincter. ____ At the o ...
Digestive System Lecture 2
... about 1,200 to 1,500 mL of pancreatic juice per day; pancreatic juice is alkaline (basic) and buffers chyme from stomach in the small intestine; pancreatic enzymes ...
... about 1,200 to 1,500 mL of pancreatic juice per day; pancreatic juice is alkaline (basic) and buffers chyme from stomach in the small intestine; pancreatic enzymes ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... * Movement in the digestive interphase MMC similar to that in the stomach * Main movement forms in digestive phase Tonic contraction: the same as in stomach Segmentation: peculiar to the small intestine Peristalsis: 0.5~2.0 cm/s Peristaltic rush: 2~25 cm/s * Regulation of small intestinal movement ...
... * Movement in the digestive interphase MMC similar to that in the stomach * Main movement forms in digestive phase Tonic contraction: the same as in stomach Segmentation: peculiar to the small intestine Peristalsis: 0.5~2.0 cm/s Peristaltic rush: 2~25 cm/s * Regulation of small intestinal movement ...
Digestive System, Chapter 19
... 5. Identify the parts of a typical tooth and compare deciduous and permanent dentitions. 6. Describe the structures and function of the pharynx 7. Describe the structures and function of the esophagus 8. Describe the general structures, histology, and functions of the stomach. 9. Describe the genera ...
... 5. Identify the parts of a typical tooth and compare deciduous and permanent dentitions. 6. Describe the structures and function of the pharynx 7. Describe the structures and function of the esophagus 8. Describe the general structures, histology, and functions of the stomach. 9. Describe the genera ...
Digestion - Angelfire
... hierarchical levels from less complex to more complex Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ system ...
... hierarchical levels from less complex to more complex Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ system ...
Lecture Exam 3 Study Guide
... they are obtained, what they involve, and their normal values (volumes). - Know how respiration is controlled neurally (brain structures). What is the Hering-Breuer reflex? Can a person “hold their breath until they die?” - How do Dalton’s law and Henry’s law relate to the transfer of gases between ...
... they are obtained, what they involve, and their normal values (volumes). - Know how respiration is controlled neurally (brain structures). What is the Hering-Breuer reflex? Can a person “hold their breath until they die?” - How do Dalton’s law and Henry’s law relate to the transfer of gases between ...
Equine GI physiology
... horses, which provided some interesting results. Basically, in contrast to the monophasic relaxation episode seen in humans and dogs after a liquid meal, we saw a distinct biphasic response to the ingestion of the solid meals. The first occurred during active ingestion, which we regarded as true “re ...
... horses, which provided some interesting results. Basically, in contrast to the monophasic relaxation episode seen in humans and dogs after a liquid meal, we saw a distinct biphasic response to the ingestion of the solid meals. The first occurred during active ingestion, which we regarded as true “re ...
Digestive System part 1
... Absorption of water Bacteria produce vitamin K, B vitamins. Secretion of mucus (lubrication of feces) Contractions move feces along large intestine and rectum, to be expelled out of the anal canal ...
... Absorption of water Bacteria produce vitamin K, B vitamins. Secretion of mucus (lubrication of feces) Contractions move feces along large intestine and rectum, to be expelled out of the anal canal ...
Intestine transplantation

Intestine transplantation, intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. The rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regiments, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.