Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis Using Fecal Bacteriotherapy
... where antibiotics have failed. While the best known application of bacteriotherapy is in the treatment of unresponsive Clostridium difficile diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis,1–10 significant clinical improvements have also been reported in other GI conditions including constipation, irritable b ...
... where antibiotics have failed. While the best known application of bacteriotherapy is in the treatment of unresponsive Clostridium difficile diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis,1–10 significant clinical improvements have also been reported in other GI conditions including constipation, irritable b ...
Viral Enteritis: A Cause of Disordered Small Intestinal Epithelial
... Prolonged, even intractable, diarrhea may begin during infancy in babies who previously have been well. Given the global prevalence of rotavirus enteritis and its capacity to damage the small intestinal mucosa, it is tempting to speculate that this invasive virus, which normally causes self-limited ...
... Prolonged, even intractable, diarrhea may begin during infancy in babies who previously have been well. Given the global prevalence of rotavirus enteritis and its capacity to damage the small intestinal mucosa, it is tempting to speculate that this invasive virus, which normally causes self-limited ...
The Digestive System - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... Before energy can be obtained from food, it must be broken down by the process of digestion. The digestive system is the organ system that is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gall bladder, the system that takes in, breaks up, and digests food and then excret ...
... Before energy can be obtained from food, it must be broken down by the process of digestion. The digestive system is the organ system that is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gall bladder, the system that takes in, breaks up, and digests food and then excret ...
Digestive System
... • Secretes serous fluid – Lubricates and prevents friction between digestive organs and surrounding viscera ...
... • Secretes serous fluid – Lubricates and prevents friction between digestive organs and surrounding viscera ...
radiological anatomy of the bowel
... Small bowel follow-through • The passage of the barium through the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine is monitored on the fluoroscope. • The test usually takes around three to six hours. ...
... Small bowel follow-through • The passage of the barium through the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine is monitored on the fluoroscope. • The test usually takes around three to six hours. ...
No Slide Title - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Jejunum - next 8 ft. (in upper abdomen) – has large tall circular folds; walls are thick, muscular – most digestion and nutrient absorption occur here ...
... • Jejunum - next 8 ft. (in upper abdomen) – has large tall circular folds; walls are thick, muscular – most digestion and nutrient absorption occur here ...
GI tract
... • Jejunum - next 8 ft. (in upper abdomen) – has large tall circular folds; walls are thick, muscular – most digestion and nutrient absorption occur here ...
... • Jejunum - next 8 ft. (in upper abdomen) – has large tall circular folds; walls are thick, muscular – most digestion and nutrient absorption occur here ...
Disorders of Absorption
... surface area is approximately 600fold greater than that of a hollow tube as a result of the presence of folds, villi (in the smaIl intestine), and microvilli. ...
... surface area is approximately 600fold greater than that of a hollow tube as a result of the presence of folds, villi (in the smaIl intestine), and microvilli. ...
Digestive System
... Liver (largest internal organ) secretes bile, which ______ fats – also stores iron ...
... Liver (largest internal organ) secretes bile, which ______ fats – also stores iron ...
digestive system
... The stones block the cystic duct, and causes a lot of pain as the bile backs up. Treatment is to cut the cystic duct and remove the gall bladder. Now that person can only eat small amounts of fats at a time. Two main types of gallstones: Stones made out of cholesterol (most common type). It has no ...
... The stones block the cystic duct, and causes a lot of pain as the bile backs up. Treatment is to cut the cystic duct and remove the gall bladder. Now that person can only eat small amounts of fats at a time. Two main types of gallstones: Stones made out of cholesterol (most common type). It has no ...
Slide 1
... • Microbes make vitamin K and some B vitamins. • They also make fatty acids from cellulose. Some of these are used for energy by large intestine epithelial cells. We can’t absorb the fatty acids, but they help absorb electrolytes such as sodium, calcium, bicarbonate, magnesium, and iron. • They outc ...
... • Microbes make vitamin K and some B vitamins. • They also make fatty acids from cellulose. Some of these are used for energy by large intestine epithelial cells. We can’t absorb the fatty acids, but they help absorb electrolytes such as sodium, calcium, bicarbonate, magnesium, and iron. • They outc ...
Anatomía del sistema digestivo
... glands in the lining of the stomach. 2. Essential constituents are the digestive enzymes pepsin and renin, hydrochloric acid, and mucus. 3. Certain cells of the stomach lining secrete intrinsic factor which is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. ...
... glands in the lining of the stomach. 2. Essential constituents are the digestive enzymes pepsin and renin, hydrochloric acid, and mucus. 3. Certain cells of the stomach lining secrete intrinsic factor which is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. ...
The Digestive System Part A Digestive System: Overview The
... Collects nutrient-rich venous blood from the digestive viscera Delivers this blood to the liver for metabolic processing and storage Histology of the Alimentary Canal From esophagus to the anal canal the walls of the GI tract have the same four tunics From the lumen outward they are the mucosa, subm ...
... Collects nutrient-rich venous blood from the digestive viscera Delivers this blood to the liver for metabolic processing and storage Histology of the Alimentary Canal From esophagus to the anal canal the walls of the GI tract have the same four tunics From the lumen outward they are the mucosa, subm ...
Identify and tell the function of each part of the
... It stores a fluid called ………………, which is made in the liver. Answer: BILE ...
... It stores a fluid called ………………, which is made in the liver. Answer: BILE ...
1-RADIOLOGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LARGE BOWEL 2nd year GI
... Sigmoid colon Descending colon Splenic flexure Transverse colon Hepatic flexure Ascending colon cecum ...
... Sigmoid colon Descending colon Splenic flexure Transverse colon Hepatic flexure Ascending colon cecum ...
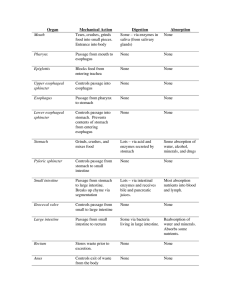
• The 2 main groups of digestive organs:
... • The digestive system converts food into raw materials that: – provide nutrients to use as energy and build new cells. ...
... • The digestive system converts food into raw materials that: – provide nutrients to use as energy and build new cells. ...
The Digestive System Key Concept Builder LESSON 2 Key Concept
... Directions: Put a check mark under the organ(s) that each item describes. ...
... Directions: Put a check mark under the organ(s) that each item describes. ...
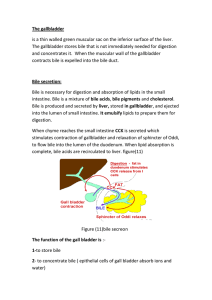
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior
... *Upon entering the small intestine the pancreas releases the enzyme pancreatic amylase to help complete the hydrolysis of starch into smaller chains of glucose molecules – monosaccharide's, which is 1 molecule of sugar. * The monosaccharide's are absorbed into the small intestine and delivered to th ...
... *Upon entering the small intestine the pancreas releases the enzyme pancreatic amylase to help complete the hydrolysis of starch into smaller chains of glucose molecules – monosaccharide's, which is 1 molecule of sugar. * The monosaccharide's are absorbed into the small intestine and delivered to th ...
The Digestive System2011
... The version of energy useful to cells ATP ADP (triphosphate to diphosphate)- loss of the phosphate releases energy Lost phos. recharges (like a battery) and bonds with an ADP to make an ATP: Energy must be available in the cells for this to occur Cellular Respiration provides the energy to regener ...
... The version of energy useful to cells ATP ADP (triphosphate to diphosphate)- loss of the phosphate releases energy Lost phos. recharges (like a battery) and bonds with an ADP to make an ATP: Energy must be available in the cells for this to occur Cellular Respiration provides the energy to regener ...
About Small Intestine Cancer What Is a Small Intestine Cancer?
... requests, please see our Content Usage Policy. ...
... requests, please see our Content Usage Policy. ...
Intestine transplantation

Intestine transplantation, intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. The rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regiments, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.