respiratory system
... foods into the esophagus and away from the airways. The glottis is in the superior portion of the larynx. It consists of a pair of mucous membrane folds called the vocal folds or true vocal cords and the space between them called the rima glottidis. Deep to the vocal folds are bands of elastic lig ...
... foods into the esophagus and away from the airways. The glottis is in the superior portion of the larynx. It consists of a pair of mucous membrane folds called the vocal folds or true vocal cords and the space between them called the rima glottidis. Deep to the vocal folds are bands of elastic lig ...
19 Digestive System MtSAC
... causes a lot of pain as the bile backs up. Treatment is to cut the cystic duct and remove the gall bladder. Now that person can only eat small amounts of fats at a time. ...
... causes a lot of pain as the bile backs up. Treatment is to cut the cystic duct and remove the gall bladder. Now that person can only eat small amounts of fats at a time. ...
Peristalsis
... then inhibited to be returned after hours mediated by autonomic fibers. It appear after meals facilitated by gastro-colic and ilio-colic reflexes. ...
... then inhibited to be returned after hours mediated by autonomic fibers. It appear after meals facilitated by gastro-colic and ilio-colic reflexes. ...
PPT File
... (b) Microvilli border of the epithelial cell increases the surface area for absorption. (c) Lacteals are vessels that transport lipids out of the small intestine into the lymphatic system. (d) In the wall of the small intestine are the blood vessels to transport absorbed products to the general circ ...
... (b) Microvilli border of the epithelial cell increases the surface area for absorption. (c) Lacteals are vessels that transport lipids out of the small intestine into the lymphatic system. (d) In the wall of the small intestine are the blood vessels to transport absorbed products to the general circ ...
Digestive System - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... absorb, defecate) 2. Accessory organs, which assist in digestive breakdown (teeth tongue and several large digestive organs) ...
... absorb, defecate) 2. Accessory organs, which assist in digestive breakdown (teeth tongue and several large digestive organs) ...
Chapter 46: Bowel Elimination
... Duodenum, jejunum, and food, liquid and digestive ileum juices; moves food into small intestines ...
... Duodenum, jejunum, and food, liquid and digestive ileum juices; moves food into small intestines ...
Study Sheet A
... Man needs food for several reasons, including the following: to supply energy to the body, to store energy for future emergencies, and to build new protoplasm. (Protoplasm is a semifluid which is the essential living matter of all body cells.) There are six groups of food. They are water, vitamins, ...
... Man needs food for several reasons, including the following: to supply energy to the body, to store energy for future emergencies, and to build new protoplasm. (Protoplasm is a semifluid which is the essential living matter of all body cells.) There are six groups of food. They are water, vitamins, ...
Large Intestine
... 3. Saliva also contains IgA antibodies and lysozyme, which help to destroy any microorganisms in the oral cavity. ...
... 3. Saliva also contains IgA antibodies and lysozyme, which help to destroy any microorganisms in the oral cavity. ...
Functions of the Liver The liver performs important digestive and
... hepatocytes and, thus, the cell size fluctuate during a given day. Hepatocytes help control blood sugar levels within very narrow limits. If a large amount of sugar enters the general circulation after a meal, it will increase the osmolality of the blood and produce hyperglycemia. This is prevented ...
... hepatocytes and, thus, the cell size fluctuate during a given day. Hepatocytes help control blood sugar levels within very narrow limits. If a large amount of sugar enters the general circulation after a meal, it will increase the osmolality of the blood and produce hyperglycemia. This is prevented ...
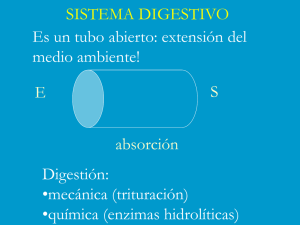
Digestive System
... mesentery is often used to refer to a double layer of visceral peritoneum. There are often blood vessels, nerves, and other structures between these layers. The space between these two layers is technically outside of the peritoneal sac, and thus not in the peritoneal cavity. Peritoneum is composed ...
... mesentery is often used to refer to a double layer of visceral peritoneum. There are often blood vessels, nerves, and other structures between these layers. The space between these two layers is technically outside of the peritoneal sac, and thus not in the peritoneal cavity. Peritoneum is composed ...
6.1 Digestion and absorption
... of the ileum shows both the folded nature of the inner wall and the outer muscular layers helping to food along and increasing the surface area in contact with digested food. ...
... of the ileum shows both the folded nature of the inner wall and the outer muscular layers helping to food along and increasing the surface area in contact with digested food. ...
Activities of amino acid metabolizing enzymes in the stomach
... glutamine synthesize glutamine, as in the perinatal period (Alemany, 1979). The activity of glutamine synthetase in he stomach was much higher than in the intestine as it has an important role in maintaining acid-base equilibrium (Arola et al., 1981a). The pattern of this enzyme followed that of ser ...
... glutamine synthesize glutamine, as in the perinatal period (Alemany, 1979). The activity of glutamine synthetase in he stomach was much higher than in the intestine as it has an important role in maintaining acid-base equilibrium (Arola et al., 1981a). The pattern of this enzyme followed that of ser ...
DIGESTION - Ray and Terry
... result in people taking over-the-counter and prescription antacids, which only exacerbate the condition. The hair mineral analysis test described in the following section on Early Detection can suggest whether you have hypochlorhydria. In the small intestine, a common genetic defect can result in in ...
... result in people taking over-the-counter and prescription antacids, which only exacerbate the condition. The hair mineral analysis test described in the following section on Early Detection can suggest whether you have hypochlorhydria. In the small intestine, a common genetic defect can result in in ...
B. True or False/Edit
... Peristaltic contractions are wavelike, due first to the squeezing action of circular muscles, followed by the shortening action of longitudinal muscles. The esophagus empties its contents into the cardiac region of the stomach. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) present in the stomach does not directly digest ...
... Peristaltic contractions are wavelike, due first to the squeezing action of circular muscles, followed by the shortening action of longitudinal muscles. The esophagus empties its contents into the cardiac region of the stomach. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) present in the stomach does not directly digest ...
Chapter 18 - Dr. Dorena Rode
... Peristaltic contractions are wavelike, due first to the squeezing action of circular muscles, followed by the shortening action of longitudinal muscles. The esophagus empties its contents into the cardiac region of the stomach. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) present in the stomach does not directly digest ...
... Peristaltic contractions are wavelike, due first to the squeezing action of circular muscles, followed by the shortening action of longitudinal muscles. The esophagus empties its contents into the cardiac region of the stomach. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) present in the stomach does not directly digest ...
Digestive System Packet
... Some of the above foods need little or no digestion. They could be placed directly into the blood stream just as people are sometimes fed intravenously. Water, vitamins, and minerals are foods of this type. However; fats, proteins, and some carbohydrates such as starches, are not ready to go into th ...
... Some of the above foods need little or no digestion. They could be placed directly into the blood stream just as people are sometimes fed intravenously. Water, vitamins, and minerals are foods of this type. However; fats, proteins, and some carbohydrates such as starches, are not ready to go into th ...
Your Digestive System and How It Works National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
... The stomach has three mechanical tasks. First, it stores the swallowed food and liq uid. To do this, the muscle of the upper part of the stomach relaxes to accept large volumes of swallowed material. The sec ond job is to mix up the food, liquid, and digestive juice produced by the stomach. The lo ...
... The stomach has three mechanical tasks. First, it stores the swallowed food and liq uid. To do this, the muscle of the upper part of the stomach relaxes to accept large volumes of swallowed material. The sec ond job is to mix up the food, liquid, and digestive juice produced by the stomach. The lo ...
Your Digestive System and How It Works
... The stomach has three mechanical tasks. First, it stores the swallowed food and liq uid. To do this, the muscle of the upper part of the stomach relaxes to accept large volumes of swallowed material. The sec ond job is to mix up the food, liquid, and digestive juice produced by the stomach. The lo ...
... The stomach has three mechanical tasks. First, it stores the swallowed food and liq uid. To do this, the muscle of the upper part of the stomach relaxes to accept large volumes of swallowed material. The sec ond job is to mix up the food, liquid, and digestive juice produced by the stomach. The lo ...
The Digestive and Renal Systems
... stomach varies. But after four hours, all food should have left your stomach. Next, in the small intestine, digestion continues and absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream begins. Give or take another 5 to 6 hours and it’s ready to move to the large intestines. Somewhere around 20 to 30 hours a ...
... stomach varies. But after four hours, all food should have left your stomach. Next, in the small intestine, digestion continues and absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream begins. Give or take another 5 to 6 hours and it’s ready to move to the large intestines. Somewhere around 20 to 30 hours a ...
Session 19 Introduction to the Gastrointestinal System
... Its major functions are listed below (1) secretion of mucus, digestive enzymes, and hormones (2) absorption of the end products of digestion into the blood, (3) protection against infectious disease. The mucosa in a particular area of the GI tract may have one or all three of these functions dependi ...
... Its major functions are listed below (1) secretion of mucus, digestive enzymes, and hormones (2) absorption of the end products of digestion into the blood, (3) protection against infectious disease. The mucosa in a particular area of the GI tract may have one or all three of these functions dependi ...
physiology of digestive system dr abdelaziz hussein
... • The stomach is divided into proximal and distal areas. • Proximal area is thin walled, holds large volumes of food (to store food) because of receptive relaxation, and contracts weakly and infrequently. • Distal area is thick walled with strong and frequent contractions that mix and propel food in ...
... • The stomach is divided into proximal and distal areas. • Proximal area is thin walled, holds large volumes of food (to store food) because of receptive relaxation, and contracts weakly and infrequently. • Distal area is thick walled with strong and frequent contractions that mix and propel food in ...
File
... Fat Bodies --Spaghetti shaped structures that have a bright orange or yellow color, if you have a particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum -- A spider web like membrane th ...
... Fat Bodies --Spaghetti shaped structures that have a bright orange or yellow color, if you have a particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum -- A spider web like membrane th ...
Digestive System and Nutrition Assimilation
... • Most due to bacterial- or viral-contaminated food or water, lack of immunizations against infectious diseases, and vitamin A, zinc, and other nutrient deficiencies that make children particularly susceptible to diarrhea. • Diarrhea depletes the body of fluid and nutrients and produces malnutritio ...
... • Most due to bacterial- or viral-contaminated food or water, lack of immunizations against infectious diseases, and vitamin A, zinc, and other nutrient deficiencies that make children particularly susceptible to diarrhea. • Diarrhea depletes the body of fluid and nutrients and produces malnutritio ...
Intestine transplantation

Intestine transplantation, intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. The rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regiments, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.