Gastro04-RvwGIPhysioPt2
... • Myenteric plexus will occur in absence of extrinsic or parasymp. nerves B. Propulsive (Peristaltic) Contractions – Distention (stretch) initiates – Usually weak »die out after few cm – Parasympathetic and myenteric nerves – Influenced by nervous signals, hormonal factors influence the relative deg ...
... • Myenteric plexus will occur in absence of extrinsic or parasymp. nerves B. Propulsive (Peristaltic) Contractions – Distention (stretch) initiates – Usually weak »die out after few cm – Parasympathetic and myenteric nerves – Influenced by nervous signals, hormonal factors influence the relative deg ...
The main function of the digestive system is to break down the food
... sphincter to hold the stool until reaching a toilet, where it then relaxes to release the contents. Like we mentioned, after most of the nutrients are removed from the food mixture there is waste left over — stuff your body can't use. This stuff needs to be passed out of the body. Can you guess wher ...
... sphincter to hold the stool until reaching a toilet, where it then relaxes to release the contents. Like we mentioned, after most of the nutrients are removed from the food mixture there is waste left over — stuff your body can't use. This stuff needs to be passed out of the body. Can you guess wher ...
Digestion 81KB 06.09.2016
... chanel (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), absorption of formed nutrients and removing from an organism of some end-products of metabolism. Numerous functions of digestive system are regulated by central and vegetative nervous system, humoral and endocrine influences. Disorders of regulation cause dist ...
... chanel (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), absorption of formed nutrients and removing from an organism of some end-products of metabolism. Numerous functions of digestive system are regulated by central and vegetative nervous system, humoral and endocrine influences. Disorders of regulation cause dist ...
GI Motility Functions - Drossman Gastroenterology
... The primary functions of the large intestine are to store food residues and to absorb water. Between what we drink and what is secreted into the stomach and intestine to help with food absorption, about 5 gallons of fluid is dumped into the large intestine every day. Most of this fluid has to be rea ...
... The primary functions of the large intestine are to store food residues and to absorb water. Between what we drink and what is secreted into the stomach and intestine to help with food absorption, about 5 gallons of fluid is dumped into the large intestine every day. Most of this fluid has to be rea ...
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Make up Instructions
... 1. Fat Bodies --Spaghetti shaped structures that have a bright orange or yellow color, if you have a particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. 2. Peritoneum A spider-web like membrane ...
... 1. Fat Bodies --Spaghetti shaped structures that have a bright orange or yellow color, if you have a particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. 2. Peritoneum A spider-web like membrane ...
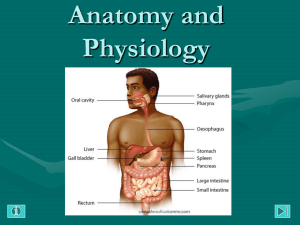
Anatomy and Physiology ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... functions. It acts as a mechanical filter by filtering blood that travels from the intestinal system. It detoxifies several metabolites including the breakdown of bilirubin and estrogen. In addition, the liver has synthetic functions, producing albumin and blood clotting factors. However, its main r ...
... functions. It acts as a mechanical filter by filtering blood that travels from the intestinal system. It detoxifies several metabolites including the breakdown of bilirubin and estrogen. In addition, the liver has synthetic functions, producing albumin and blood clotting factors. However, its main r ...
Anatomy Review: Digestive System
... Goblet cells secrete mucus (a hydrated mucin protein), while other mucosal epithelial cells secrete digestive fluids and other substances such as water and salts. Enteroendocrine cells of the mucosa produce hormones that are released into the blood via the capillaries of the lamina propria. Nutrient ...
... Goblet cells secrete mucus (a hydrated mucin protein), while other mucosal epithelial cells secrete digestive fluids and other substances such as water and salts. Enteroendocrine cells of the mucosa produce hormones that are released into the blood via the capillaries of the lamina propria. Nutrient ...
Anatomy Review: Digestive System
... Goblet cells secrete mucus (a hydrated mucin protein), while other mucosal epithelial cells secrete digestive fluids and other substances such as water and salts. Enteroendocrine cells of the mucosa produce hormones that are released into the blood via the capillaries of the lamina propria. Nutrient ...
... Goblet cells secrete mucus (a hydrated mucin protein), while other mucosal epithelial cells secrete digestive fluids and other substances such as water and salts. Enteroendocrine cells of the mucosa produce hormones that are released into the blood via the capillaries of the lamina propria. Nutrient ...
Liver - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... nerves serve small intestine • Superior mesenteric artery brings blood supply • Veins (carrying nutrient-rich blood) drain into superior mesenteric veins hepatic portal vein liver ...
... nerves serve small intestine • Superior mesenteric artery brings blood supply • Veins (carrying nutrient-rich blood) drain into superior mesenteric veins hepatic portal vein liver ...
Frog Dissection Worksheet
... 16. Suppose in a living frog the spinal nerve extending to the leg muscles were cut. What ability would the frog lose? Why? 17. The abdominal cavity of a frog at the end of hibernation season would contain very small fat bodies or none at all. What is the function of the fat bodies? ...
... 16. Suppose in a living frog the spinal nerve extending to the leg muscles were cut. What ability would the frog lose? Why? 17. The abdominal cavity of a frog at the end of hibernation season would contain very small fat bodies or none at all. What is the function of the fat bodies? ...
Powerpoint 23 Digestion
... Accomplishments of digestion to this point in the GI tract starch maltose by salivary amylase (action stops in stomach) proteins partially digested proteins (action of pepsin) lipids partially digested fats (action of lingual and gastric lipase) creation of chyme from food, drink, saliva, and ...
... Accomplishments of digestion to this point in the GI tract starch maltose by salivary amylase (action stops in stomach) proteins partially digested proteins (action of pepsin) lipids partially digested fats (action of lingual and gastric lipase) creation of chyme from food, drink, saliva, and ...
Digestion - Holy Family Regional School
... Small Intestine The nutrients are broken down small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine, and into the blood (diffusion). Nutrients are carried away to the liver and other body parts to be processed, stored and distributed. ...
... Small Intestine The nutrients are broken down small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine, and into the blood (diffusion). Nutrients are carried away to the liver and other body parts to be processed, stored and distributed. ...
How is food digested?
... Small Intestine The nutrients are broken down small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine, and into the blood (diffusion). Nutrients are carried away to the liver and other body parts to be processed, stored and distributed. ...
... Small Intestine The nutrients are broken down small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine, and into the blood (diffusion). Nutrients are carried away to the liver and other body parts to be processed, stored and distributed. ...
Digestive Terminology A. Digestion- the process of breaking feed
... 2. Description: Round, muscular part of stomach with many layers of tissue that squeezes feed and removes some liquid. F. Abomasum 1. Function: Enzymes and gastric juices act on feed. The abomasums is the only functional portion of the ruminant’s stomach when animals are born. 2. Description: Elonga ...
... 2. Description: Round, muscular part of stomach with many layers of tissue that squeezes feed and removes some liquid. F. Abomasum 1. Function: Enzymes and gastric juices act on feed. The abomasums is the only functional portion of the ruminant’s stomach when animals are born. 2. Description: Elonga ...
ansci1digestion - Duplin County Schools
... layers of tissue that squeezes feed and removes some liquid. ...
... layers of tissue that squeezes feed and removes some liquid. ...
Biology 12 Human Biology – The Digestive System Chapter 21
... 1. Provides bulk for elimination of digestive waste 2. Provides nutrient for vitamin producing bacteria. The large intestine (colon) contains a very large population of anaerobic bacteria. In fact 1/3 of your feces is bacteria. E. coli is a common bacterium in your colon. Your body actually has more ...
... 1. Provides bulk for elimination of digestive waste 2. Provides nutrient for vitamin producing bacteria. The large intestine (colon) contains a very large population of anaerobic bacteria. In fact 1/3 of your feces is bacteria. E. coli is a common bacterium in your colon. Your body actually has more ...
digestion1 united streaming
... Ulcerative colitis is similar to Crohn’s disease, but it affects only the colon (large intestine). When a person has ulcerative colitis, the lining of their colon develops ulcers, or tears. This can lead to stomach pain, bloody diarrhea, bleeding from tears around the anus, weight loss and decreased ...
... Ulcerative colitis is similar to Crohn’s disease, but it affects only the colon (large intestine). When a person has ulcerative colitis, the lining of their colon develops ulcers, or tears. This can lead to stomach pain, bloody diarrhea, bleeding from tears around the anus, weight loss and decreased ...
Duodenal Switch web - Laparoscopic Obesity Surgery
... The duodenal switch can be performed laparoscopically and is the most extreme procedure done today for weight loss. It is a more complex surgery and is usually reserved for those patients with a BMI over 55. (see figure) The restrictive component involves reducing the size of the stomach. The surgeo ...
... The duodenal switch can be performed laparoscopically and is the most extreme procedure done today for weight loss. It is a more complex surgery and is usually reserved for those patients with a BMI over 55. (see figure) The restrictive component involves reducing the size of the stomach. The surgeo ...
Monogastric Digestive System
... a) Striated muscles for first 2/3 b) Smooth muscles for last 1/3 c) In horse, esophagus joins stomach at an oblique angle and cardiac sphincter (the valve between the stomach and esophagus) only allows one-way flow MOST horses cannot belch out gas or vomit 4. Dog: Striated muscles throughout allow ...
... a) Striated muscles for first 2/3 b) Smooth muscles for last 1/3 c) In horse, esophagus joins stomach at an oblique angle and cardiac sphincter (the valve between the stomach and esophagus) only allows one-way flow MOST horses cannot belch out gas or vomit 4. Dog: Striated muscles throughout allow ...
Chapter 12 Digestive System
... colonoscopy. During any of these procedures the physician has the opportunity of taking a small sample of tissue (biopsy) as well as visually looking at the tissue. One common progressive degenerative condition of the liver is cirrhosis which is often linked to an excessive intake of alcohol over a ...
... colonoscopy. During any of these procedures the physician has the opportunity of taking a small sample of tissue (biopsy) as well as visually looking at the tissue. One common progressive degenerative condition of the liver is cirrhosis which is often linked to an excessive intake of alcohol over a ...
Chapter 12 Digestive System
... colonoscopy. During any of these procedures the physician has the opportunity of taking a small sample of tissue (biopsy) as well as visually looking at the tissue. One common progressive degenerative condition of the liver is cirrhosis which is often linked to an excessive intake of alcohol over a ...
... colonoscopy. During any of these procedures the physician has the opportunity of taking a small sample of tissue (biopsy) as well as visually looking at the tissue. One common progressive degenerative condition of the liver is cirrhosis which is often linked to an excessive intake of alcohol over a ...
Digestive Tract Comparison
... •Some species of birds such as pigeons and parrots do not have a gall bladder, much like the horse. •In these species bile is released into the duodenum directly from the liver. Large Intestine •The large intestine is made of a pair of caeca which can be developed or undeveloped depending on the spe ...
... •Some species of birds such as pigeons and parrots do not have a gall bladder, much like the horse. •In these species bile is released into the duodenum directly from the liver. Large Intestine •The large intestine is made of a pair of caeca which can be developed or undeveloped depending on the spe ...
Human Coelomic Divisions Coelomic Cavities Coelomic Cavities
... • Oral Cavity = mouth to pharynx, no separate nasal cavity in vertebrates without a secondary palate. • Mammals, crocodylians, & many turtles have a secondary palate, all other verts. lack this. • Salivary Glands = Present as multicellular, large glands only in Tetrapods, largest in amniotes. ...
... • Oral Cavity = mouth to pharynx, no separate nasal cavity in vertebrates without a secondary palate. • Mammals, crocodylians, & many turtles have a secondary palate, all other verts. lack this. • Salivary Glands = Present as multicellular, large glands only in Tetrapods, largest in amniotes. ...
Digestive System
... Oral Cavity = mouth to pharynx, no separate nasal cavity in vertebrates without a secondary palate. Mammals, crocodylians, & many turtles have a secondary palate, all other verts. lack this. Salivary Glands = Present as multicellular, large glands only in Tetrapods, largest in amniotes. ...
... Oral Cavity = mouth to pharynx, no separate nasal cavity in vertebrates without a secondary palate. Mammals, crocodylians, & many turtles have a secondary palate, all other verts. lack this. Salivary Glands = Present as multicellular, large glands only in Tetrapods, largest in amniotes. ...
Intestine transplantation

Intestine transplantation, intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. The rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regiments, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.