Identification of ORC1/CDC6-interacting factors in
... -You work in teams of two, presenting groups are randomly chosen at each data* - Introductions (given in red letters) are presented by volunteers (who don´t have to prepare the paper seminars) - The group that presented one paper will not be presenting another on the same day - Imagine you did the s ...
... -You work in teams of two, presenting groups are randomly chosen at each data* - Introductions (given in red letters) are presented by volunteers (who don´t have to prepare the paper seminars) - The group that presented one paper will not be presenting another on the same day - Imagine you did the s ...
1) Two identical daughter cells result
... A two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) B two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed stop sequence C three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) D three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed start sequence ...
... A two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) B two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed stop sequence C three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) D three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed start sequence ...
Unique Human Subjects Concerns for j Genetic Research
... Goal of study is determining what genes are “turned on” or “turned off” in different diseases or situations –Does not focus on gene variations –RNA (single strand “messenger” produced by DNA) or proteins are indicators of gene activity ...
... Goal of study is determining what genes are “turned on” or “turned off” in different diseases or situations –Does not focus on gene variations –RNA (single strand “messenger” produced by DNA) or proteins are indicators of gene activity ...
Study Guide Genetics Final 2014
... 5. Where are proteins synthesized (in the process of translation) and how is this done? Explain each step. ...
... 5. Where are proteins synthesized (in the process of translation) and how is this done? Explain each step. ...
Genetics
... molecules, the DNA is usually found attached to the cell membrane at some point or points. Although bacteria do not possess a nucleus, the DNA is localized in a distinct area with in the cell called the nucleoid region. There is no membrane around the nucleoid region and lies free in the cytoplasm o ...
... molecules, the DNA is usually found attached to the cell membrane at some point or points. Although bacteria do not possess a nucleus, the DNA is localized in a distinct area with in the cell called the nucleoid region. There is no membrane around the nucleoid region and lies free in the cytoplasm o ...
Unit I: Genes, Nucleic A...d Chromosomes - BioWiki
... polypeptide. In most organisms the pathway for gene expression is the transcription of DNA into RNA, which is then translated into protein. Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant D ...
... polypeptide. In most organisms the pathway for gene expression is the transcription of DNA into RNA, which is then translated into protein. Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant D ...
Homework for Introduction to Pathophysiology Terms and
... A) alleles at a given locus that are different from one another. B) alleles at a given locus that are the same. C) alleles at different loci that are the same. D) a recessive gene on chromosomal pairs. 30. A couple is planning to have children. The father is affected by an autosomal dominant disease ...
... A) alleles at a given locus that are different from one another. B) alleles at a given locus that are the same. C) alleles at different loci that are the same. D) a recessive gene on chromosomal pairs. 30. A couple is planning to have children. The father is affected by an autosomal dominant disease ...
Honors Biology Syllabus
... In this unit we will endeavor to understand how genetic information (DNA) in the cell is encoded at the molecular level and provides genetic continuity between generations. You should be able to: Describe the role of chromosomes in reproduction (i.e. parents pass on chromosomes, which contain gene ...
... In this unit we will endeavor to understand how genetic information (DNA) in the cell is encoded at the molecular level and provides genetic continuity between generations. You should be able to: Describe the role of chromosomes in reproduction (i.e. parents pass on chromosomes, which contain gene ...
Dr.A.K.AL-Yassari lect.2 2016-2017 Microbiology Year:third
... b) Cell wall structure: differences in cell wall compositions Biochemical Tests: there are many examples of biochemical tests that can ascertain the presence of characteristic metabolic functions and be used to group bacteria into a specific taxon such as oxidase test, catalase test, ….etc. Immu ...
... b) Cell wall structure: differences in cell wall compositions Biochemical Tests: there are many examples of biochemical tests that can ascertain the presence of characteristic metabolic functions and be used to group bacteria into a specific taxon such as oxidase test, catalase test, ….etc. Immu ...
Heredity
... • Fraternal - two independent eggs are fertilized by two independent sperm. Genetically, this type of twins is the same as regular siblings that happen to be born at the same time. • Identical - one egg is fertilized by one sperm then that zygote splits completely in half to become two people with i ...
... • Fraternal - two independent eggs are fertilized by two independent sperm. Genetically, this type of twins is the same as regular siblings that happen to be born at the same time. • Identical - one egg is fertilized by one sperm then that zygote splits completely in half to become two people with i ...
PART
... g. DNA polymerase synthesizes the missing strand according to base-pairing rules. h. DNA ligase joins the end of the new strand to the old one. i. DNA polymerase only synthesizes new strands in the direction of 5' to 3'. The parent DNA strands are antiparallel, so synthesis along one of the strands ...
... g. DNA polymerase synthesizes the missing strand according to base-pairing rules. h. DNA ligase joins the end of the new strand to the old one. i. DNA polymerase only synthesizes new strands in the direction of 5' to 3'. The parent DNA strands are antiparallel, so synthesis along one of the strands ...
S2 rev pkt 2013(evol - body)
... biome is dry, with little rain. The dominant plants are cacti and succulents. The biome are covered with grasses, and include predators such as lions, leopards, and cheetahs. In the biome, permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil) results in plants that are small and stunted. The biome has both decidu ...
... biome is dry, with little rain. The dominant plants are cacti and succulents. The biome are covered with grasses, and include predators such as lions, leopards, and cheetahs. In the biome, permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil) results in plants that are small and stunted. The biome has both decidu ...
Name__________________________ Period ______ Exam
... Unit Three: Meiosis and Reproduction 1. What are the two main differences between asexual and sexual reproduction? 2. What type of reproduction, asexual or sexual, do organisms that undergo meiosis have? 3. What type of reproduction do most bacteria undergo? 4. What is binary fission? 5. What type o ...
... Unit Three: Meiosis and Reproduction 1. What are the two main differences between asexual and sexual reproduction? 2. What type of reproduction, asexual or sexual, do organisms that undergo meiosis have? 3. What type of reproduction do most bacteria undergo? 4. What is binary fission? 5. What type o ...
14-1 - Fort Bend ISD
... Genes are found by locating promotors (DNA sites known for being bonding sites for RNA polymerase) Promoters indicate the start of a gene Locate introns and exons ...
... Genes are found by locating promotors (DNA sites known for being bonding sites for RNA polymerase) Promoters indicate the start of a gene Locate introns and exons ...
Mendel and His Peas Lesson Quiz A Multiple Choice LESSON 1
... 1. Why did Mendel use cross-pollination in his experiments? A. to speed up self-pollination B. to control which plants pollinated other plants C. to make sure dominant factors were always produced 2. What did Mendel conclude about inherited traits? A. One factor controls each inherited trait. B. Two ...
... 1. Why did Mendel use cross-pollination in his experiments? A. to speed up self-pollination B. to control which plants pollinated other plants C. to make sure dominant factors were always produced 2. What did Mendel conclude about inherited traits? A. One factor controls each inherited trait. B. Two ...
chapter outline - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... A. Transformation—a naked DNA molecule from the environment is taken up by the cell and incorporated into its chromosome in some heritable form B. A competent cell is one that is capable of taking up DNA and therefore acting as a recipient; only a limited number of species are naturally competent; t ...
... A. Transformation—a naked DNA molecule from the environment is taken up by the cell and incorporated into its chromosome in some heritable form B. A competent cell is one that is capable of taking up DNA and therefore acting as a recipient; only a limited number of species are naturally competent; t ...
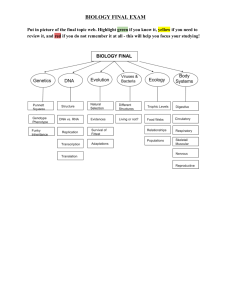
biology final exam - bhsbiologycheever
... 17. Which of the following statements explains why viruses are able to reproduce only inside host cells instead of being able to reproduce on their own? a. viruses cannot function at temperature other than 98.6°F b. viruses lack spindle fibers that correctly align chromosomes for division c. vir ...
... 17. Which of the following statements explains why viruses are able to reproduce only inside host cells instead of being able to reproduce on their own? a. viruses cannot function at temperature other than 98.6°F b. viruses lack spindle fibers that correctly align chromosomes for division c. vir ...
Genetic cause
... is inability to conceive a child during one up to two years of frequent intercourse without the use of contraceptives ...
... is inability to conceive a child during one up to two years of frequent intercourse without the use of contraceptives ...
100 colorectal adenomatous polyps
... I am writing to request coverage for analysis of the APC and MYH genes for __________________________________________________due to a personal history of ________________________________________________________ diagnosed at age(s) ______________________________. The number of adenomatous colorectal ...
... I am writing to request coverage for analysis of the APC and MYH genes for __________________________________________________due to a personal history of ________________________________________________________ diagnosed at age(s) ______________________________. The number of adenomatous colorectal ...
Slide 1
... produced through the process of genetic engineering. Genetic engineering takes DNA from one organism and inserts it into the DNA or another organism. Canola is an example of a transgenic plant. A variety of canola contains DNA from a flounder which allows the canola to be grown in colder regions str ...
... produced through the process of genetic engineering. Genetic engineering takes DNA from one organism and inserts it into the DNA or another organism. Canola is an example of a transgenic plant. A variety of canola contains DNA from a flounder which allows the canola to be grown in colder regions str ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
... process and the offspring were essentially a "dilution"of the different parental characteristics. ...
... process and the offspring were essentially a "dilution"of the different parental characteristics. ...
Genetic Technology - Solon City Schools
... the last few years, and will become more important as genetic diseases become more prevalent and agricultural area is reduced. Below are some of the areas where Recombinant DNA will have an impact: ...
... the last few years, and will become more important as genetic diseases become more prevalent and agricultural area is reduced. Below are some of the areas where Recombinant DNA will have an impact: ...
TE content correlates positively with genome size
... Explain how transposable elements can cause variation among individuals within a species or between species? Explain how transposable elements ...
... Explain how transposable elements can cause variation among individuals within a species or between species? Explain how transposable elements ...
jones et al - markers and mapping - we are all geneticists
... 24. Define the term “transgressive segregation”? How might this be explained genetically? (173) 25. What is marker assisted selection (MAS)? What is the value of MAS? (173) 26. What is the definition of synteny from a molecular marker perspective? (173) 27. Why is the fact that the genetic distance ...
... 24. Define the term “transgressive segregation”? How might this be explained genetically? (173) 25. What is marker assisted selection (MAS)? What is the value of MAS? (173) 26. What is the definition of synteny from a molecular marker perspective? (173) 27. Why is the fact that the genetic distance ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.