Diapositiva 1
... the relationships between heat and work. It can be regarded as a generalization of an enormous body of empirical evidence. It is extremely general: there are no hypotheses made concerning the structure and type of matter that we deal with. Thermodynamics is used to describe the performance of propul ...
... the relationships between heat and work. It can be regarded as a generalization of an enormous body of empirical evidence. It is extremely general: there are no hypotheses made concerning the structure and type of matter that we deal with. Thermodynamics is used to describe the performance of propul ...
thermodynamics - La Salle High School
... Third Law of Thermodynamics If the entropy of each element in its most state is taken as zero at the absolute zero of temperature, every substance has a positive entropy. But at 0K, the entropy of substance may equals to 0, and does become zero in perfect crystalline solids. Implication: all perfec ...
... Third Law of Thermodynamics If the entropy of each element in its most state is taken as zero at the absolute zero of temperature, every substance has a positive entropy. But at 0K, the entropy of substance may equals to 0, and does become zero in perfect crystalline solids. Implication: all perfec ...
název projektu
... If the two thermodynamic objects are in equillibrium and stay in it after heat transfer is enabled, they have the same ...
... If the two thermodynamic objects are in equillibrium and stay in it after heat transfer is enabled, they have the same ...
Document
... The rusting of iron is a very spontaneous reaction! 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 Fe2O3(s) o The reverse reaction, the refining ∆Grxn = -1487 kJ of iron is very non-spontaneous! ...
... The rusting of iron is a very spontaneous reaction! 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 Fe2O3(s) o The reverse reaction, the refining ∆Grxn = -1487 kJ of iron is very non-spontaneous! ...
CHEM 240 Who am I?
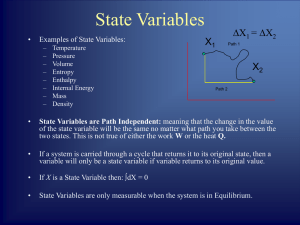
... constant, its pressure my vary over a range of values. • If the pressure of one of these systems is held constant, its volume my vary over a range of values. • Thus, V and P are independent thermodynamic variables. • When one of the systems reach equilibrium at a certain P and V, all its macroscopic ...
... constant, its pressure my vary over a range of values. • If the pressure of one of these systems is held constant, its volume my vary over a range of values. • Thus, V and P are independent thermodynamic variables. • When one of the systems reach equilibrium at a certain P and V, all its macroscopic ...
ENT 211 Tutorial Week 1
... surface sticks to the surface and there is no slip. This is known as the no-slip condition, and it is due to the viscosity of the fluid. There is no such thing as an inviscid fluid, since all fluids have viscosity. ...
... surface sticks to the surface and there is no slip. This is known as the no-slip condition, and it is due to the viscosity of the fluid. There is no such thing as an inviscid fluid, since all fluids have viscosity. ...
Thermochemistry
... to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
... to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
Introduction into thermodynamics Thermodynamic variables
... Chemical thermodynamics deals with reactions between substances and species. Mechanical thermodynamics, on the other hand, works with engines and their performance. In this class, we will explore chemical thermodynamics. We will ask and nd the answer to questions such as why does ice melt at room t ...
... Chemical thermodynamics deals with reactions between substances and species. Mechanical thermodynamics, on the other hand, works with engines and their performance. In this class, we will explore chemical thermodynamics. We will ask and nd the answer to questions such as why does ice melt at room t ...
here
... If A and B are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium means that two bodies are in states such that if they are connected, then their condition will not change. ...
... If A and B are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium means that two bodies are in states such that if they are connected, then their condition will not change. ...
Thermodynamics - Clayton State University
... However, it is much easier to convert useful mechanical energy into heat energy than it is to convert heat energy into useful mechanical energy. Heat energy is based on random movement of molecules, so it is a disorganized form of energy. It is much easier to produce disorganized motion than organiz ...
... However, it is much easier to convert useful mechanical energy into heat energy than it is to convert heat energy into useful mechanical energy. Heat energy is based on random movement of molecules, so it is a disorganized form of energy. It is much easier to produce disorganized motion than organiz ...
B E , 2013
... fitted horizontally to a vessel kept full of alcohol of density 0.8 gm/cc. The depth of the centre of the capillary tube below the surface of alcohol is 30 cms. If the viscosity of alcohol is 0.012 cgs units, find the amount that will flow out ...
... fitted horizontally to a vessel kept full of alcohol of density 0.8 gm/cc. The depth of the centre of the capillary tube below the surface of alcohol is 30 cms. If the viscosity of alcohol is 0.012 cgs units, find the amount that will flow out ...
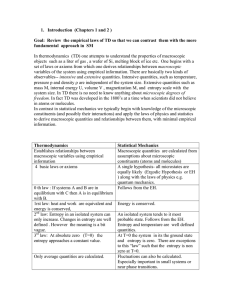
1. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2 ) Goal: Review the empirical laws
... basically energy conservation. Note W and Q are not state functions since they are not functions of state variables (e.g. p, V for a gas with NA kmoles ). In differential form the first law of TD is: dU Q pdV For example one can move the system from points A to C through different paths (throug ...
... basically energy conservation. Note W and Q are not state functions since they are not functions of state variables (e.g. p, V for a gas with NA kmoles ). In differential form the first law of TD is: dU Q pdV For example one can move the system from points A to C through different paths (throug ...
Basic thermodynamics` definitions. Units and conversions.
... and second Law of Thermodynamics and its applications in environmental engineering field. Thermodynamics helps to understand the physical processes of the nature (e.g. outer and inner climate shaping). The engineering applications of thermodynamics could be in heating, air conditioning etc. The vari ...
... and second Law of Thermodynamics and its applications in environmental engineering field. Thermodynamics helps to understand the physical processes of the nature (e.g. outer and inner climate shaping). The engineering applications of thermodynamics could be in heating, air conditioning etc. The vari ...
Heat Chapter 12: Thermodynamics
... The Second Law of Thermodynamics specifies the direction in which a process can naturally or spontaneously take place. • Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder to a warmer body. • In a thermal cycle, heat energy cannot be completely transformed into mechanical work. • The total entropy of t ...
... The Second Law of Thermodynamics specifies the direction in which a process can naturally or spontaneously take place. • Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder to a warmer body. • In a thermal cycle, heat energy cannot be completely transformed into mechanical work. • The total entropy of t ...
... Consider a crystal containing N=5x1023 atoms, which may be found in one of the following states: the ground state with E0=0 and an exited state with E1=ε=4x10-20J. a. In the beginning ¼ of the atoms were in the exited state. What is the temperature of the crystal? b. The crystal is placed in thermal ...
Chap 7 - College of Science | Oregon State University
... Instead of moving thermal energy around to output work (motion), we put in the work (a motor drives a compressor for example) and thus move thermal energy around. Form 3: Entropy is increasing. (In any physical process within some system, the total entropy of the system either stays constant or incr ...
... Instead of moving thermal energy around to output work (motion), we put in the work (a motor drives a compressor for example) and thus move thermal energy around. Form 3: Entropy is increasing. (In any physical process within some system, the total entropy of the system either stays constant or incr ...
PY2104 - Introduction to thermodynamics and Statistical physics
... heats at constant pressure and constant volume, cp and cv for this gas. 2) (i) Show that for a perfect gas undergoing adiabatic expansion, pV γ is constant, where γ = cp /cv . (ii) What is the physical reason for the difference between cp and cv ? 3) Consider a paramagnetic system. From a thermodyna ...
... heats at constant pressure and constant volume, cp and cv for this gas. 2) (i) Show that for a perfect gas undergoing adiabatic expansion, pV γ is constant, where γ = cp /cv . (ii) What is the physical reason for the difference between cp and cv ? 3) Consider a paramagnetic system. From a thermodyna ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... Statistical Thermodynamics Introduction and Definitions Statistical Thermodynamics: is the application of probability theory, which includes mathematical tools for dealing with large populations, to the field of mechanics, which is concerned with the motion of particles when subjected to a force. - ...
... Statistical Thermodynamics Introduction and Definitions Statistical Thermodynamics: is the application of probability theory, which includes mathematical tools for dealing with large populations, to the field of mechanics, which is concerned with the motion of particles when subjected to a force. - ...
20 · Entropy and Free Energy
... ionic solids with strong attractions to ionic solids with weaker attractions separate solute & solvent to solutions gas dissolved in water to escaped gas ...
... ionic solids with strong attractions to ionic solids with weaker attractions separate solute & solvent to solutions gas dissolved in water to escaped gas ...
Statistical - Jordan University of Science and Technology
... Q1-a: Assume that at very low temperature, the molar heat capacity of copper is equal to ( 7x10-4 T ) J K-1 mole-1 , where T is the absolute temperature. Show that if ( 10-7 ) J of heat is added to a mole of copper, which is initially at the absolute zero, the temperature of the copper rises to (0.0 ...
... Q1-a: Assume that at very low temperature, the molar heat capacity of copper is equal to ( 7x10-4 T ) J K-1 mole-1 , where T is the absolute temperature. Show that if ( 10-7 ) J of heat is added to a mole of copper, which is initially at the absolute zero, the temperature of the copper rises to (0.0 ...
Thermodynamic principles. - med.muni
... – Thermodynamic system: A region of space bounded by arbitrary surfaces which delineate the portion of the universe we are interested in – Isolated system: one which cannot exchange particles or energy with its environment. – Open system: one which can exchanges both particles and energy with its en ...
... – Thermodynamic system: A region of space bounded by arbitrary surfaces which delineate the portion of the universe we are interested in – Isolated system: one which cannot exchange particles or energy with its environment. – Open system: one which can exchanges both particles and energy with its en ...
3.012 Practice Problems for Recitation 1 (09.13.05) Part I. System
... If we can imagine the object above, it is an adiabatic system. Mechanical work may be performed by pressing on the ball, but heat cannot travel through the insulating rubber. Also note that this system is closed to matter. 1. What type of system is the earth? The earth is approximately a closed sys ...
... If we can imagine the object above, it is an adiabatic system. Mechanical work may be performed by pressing on the ball, but heat cannot travel through the insulating rubber. Also note that this system is closed to matter. 1. What type of system is the earth? The earth is approximately a closed sys ...