Chapter 17 Applications of Molecular Genetics
... nucleotide sequences of genes to devise procedures for isolating null mutations in them or shutting off their expression. The function of a gene often can be deduced by studying organisms lacking any functional product of the gene. ...
... nucleotide sequences of genes to devise procedures for isolating null mutations in them or shutting off their expression. The function of a gene often can be deduced by studying organisms lacking any functional product of the gene. ...
Plant Breeding is the actual application of the genetics research
... 2. The genetically modified crop may interbreed with closely related weed type species, thus making these weeds difficult to control with some specific herbicides. 3. It is also thought that the genetically modified crop itself may become a weed in its own right due to its resistance to chemicals a ...
... 2. The genetically modified crop may interbreed with closely related weed type species, thus making these weeds difficult to control with some specific herbicides. 3. It is also thought that the genetically modified crop itself may become a weed in its own right due to its resistance to chemicals a ...
Genetic Engineering and The Human Genome
... BioTechnology- Genetic engineering • Genetic engineering- the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. ...
... BioTechnology- Genetic engineering • Genetic engineering- the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. ...
consumer perceptions of food biotechnology
... American Association for the Advancement of Science Center for Science in the Public Interest ...
... American Association for the Advancement of Science Center for Science in the Public Interest ...
Genetic Technology
... hormone to treat dwarfism, and insulin to treat diabetes. Transgenic animals are used to study human chromosomes so that scientists can learn how to treat diseases in humans. Recombinant bacteria used on crops can prevent frost damage. Plants have been genetically engineered to resist herbicides, pr ...
... hormone to treat dwarfism, and insulin to treat diabetes. Transgenic animals are used to study human chromosomes so that scientists can learn how to treat diseases in humans. Recombinant bacteria used on crops can prevent frost damage. Plants have been genetically engineered to resist herbicides, pr ...
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells that carries the DNA. Each human has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one of each parent. Gene: A gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that contains the “instructions” of how, when and where our bodies function. These instructi ...
... Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells that carries the DNA. Each human has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one of each parent. Gene: A gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that contains the “instructions” of how, when and where our bodies function. These instructi ...
Genetically Engineered Foods
... Gene guns: fire tiny metal particles coated with DNA into tissue culture of cells direct injection into nucleus - generally used for genetic engineering of animals ...
... Gene guns: fire tiny metal particles coated with DNA into tissue culture of cells direct injection into nucleus - generally used for genetic engineering of animals ...
Advances in Genetics
... • Removed egg cell from one sheep • Nucleus in egg cell replaced with nucleus from a sixyear old sheep • Egg implanted into uterus of 3rd sheep • Dolly born 5 months later, genetically identical to the six-year old sheep ...
... • Removed egg cell from one sheep • Nucleus in egg cell replaced with nucleus from a sixyear old sheep • Egg implanted into uterus of 3rd sheep • Dolly born 5 months later, genetically identical to the six-year old sheep ...
Chapter 5-3 - Mahtomedi Middle School
... c. It’s easier to clone an animal than it is to clone a plant. ...
... c. It’s easier to clone an animal than it is to clone a plant. ...
Genetic Engineering
... because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g. a gene for luminescence from a jellyfish can be added to a frog, making it ...
... because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g. a gene for luminescence from a jellyfish can be added to a frog, making it ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
Advances in Genetics - Madison County Schools
... • Removed egg cell from one sheep • Nucleus in egg cell replaced with nucleus from a sixyear old sheep • Egg implanted into uterus of 3rd sheep • Dolly born 5 months later, genetically identical to the ...
... • Removed egg cell from one sheep • Nucleus in egg cell replaced with nucleus from a sixyear old sheep • Egg implanted into uterus of 3rd sheep • Dolly born 5 months later, genetically identical to the ...
Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Study Guide
... 11. List two possible benefits and two possible harmful effects of genetic modification. ...
... 11. List two possible benefits and two possible harmful effects of genetic modification. ...
Vector - Manhasset Public Schools
... increase the production of beta-carotene (an important precursor of Vitamin A). ...
... increase the production of beta-carotene (an important precursor of Vitamin A). ...
Genetically Modified Foods and Organisms
... Traditional plant breeding DNA is a strand of genes, much like a strand of pearls. Traditional plant breeding combines many genes at ...
... Traditional plant breeding DNA is a strand of genes, much like a strand of pearls. Traditional plant breeding combines many genes at ...
English - iGEM 2016
... Genetically modified food Why do we use it? • Protected better • More nutrient value • Prettier Not totally new ...
... Genetically modified food Why do we use it? • Protected better • More nutrient value • Prettier Not totally new ...
Biotechnology Need To Know List
... The technique of DNA sequencing How a recombinant plasmid gets inside a bacterial cell What is most often used as a genetic marker in plasmids The advantage of producing transgenic plants The technique of cloning (sheep example) The breeding practice most likely to bring together two recessive allel ...
... The technique of DNA sequencing How a recombinant plasmid gets inside a bacterial cell What is most often used as a genetic marker in plasmids The advantage of producing transgenic plants The technique of cloning (sheep example) The breeding practice most likely to bring together two recessive allel ...
15.3_Applications_of_Genetic_Engineering
... One genetic modification uses bacterial genes that produce a protein known as Bt toxin Toxin is harmless to humans and most other animals, but kills insects Plants with the Bt gene do not have to be sprayed with pesticides. ...
... One genetic modification uses bacterial genes that produce a protein known as Bt toxin Toxin is harmless to humans and most other animals, but kills insects Plants with the Bt gene do not have to be sprayed with pesticides. ...
Ch 15 Genetic Engineering
... One genetic modification uses bacterial genes that produce a protein known as Bt toxin Toxin is harmless to humans and most other animals, but kills insects Plants with the Bt gene do not have to be sprayed with pesticides. ...
... One genetic modification uses bacterial genes that produce a protein known as Bt toxin Toxin is harmless to humans and most other animals, but kills insects Plants with the Bt gene do not have to be sprayed with pesticides. ...
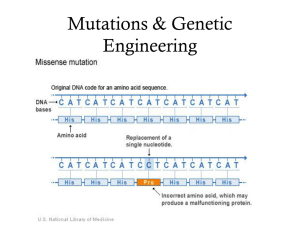
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
... Stem Cells Cells that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cells Why study stem cells? 1. They are unspecialized & can reproduce (mitosis) 2. They can be induced to become specific cells with specific functions. Two types: ...
... Stem Cells Cells that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cells Why study stem cells? 1. They are unspecialized & can reproduce (mitosis) 2. They can be induced to become specific cells with specific functions. Two types: ...
Applied Genetics
... • Plants have been developed that have a trait that kills developing embryos in seeds so that seeds from crops cannot be saved & planted the following season ...
... • Plants have been developed that have a trait that kills developing embryos in seeds so that seeds from crops cannot be saved & planted the following season ...