Biology Communique_2015_16_LP8 SUBJECT: Biology B
... Materials: BSCS Biology textbook; Biozone NGSS workbook; Biology lab at MVRC with interactive instruction; parent selected materials Grade LS4.A: Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity Genetic information provides evidence of evolution. DNA sequences vary among species, but there are many overlap ...
... Materials: BSCS Biology textbook; Biozone NGSS workbook; Biology lab at MVRC with interactive instruction; parent selected materials Grade LS4.A: Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity Genetic information provides evidence of evolution. DNA sequences vary among species, but there are many overlap ...
Population Genetics
... the rule in natural populations. – Gene mutations provide new alleles, and therefore are the ultimate source of variation. a. A gene mutation is an alteration in the DNA nucleotide sequence of an allele. b. Mutations may not immediately affect the phenotype. c. Mutations can be beneficial, neutral, ...
... the rule in natural populations. – Gene mutations provide new alleles, and therefore are the ultimate source of variation. a. A gene mutation is an alteration in the DNA nucleotide sequence of an allele. b. Mutations may not immediately affect the phenotype. c. Mutations can be beneficial, neutral, ...
Lamarck said Organisms acquire or lose certain traits during their
... generation and those who can’t adapt will die or leave fewer offspring. Natural selection: Species change over time because of changes in the environment. Example: Species compete for food, space, and mates. ...
... generation and those who can’t adapt will die or leave fewer offspring. Natural selection: Species change over time because of changes in the environment. Example: Species compete for food, space, and mates. ...
Evolution Terms to Know
... analogous structures domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, artificial selection family, genus, species binomial nomenclature (genus, species) Evidence of evolution biogeography evolutionary adaptation bottleneck effect founder effect coevolution gene flow convergent evolutio ...
... analogous structures domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, artificial selection family, genus, species binomial nomenclature (genus, species) Evidence of evolution biogeography evolutionary adaptation bottleneck effect founder effect coevolution gene flow convergent evolutio ...
frequency
... 1. Define the following terms: Genetic drift: random change in a gene frequency that is caused by a series of chance occurrences that cause an allele to become more or less common in a population Gene pool: a stock of different genes in an interbreeding population Genetic equilibrium: situatio ...
... 1. Define the following terms: Genetic drift: random change in a gene frequency that is caused by a series of chance occurrences that cause an allele to become more or less common in a population Gene pool: a stock of different genes in an interbreeding population Genetic equilibrium: situatio ...
Chapter 23 EVOLUTION AND GENETIC VARIATION
... 3. Disruptive Selection • When individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle • Can create 2 distinct phenotypes ...
... 3. Disruptive Selection • When individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle • Can create 2 distinct phenotypes ...
Gene pool
... B. Causes of microevolution 1.Natural selection a. gradualism – species evolve at a slow and constant pace b. punctuated equilibrium – species evolve rapidly over short time then remain the same for long periods ...
... B. Causes of microevolution 1.Natural selection a. gradualism – species evolve at a slow and constant pace b. punctuated equilibrium – species evolve rapidly over short time then remain the same for long periods ...
Answer Key - castellanoscience
... promoting extreme types. Individuals become more similar, and genetic diversity decreases. The three major ways that genotypic variation occurs are by mutations, by recombination during meiosis, and by the random pairing of gametes. disruptive selection The extreme traits of body color are being sel ...
... promoting extreme types. Individuals become more similar, and genetic diversity decreases. The three major ways that genotypic variation occurs are by mutations, by recombination during meiosis, and by the random pairing of gametes. disruptive selection The extreme traits of body color are being sel ...
Lamarckism
... complex creatures evolved from simpler ancestors naturally over time. Although the theory of Darwinian evolution is a relatively young archetype, the evolutionary worldview itself is as old as antiquity. Charles Darwin simply brought something new to the old philosophy - a plausible mechanism called ...
... complex creatures evolved from simpler ancestors naturally over time. Although the theory of Darwinian evolution is a relatively young archetype, the evolutionary worldview itself is as old as antiquity. Charles Darwin simply brought something new to the old philosophy - a plausible mechanism called ...
Biology-Chapter-15
... Evidence from fossil records indicates that modern-day birds, mammals, and reptiles descended from reptilian ancestors including dinosaurs. Evolutionary Theory evolves with Genetic drift-the absences of natural selection. This kind of random change in the frequency of a gene is called genetic drif ...
... Evidence from fossil records indicates that modern-day birds, mammals, and reptiles descended from reptilian ancestors including dinosaurs. Evolutionary Theory evolves with Genetic drift-the absences of natural selection. This kind of random change in the frequency of a gene is called genetic drif ...
Trimester 2 final exam study guide
... *Inherited variation and artificial selection *Evolution by Natural Selection (struggle for existence, “fitness”, survival of the fittest, adaptations, decent with modification) *Evidence for Evolution (fossil record, geographic distribution of organisms, homologous structures, vestigial organs, emb ...
... *Inherited variation and artificial selection *Evolution by Natural Selection (struggle for existence, “fitness”, survival of the fittest, adaptations, decent with modification) *Evidence for Evolution (fossil record, geographic distribution of organisms, homologous structures, vestigial organs, emb ...
1. Explain what is meant by the “modern synthesis”.
... In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, what symbolizes the dominant allele? Name one way in which natural populations do not fit Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Any change in the allele frequencies of a population is called _____. ...
... In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, what symbolizes the dominant allele? Name one way in which natural populations do not fit Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Any change in the allele frequencies of a population is called _____. ...
Darwin info Sheet
... While Darwin's Theory of Evolution is a relatively young archetype, the evolutionary worldview itself is as old as antiquity. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Anaximander postulated the development of life from non-life and the evolutionary descent of man from animal. Charles Darwin simply brought ...
... While Darwin's Theory of Evolution is a relatively young archetype, the evolutionary worldview itself is as old as antiquity. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Anaximander postulated the development of life from non-life and the evolutionary descent of man from animal. Charles Darwin simply brought ...
Molecular Evolution and Population Genetics
... • When gametes containing either of two alleles, A or a, unite at random to form the next generation, the genotype frequencies among the zygotes are given by the ratio p2 : 2pq : q2 this constitutes the Hardy–Weinberg (HW) Principle ...
... • When gametes containing either of two alleles, A or a, unite at random to form the next generation, the genotype frequencies among the zygotes are given by the ratio p2 : 2pq : q2 this constitutes the Hardy–Weinberg (HW) Principle ...
chapter 15 POPULATIONS
... Old Order Amish populations are derived from a few dozen colonists who escaped religious persecution in Germany in 1719 to settle in Pennsylvania. ...
... Old Order Amish populations are derived from a few dozen colonists who escaped religious persecution in Germany in 1719 to settle in Pennsylvania. ...
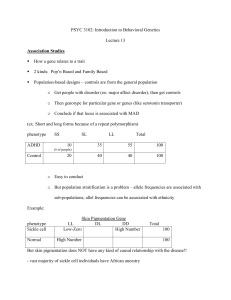
Lecture 13
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
Gene Pool
... • DNA can _____________ and these changes are nearly impossible to predict. – DNA mutations are caused by: crossing over, sexual reproduction, basepair changes, mutagens. – Mutations can _________________ or ______________ an individual’s chance of survival. 5) Natural Selection • Allows for the mos ...
... • DNA can _____________ and these changes are nearly impossible to predict. – DNA mutations are caused by: crossing over, sexual reproduction, basepair changes, mutagens. – Mutations can _________________ or ______________ an individual’s chance of survival. 5) Natural Selection • Allows for the mos ...
1. Explain what is meant by the “modern synthesis”.
... In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, what symbolizes the dominant allele? Name one way in which natural populations do not fit Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Any change in the allele frequencies of a population is called _____. ...
... In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, what symbolizes the dominant allele? Name one way in which natural populations do not fit Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Any change in the allele frequencies of a population is called _____. ...
The Evolution of Populations The Evolution of Populations
... Theory of natural selection (Darwin): 1) Genetic variation: Individuals within a species differ from each other 2) Inheritance: Offspring are similar to their parents 3) Excess of reproduction: More offspring are generally produced than those to survive to maturity. Factors like predation, disease ...
... Theory of natural selection (Darwin): 1) Genetic variation: Individuals within a species differ from each other 2) Inheritance: Offspring are similar to their parents 3) Excess of reproduction: More offspring are generally produced than those to survive to maturity. Factors like predation, disease ...
Insect Evolution
... used pesticide. Although it is no longer used or produced in the United States, we continue to find DDT in our environment. Other parts of the world continue to use DDT in agricultural practices and in disease‐control programs. Therefore, atmospheric deposition is the current source of new DDT ...
... used pesticide. Although it is no longer used or produced in the United States, we continue to find DDT in our environment. Other parts of the world continue to use DDT in agricultural practices and in disease‐control programs. Therefore, atmospheric deposition is the current source of new DDT ...
File
... Each species produces more offspring than can survive These offspring compete with one another for available resources Organisms of the same species from different populations vary The offspring with the most favourable traits are more likely to survive and produce more offspring 4. Jean-Bap ...
... Each species produces more offspring than can survive These offspring compete with one another for available resources Organisms of the same species from different populations vary The offspring with the most favourable traits are more likely to survive and produce more offspring 4. Jean-Bap ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.