2. Evolution
... -two extreme traits are selected against- these are less common traits found on both edges of the curve -population does not shift, but has less variety of traits -the average does not change, but the FREQUENCY of the average trait has increased e.g. flower colour; selection against white and red fl ...
... -two extreme traits are selected against- these are less common traits found on both edges of the curve -population does not shift, but has less variety of traits -the average does not change, but the FREQUENCY of the average trait has increased e.g. flower colour; selection against white and red fl ...
genetics Study Guide(fall 2014 for old book)
... Genetics Unit Test Study Guide This is not a complete list of all the material that could potentially be on your genetics unit test – use your class notes as a guide ...
... Genetics Unit Test Study Guide This is not a complete list of all the material that could potentially be on your genetics unit test – use your class notes as a guide ...
Essay Question #2: Due Monday 23 July 2012 (
... In an essay of between four and eight pages, you must first explain why natural selection had fallen from favor among biologists, especially Mendelian geneticists. Then, you must explain what new ideas eventually led to the resurrection of natural selection as the core mechanism of biological evolut ...
... In an essay of between four and eight pages, you must first explain why natural selection had fallen from favor among biologists, especially Mendelian geneticists. Then, you must explain what new ideas eventually led to the resurrection of natural selection as the core mechanism of biological evolut ...
1199703darwin
... • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occur during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. ...
... • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occur during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. ...
6 slides
... evolution does not occur • Gene frequencies stay constant over time (genetic equilibrium) • Hardy-Weinberg Principle Conditions that Must Exist in Population: 1) Mutations must not occur 2) Gene flow must not occur • net migration of alleles between populations ...
... evolution does not occur • Gene frequencies stay constant over time (genetic equilibrium) • Hardy-Weinberg Principle Conditions that Must Exist in Population: 1) Mutations must not occur 2) Gene flow must not occur • net migration of alleles between populations ...
PART II: The purposes of this part of the assignment are to study the
... PART IIb. Random genetic drift. Random genetic drift can be simulated by using a Monte-Carlo approach. You will create a second model (using Visual Basic) that simulates effects of random mating in finite populations. For each individual, you first randomly select a genotype for each parent and then ...
... PART IIb. Random genetic drift. Random genetic drift can be simulated by using a Monte-Carlo approach. You will create a second model (using Visual Basic) that simulates effects of random mating in finite populations. For each individual, you first randomly select a genotype for each parent and then ...
Water Resources - Southgate Community School District
... Talk About It The Great Lakes are home to more than 20 native mussel species. Why are the zebra and quagga mussels so much more destructive than the ...
... Talk About It The Great Lakes are home to more than 20 native mussel species. Why are the zebra and quagga mussels so much more destructive than the ...
7.1: Variations, Mutations, and Selective Advantage Learning Check:
... a gene. Mutations that occur in somatic cells can have significant effects on the individual, but will not be passed on to the next generation. Mutation can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial to an organism. Mutations that occur in gamete cells can be passed onto the next generation. Mutations resul ...
... a gene. Mutations that occur in somatic cells can have significant effects on the individual, but will not be passed on to the next generation. Mutation can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial to an organism. Mutations that occur in gamete cells can be passed onto the next generation. Mutations resul ...
Chapter 14: Human Heredity - Southington Public Schools
... Recognize the patterns of three common modes of inheritance—autosomal dominance, autosomal recessive and sex-linked recessive—on a pedigree chart. Describe the inheritance of blood type in humans, including what is physically different on the blood cells with various allele combinations. Descr ...
... Recognize the patterns of three common modes of inheritance—autosomal dominance, autosomal recessive and sex-linked recessive—on a pedigree chart. Describe the inheritance of blood type in humans, including what is physically different on the blood cells with various allele combinations. Descr ...
Natural Selection - Alex LeMay – Science
... What does Natural Selection mean? Organisms that are better adapted to their environment tend to survive longer. (Nature has “selected” them to survive because they have more useful traits.) The survivors tend to produce more offspring than the less well adapted, so those useful genetic traits beco ...
... What does Natural Selection mean? Organisms that are better adapted to their environment tend to survive longer. (Nature has “selected” them to survive because they have more useful traits.) The survivors tend to produce more offspring than the less well adapted, so those useful genetic traits beco ...
Evolution - Cloudfront.net
... • A population evolves, not an individual organism • Natural Selection occurs through interactions between individuals • Variations in a population are heritable that are not “acquired in their lifetime” • Natural selection is the “mechanism” of evolution • The accumulation of small gradual changes ...
... • A population evolves, not an individual organism • Natural Selection occurs through interactions between individuals • Variations in a population are heritable that are not “acquired in their lifetime” • Natural selection is the “mechanism” of evolution • The accumulation of small gradual changes ...
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
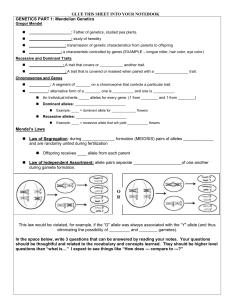
... Law of Segregation: during ______________ formation (MEIOSIS) pairs of alleles _____________ and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete forma ...
... Law of Segregation: during ______________ formation (MEIOSIS) pairs of alleles _____________ and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete forma ...
Natural Selection
... Sometime later, another mutation arose, which lengthened necks even more, and it spread through the population in a similar manner. Eventually, a number of mutations, each of which helped lengthen necks, spread throughout the population, resulting in the long necks we see today. ...
... Sometime later, another mutation arose, which lengthened necks even more, and it spread through the population in a similar manner. Eventually, a number of mutations, each of which helped lengthen necks, spread throughout the population, resulting in the long necks we see today. ...
Bottlenecks and Founder Effects
... Target III: Describe the two main causes of microevolution: genetic drift (bottleneck effect & founder effect) and natural selection. Text Reference: 23.3 Pre-lab Questions: Read the procedures before you answer the pre-lab questions. This may be checked, collected, or possibly be used on a pre lab ...
... Target III: Describe the two main causes of microevolution: genetic drift (bottleneck effect & founder effect) and natural selection. Text Reference: 23.3 Pre-lab Questions: Read the procedures before you answer the pre-lab questions. This may be checked, collected, or possibly be used on a pre lab ...
population - Damien Rutkoski
... was “rediscovered” and scientists began to combine the ideas of many branches of biology to develop a modern theory of evolution. When studying evolution today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
... was “rediscovered” and scientists began to combine the ideas of many branches of biology to develop a modern theory of evolution. When studying evolution today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
Power Point Presentation
... Some physical traits (e.g. extremely large or long tails) may make survival ...
... Some physical traits (e.g. extremely large or long tails) may make survival ...
BB - SmartSite
... Natural selection • Natural selection changes allele frequency in three ways – Stabilizing selection: Minimizes extreme phenotypes (example – average birth weights – higher mortality rates in very small or very large babies) – Directional selection: Shifts phenotype to one extreme (often caused by ...
... Natural selection • Natural selection changes allele frequency in three ways – Stabilizing selection: Minimizes extreme phenotypes (example – average birth weights – higher mortality rates in very small or very large babies) – Directional selection: Shifts phenotype to one extreme (often caused by ...
Evolution Notes
... 3. May occur in an area that provides very different resources a. Galapagos finches had a variety of food choices: smaller birds fed on small seeds, larger birds feed on large seeds. Natural selection favors both but not the average who would compete for both resources. C. Evidence for Evolution i. ...
... 3. May occur in an area that provides very different resources a. Galapagos finches had a variety of food choices: smaller birds fed on small seeds, larger birds feed on large seeds. Natural selection favors both but not the average who would compete for both resources. C. Evidence for Evolution i. ...
Selection Pressure
... • [1]This is used in the selection mechanism of the GA. This is the number of top individuals that are guaranteed to survive into the next generation. • Crossover and mutation are performed on random members of the population according to user-defined rates of crossover and mutation. First, crossove ...
... • [1]This is used in the selection mechanism of the GA. This is the number of top individuals that are guaranteed to survive into the next generation. • Crossover and mutation are performed on random members of the population according to user-defined rates of crossover and mutation. First, crossove ...
Ch 8 Notes
... • Light coat color evolved independently in different populations Evolution in response to natural selection is inevitable if: – There is variation in a trait – Variation is heritable – Some variants reproduce more than others Specific features of the environment can generate natural selection on a ...
... • Light coat color evolved independently in different populations Evolution in response to natural selection is inevitable if: – There is variation in a trait – Variation is heritable – Some variants reproduce more than others Specific features of the environment can generate natural selection on a ...
For an overall summary of the Theory of Evolution
... 1. Many more individuals are born in each generation than will survive and reproduce. 2. There is variation among individuals; they are not identical in all their characteristics a. SOURCE OF VARIATION IS MUTATION: A RANDOM PROCESS. b. Mutation - any novel genetic change in the gene complement or ge ...
... 1. Many more individuals are born in each generation than will survive and reproduce. 2. There is variation among individuals; they are not identical in all their characteristics a. SOURCE OF VARIATION IS MUTATION: A RANDOM PROCESS. b. Mutation - any novel genetic change in the gene complement or ge ...
Are Humans Evolving (PowerPoint) Madison 2004
... • Class 1: Class Phenotype activity (phenotype, genotype and allele frequencies, H-W formula) • Class 2: Define evolution, Students work with real data • Class 3: Human evolution: are humans evolving? • Summative Assessment ...
... • Class 1: Class Phenotype activity (phenotype, genotype and allele frequencies, H-W formula) • Class 2: Define evolution, Students work with real data • Class 3: Human evolution: are humans evolving? • Summative Assessment ...
Unit12-Microevolution
... – some phenotypes are better at promoting fitness (better adaptation to the environment) – natural selection will occur – survival and reproductive rates will increase for those individuals who have set of genes (traits) that promote the best fitness to the environment ...
... – some phenotypes are better at promoting fitness (better adaptation to the environment) – natural selection will occur – survival and reproductive rates will increase for those individuals who have set of genes (traits) that promote the best fitness to the environment ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.